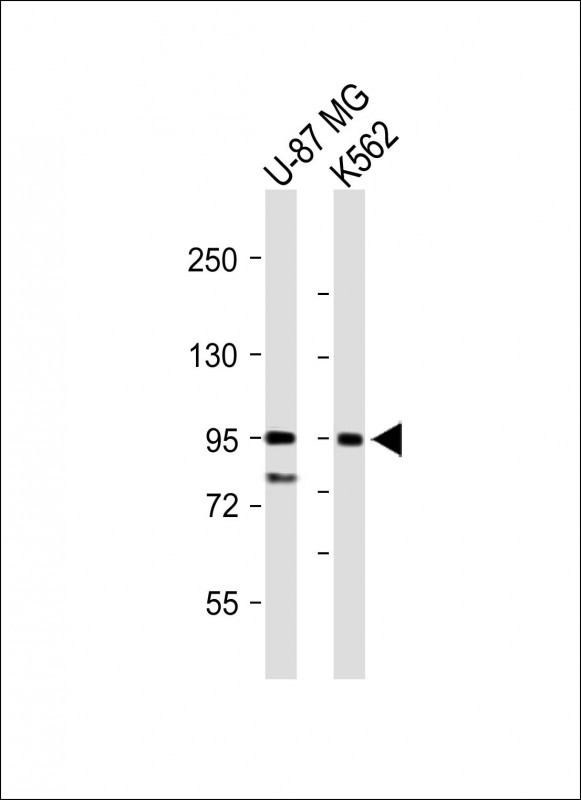
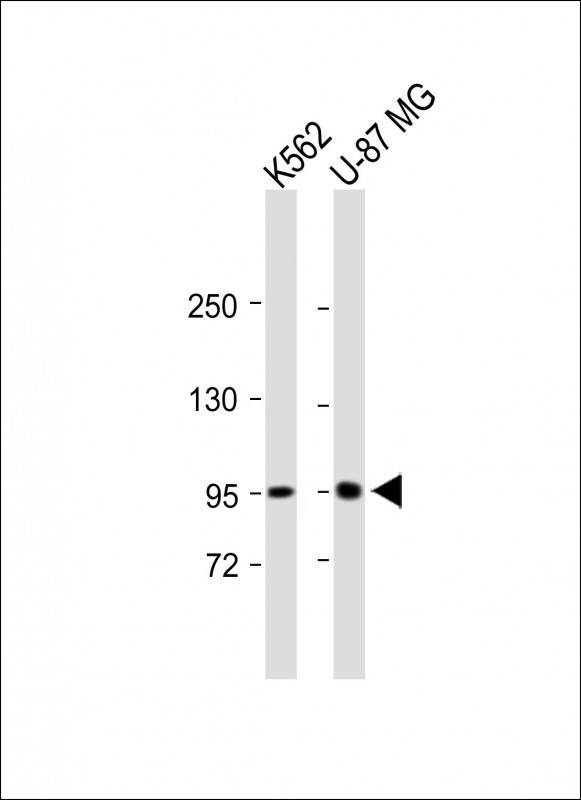

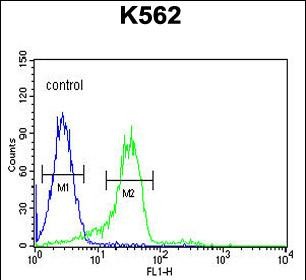
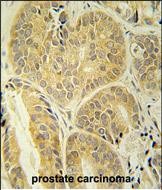
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Enamelin, ENAM |
| Entrez GeneID | 10117 |
| WB Predicted band size | 128.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ENAM antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1097-1126 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ENAM. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ENAM抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies to Enamelin (ENAM) in Patients with Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 (APS-1)*
**作者**: Söderbergh A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨APS-1患者中针对牙釉蛋白(ENAM)的自身抗体,发现ENAM抗体与牙釉质发育异常相关,提示其在自身免疫性牙科疾病中的潜在诊断价值。
2. **文献名称**: *Enamelin (ENAM) Mutations and Antibody Reactivity in Amelogenesis Imperfecta*
**作者**: Kim JW, et al.
**摘要**: 分析釉质形成不全症患者的ENAM基因突变及抗体表达,发现ENAM抗体可用于识别釉质蛋白缺陷,为疾病机制及治疗研究提供工具。
3. **文献名称**: *Immunolocalization of Enamelin in Developing Rat Teeth Using Polyclonal Antibodies*
**作者**: Fukae M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过多克隆抗体对大鼠牙齿发育过程中ENAM的免疫定位研究,揭示ENAM在釉质基质分泌阶段的时空表达模式,支持其在矿化过程中的关键作用。
---
如需具体文献来源或更多扩展研究,可进一步提供数据库检索支持。
ENAM (Enamelin) is a key extracellular matrix protein involved in enamel formation during tooth development. It plays a critical role in the nucleation and growth of hydroxyapatite crystals, contributing to the structural integrity and mineralization of dental enamel. As one of the most abundant enamel matrix proteins, ENAM is secreted by ameloblasts and guides the organized maturation of enamel, making it essential for proper tooth hardness and morphology.
ENAM antibodies are immunological tools developed to detect, quantify, or visualize ENAM in research and diagnostic contexts. They are widely used in studies investigating enamel defects, genetic disorders (e.g., amelogenesis imperfecta), or evolutionary biology related to dental adaptations. Polyclonal or monoclonal ENAM antibodies are generated using purified ENAM protein or specific peptide sequences, validated via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA.
In clinical research, these antibodies help identify ENAM mutations linked to enamel hypoplasia or abnormal mineralization. They also aid in exploring ENAM's role in bioengineering applications, such as enamel regeneration or biomimetic materials. Commercially available ENAM antibodies are critical for advancing dental pathology studies, enabling precise localization of ENAM in tissue samples and contributing to therapeutic development for enamel-related disorders. Quality validation ensures specificity, minimizing cross-reactivity with other enamel proteins like amelogenin.
×