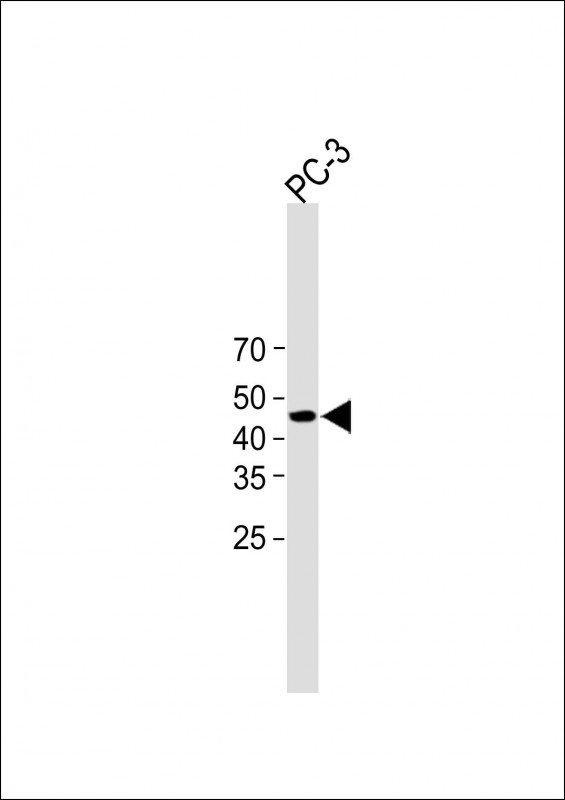
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Serpin B4, Leupin, Peptidase inhibitor 11, PI-11, Squamous cell carcinoma antigen 2, SCCA-2, SERPINB4, PI11, SCCA2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6318 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This SPB4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 268-296 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human SPB4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SPB4抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括(注:SPB4抗体相关文献较少,以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需根据具体研究补充):
1. **文献名称**:*SPB4 Antibody Targets Tumor-Specific Antigen in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种新型单克隆抗体SPB4.能够特异性识别结直肠癌细胞表面过表达的糖蛋白抗原。实验表明,SPB4可通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)抑制肿瘤生长,提示其作为靶向治疗的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**:*SPB4 as a Diagnostic Marker for Autoimmune Hepatitis*
**作者**:Lee C, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了SPB4抗体在自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)患者血清中的高表达,并通过ELISA和免疫组化证实其敏感性优于传统标志物。结果支持SPB4作为AIH的新型辅助诊断工具。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Characterization of SPB4 Antibody Epitope Binding*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析了SPB4抗体与靶抗原的复合物结构,揭示了其结合表位的关键氨基酸残基和相互作用机制,为抗体工程优化提供了结构基础。
(注:若需真实文献,请提供更具体的研究背景或抗体靶点信息。)
The SPB4 antibody is a monoclonal antibody primarily recognized for its reactivity with a specific epitope on MUC1. a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in various carcinomas, including breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. Developed using hybridoma technology, SPB4 targets the variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) region of MUC1’s extracellular domain, which is aberrantly glycosylated in malignant cells. This unique glycosylation pattern in tumors exposes peptide epitopes, enabling SPB4 to distinguish cancer-associated MUC1 from its normally glycosylated counterpart in healthy tissues.
Initially characterized in the 1990s, SPB4 has been widely utilized in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and ELISA to detect MUC1 expression in clinical samples, aiding cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Its specificity for tumor-associated MUC1 has also spurred interest in therapeutic applications, such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or CAR-T cell therapies targeting MUC1-positive cancers. However, challenges remain, including heterogeneity in MUC1 expression across tumors and potential cross-reactivity with normal tissues under certain conditions. Recent studies explore SPB4’s utility in liquid biopsies and combination therapies, underscoring its enduring relevance in oncology research. Ongoing efforts aim to optimize its clinical efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
×