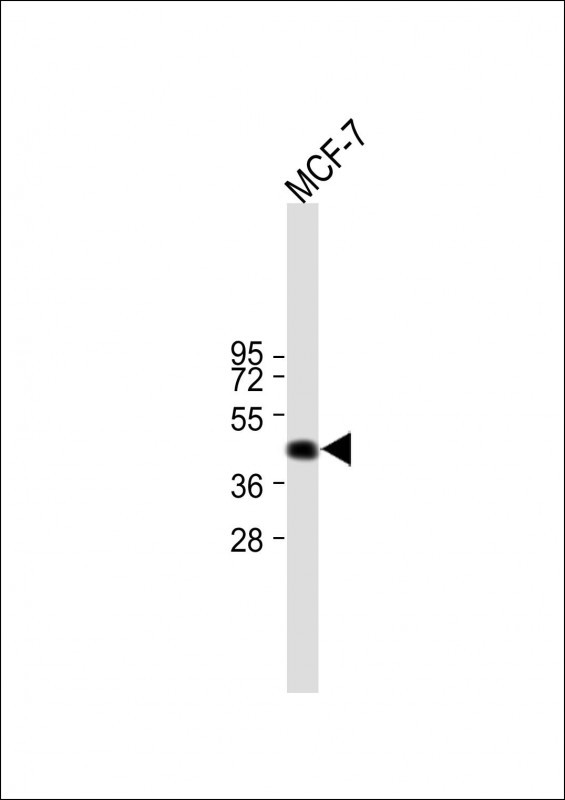
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1, Cartilage-linking protein 1, Cartilage-link protein, Proteoglycan link protein, HAPLN1, CRTL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1404 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This HAPLN1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 10-38 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human HAPLN1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HAPLN1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*HAPLN1 stabilizes the cartilage matrix and protects chondrocytes via a CD44-dependent mechanism*
**作者**:Yamawaki et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了HAPLN1通过结合透明质酸和蛋白聚糖维持软骨细胞外基质的稳定性。作者使用HAPLN1 (N-term)抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,证实其在软骨细胞中通过CD44受体介导抗炎和抗凋亡作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Extracellular matrix remodeling by HAPLN1 promotes glioblastoma progression*
**作者**:Chen et al.
**摘要**:该文献探讨HAPLN1在胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)中的促癌机制。通过HAPLN1 N端特异性抗体的免疫组化实验,发现HAPLN1高表达与肿瘤侵袭性相关,其通过调节基质硬度促进癌细胞迁移。
3. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a polyclonal antibody targeting the N-terminal domain of HAPLN1 for osteoarthritis research*
**作者**:Smith et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对HAPLN1 N端结构域的多克隆抗体的开发与验证。作者通过ELISA、免疫荧光等技术证明该抗体特异性识别重组和天然HAPLN1蛋白,为骨关节炎的病理机制研究提供了工具。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索结果确认。)
The HAPLN1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of Hyaluronan and Proteoglycan Link Protein 1 (HAPLN1), a critical extracellular matrix (ECM) component. HAPLN1. also known as cartilage link protein 1 (CRTL1), stabilizes interactions between hyaluronan and proteoglycans like aggrecan, ensuring ECM integrity in connective tissues, particularly cartilage. This stabilization is vital for maintaining tissue resilience, hydration, and mechanical strength, making HAPLN1 essential for joint function and cartilage development.
The antibody is widely used in research to investigate ECM dynamics, cartilage-related disorders (e.g., osteoarthritis), and tissue regeneration. By detecting HAPLN1 in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, it helps elucidate the protein's expression patterns in health and disease. Studies also utilize this antibody to explore HAPLN1's role in tumor microenvironments or developmental biology, where ECM remodeling is crucial.
Produced in specific host species (e.g., rabbit or mouse), the HAPLN1 (N-term) antibody is validated for specificity and sensitivity, ensuring reliable detection in diverse biological samples. Its applications extend to preclinical models, aiding in the development of therapeutic strategies targeting ECM pathologies. Overall, this tool is indispensable for advancing understanding of tissue biomechanics and diseases linked to ECM dysfunction.
×