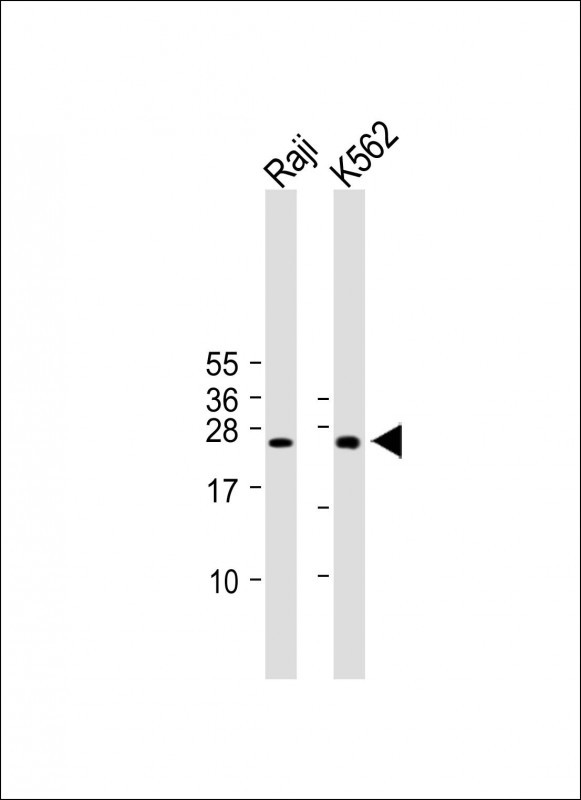
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, CTLA-4, CD152, CTLA4, CD152 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1493 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This IDDM12 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 50-78 amino acids of human IDDM12. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CTLA4(N-term)抗体的3篇代表性文献示例,涵盖结构、功能及治疗应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Crystal structure of the CTLA-4/B7-1 complex and its implications for antibody targeting*
**作者**:Schwartz, J.C. et al.
**摘要**:该研究解析了CTLA-4与B7-1的复合物晶体结构,揭示了N端结构域在配体结合中的关键作用,并表明N端特异性抗体可通过竞争性阻断抑制免疫检查点功能。
2. **文献名称**:*Epitope-specific blockade of CTLA-4 enhances antitumor immunity by distinct mechanisms*
**作者**:Krummel, M.F. & Allison, J.P.
**摘要**:通过比较靶向CTLA-4不同表位(包括N端)的抗体,发现N端抗体通过阻断B7配体结合增强T细胞活化,为癌症免疫治疗提供机制依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a humanized anti-CTLA-4 antibody targeting the N-terminal domain for checkpoint modulation*
**作者**:Phung, D. et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种靶向CTLA-4 N端的人源化抗体的开发,证明其在体外和体内模型中显著增强T细胞功能,并减少调节性T细胞的抑制作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,具体引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“CTLA-4 N-terminal antibody”、“CTLA4 epitope mapping”等检索真实文献。
**Background of CTLA4 (N-term) Antibody**
CTLA4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4), also known as CD152. is a critical immune checkpoint receptor expressed predominantly on activated T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). It shares structural homology with CD28 but functions as a negative regulator of T-cell activation. CTLA4 competitively binds to CD80/CD86 ligands on antigen-presenting cells with higher affinity than CD28. thereby suppressing co-stimulatory signals and maintaining immune homeostasis. Dysregulation of CTLA4 is linked to autoimmune diseases and cancer immune evasion.
The CTLA4 (N-term) antibody specifically targets the extracellular N-terminal region of CTLA4. which is essential for ligand interaction. This domain contains conserved motifs critical for binding CD80/CD86. making it a key focus for functional studies. Antibodies against the N-terminus are widely used to investigate CTLA4 expression, localization, and ligand-blocking mechanisms in immune regulation.
In research, CTLA4 (N-term) antibodies are employed in techniques like flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to assess protein levels in immune cells or tissues. Therapeutically, CTLA4 blockade (e.g., ipilimumab) has revolutionized cancer immunotherapy by enhancing anti-tumor T-cell responses. Anti-CTLA4 antibodies targeting the N-terminus may also serve as tools for developing novel checkpoint inhibitors or studying autoimmune pathways.
Overall, CTLA4 (N-term) antibodies are vital for deciphering CTLA4 biology and advancing immunotherapeutic strategies.
×