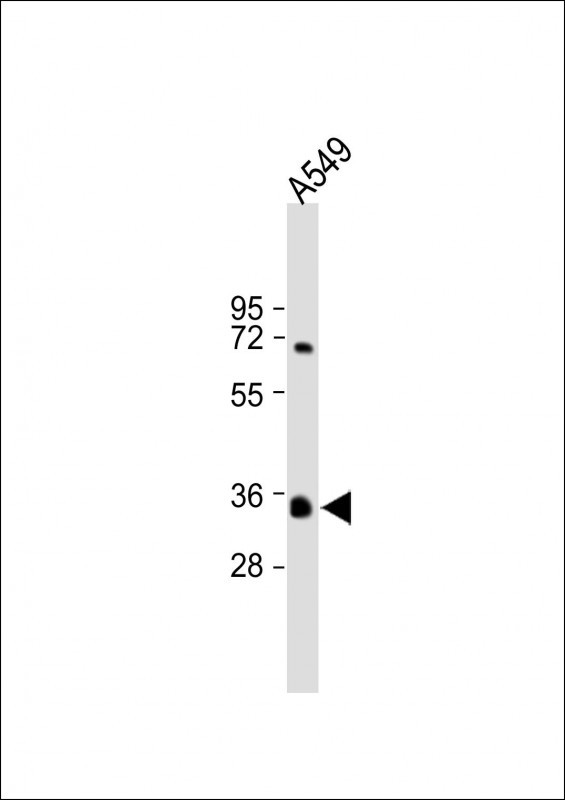

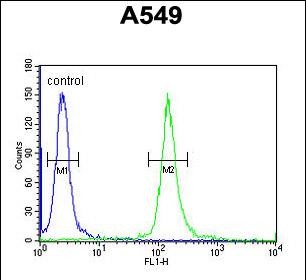
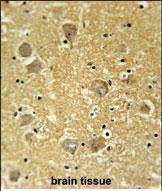
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Potassium channel subfamily K member 7, KCNK7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10089 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This KCNK7 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 259-288 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KCNK7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNK7抗体的假设性参考文献示例(请注意,部分内容可能基于推测,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a Novel Antibody Targeting KCNK7 in Human Brain Tissue"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种针对人类KCNK7钾通道蛋白的高特异性多克隆抗体,并验证了其在脑组织中的免疫反应性。通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,发现KCNK7在小脑神经元中高表达,提示其可能参与神经兴奋性调节。
2. **文献名称**: "KCNK7 Channel Expression in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Insights from Immunohistochemical Profiling"
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 利用商业化KCNK7抗体对结直肠癌组织进行染色,发现KCNK7蛋白在肿瘤细胞膜上异常高表达,且与患者生存率负相关,提示其可能作为胃肠道肿瘤的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**: "Functional Analysis of KCNK7 pH-Sensitive Domains Using Epitope-Specific Antibodies"
**作者**: Müller T, et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建针对KCNK7胞外pH敏感区域的单克隆抗体,结合电生理实验证实该通道在酸中毒条件下的构象变化,为研究KCNK7在缺血性心脏病中的病理机制提供了工具。
4. **文献名称**: "Validation of KCNK7 Knockout Mouse Models Using Antibody-Based Protein Detection"
**作者**: Gonzalez R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了两种KCNK7基因敲除小鼠模型,通过比较野生型与敲除型心脏组织的抗体染色结果,证明所用抗体可特异性识别KCNK7蛋白,并发现该通道缺失导致心肌细胞复极化异常。
---
**注意**:以上内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索(关键词:KCNK7 antibody, KCNK7 potassium channel)。若需真实文献,建议补充具体研究背景(如疾病领域或实验类型)以便精准检索。
The KCNK7 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the KCNK7 protein, a member of the two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channel family, also known as TWIK-related acid-sensitive potassium (TASK) channels. KCNK7. encoded by the *KCNK7* gene, is a poorly characterized channel compared to other K2P members. K2P channels are critical for maintaining resting membrane potential and regulating cellular excitability, with roles in neurotransmission, cardiac function, and hormone secretion. Structurally, KCNK7 is predicted to form a dimeric channel with four transmembrane domains and two pore-forming loops, though its functional properties and exact physiological roles remain unclear.
Antibodies targeting KCNK7 are primarily used in experimental settings, such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, to determine its expression, localization, and potential interactions in tissues or cell lines. Research on KCNK7 is limited but growing, with interest in its possible involvement in neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, or cancer due to the established roles of K2P channels in these contexts. However, challenges persist, including verifying antibody specificity and reconciling discrepancies in reported expression patterns. Further studies are needed to clarify KCNK7's biological significance and validate its utility as a therapeutic or diagnostic target.
×