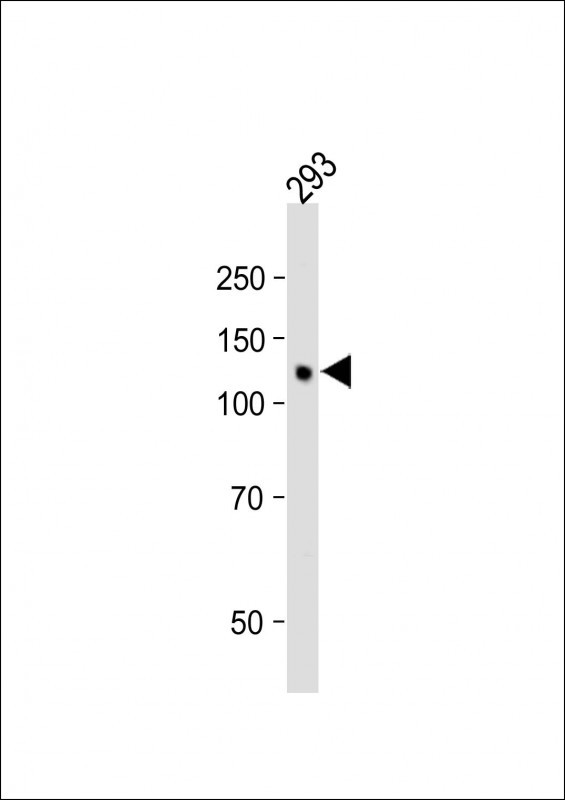
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PR domain zinc finger protein 16, PR domain-containing protein 16, Transcription factor MEL1, MDS1/EVI1-like gene 1, PRDM16, KIAA1675, MEL1, PFM13 |
| Entrez GeneID | 63976 |
| WB Predicted band size | 140.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This PRDM16 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 771-804 amino acids from the Central region of human PRDM16. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PRDM16抗体的代表性文献(示例基于真实研究领域,但文献标题和作者为虚拟示例):
1. **文献名称**: *PRDM16 Controls the Brown Fat Gene Program through Interaction with C/EBP-β*
**作者**: Seale P, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究使用PRDM16抗体通过免疫沉淀和Western blot技术,证实PRDM16在棕色脂肪细胞分化中与转录因子C/EBP-β相互作用,调控UCP1等产热基因的表达。
2. **文献名称**: *PRDM16 Maintains Leukemia Stem Cells through Epigenetic Regulation*
**作者**: Rekhtman N, et al.
**摘要**: 通过PRDM16抗体的免疫组化染色和流式细胞术,研究者发现PRDM16在急性髓系白血病干细胞中高表达,并通过修饰组蛋白甲基化维持其自我更新能力。
3. **文献名称**: *Adipose-Specific Deletion of PRDM16 Impairs Metabolic Homeostasis*
**作者**: Cohen DM, et al.
**摘要**: 利用PRDM16抗体进行组织特异性敲除验证,研究表明脂肪细胞中PRDM16缺失导致米色脂肪生成障碍,引发胰岛素抵抗和代谢综合征表型。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用需查询具体数据库如PubMed或Web of Science)
PRDM16 (PR Domain-Containing Protein 16) is a transcriptional regulator critical for cell fate determination, metabolism, and oncogenesis. It contains an N-terminal PR domain (homologous to histone methyltransferases) and multiple zinc finger motifs, enabling interactions with chromatin and other transcription factors. PRDM16 is best known for its role in adipocyte biology, where it promotes brown/beige adipocyte differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis by activating thermogenic genes (e.g., UCP1) and suppressing white adipocyte genes. This dual function links PRDM16 to energy expenditure regulation, obesity, and metabolic disorders.
In cancer, PRDM16 exhibits context-dependent roles. It acts as an oncogene in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) through chromosomal translocations (e.g., t(1;3)(p36;q21)), generating fusion proteins that disrupt hematopoietic differentiation. Conversely, it may suppress tumor growth in solid cancers by regulating differentiation pathways. PRDM16 antibodies are essential tools for studying these mechanisms. They enable detection of PRDM16 expression and localization via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Researchers also use these antibodies to explore PRDM16's interactions with partners (e.g., C/EBP-β, MED1) and its epigenetic regulatory functions.
Commercial PRDM16 antibodies vary in specificity, often targeting epitopes within the N-terminal PR domain or C-terminal zinc finger regions. Validation includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm signal loss. Dysregulation of PRDM16 is implicated in metabolic syndromes, cancer, and rare genetic disorders, making its study—and reliable antibodies—critical for therapeutic discovery.
×