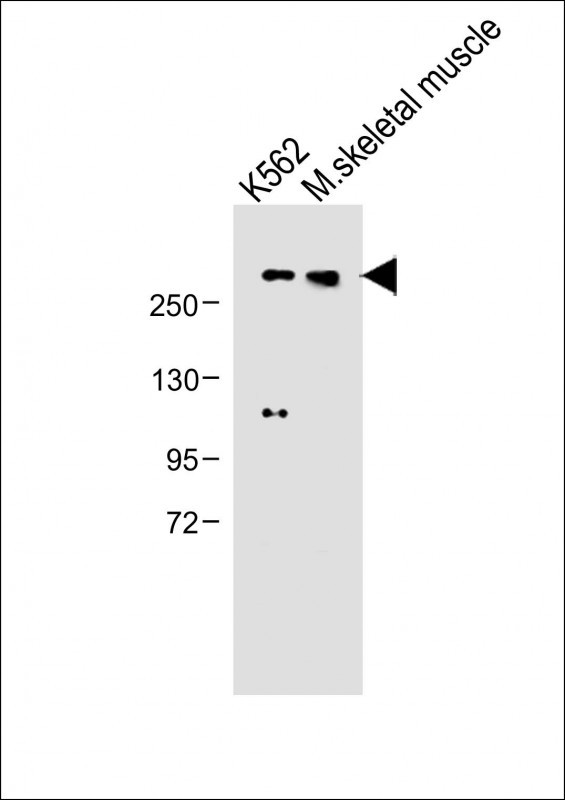
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 13, ADAM-TS 13, ADAM-TS13, ADAMTS-13, von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease, vWF-CP, vWF-cleaving protease, ADAMTS13, C9orf8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 11093 |
| WB Predicted band size | 153.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ADAMTS13 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 829-858 amino acids from the Central region of human ADAMTS13. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ADAMTS13抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括列举:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura"*
**作者**:Y. Fujimura et al.
**摘要**:该研究分析了获得性血栓性血小板减少性紫癜(TTP)患者中ADAMTS13自身抗体的特性,发现这些抗体通过抑制酶活性或加速清除导致ADAMTS13功能缺陷,进而引发微血管血栓形成。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Mechanisms of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody production in immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura"*
**作者**:S. Sukumar et al.
**摘要**:探讨了免疫介导型TTP患者产生ADAMTS13抗体的潜在机制,提出B细胞异常活化和表位扩散可能驱动自身抗体生成,为靶向免疫治疗(如利妥昔单抗)提供了理论依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Clinical significance of ADAMTS13-specific immune complexes in patients with acquired TTP"*
**作者**:M. Scully et al.
**摘要**:通过回顾性临床研究,发现ADAMTS13-抗体复合物的水平与疾病严重程度和复发风险相关,强调了抗体定量检测在TTP预后评估中的重要性。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"ADAMTS13 antibody depletion by plasma exchange in acute TTP"*
**作者**:L. Lotta et al.
**摘要**:研究证实血浆置换可有效清除患者体内的ADAMTS13抑制性抗体,恢复酶活性,为急性TTP的一线治疗方案提供了病理生理学支持。
---
以上文献均聚焦于ADAMTS13抗体的致病机制、检测方法及临床干预策略,覆盖基础研究和临床应用方向。
ADAMTS13 is a plasma metalloprotease primarily responsible for cleaving von Willebrand factor (VWF) multimers, preventing microvascular thrombosis. Autoantibodies against ADAMTS13 are central to the pathogenesis of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP), a rare but life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy. These antibodies, typically IgG, arise through autoimmune dysregulation and directly inhibit ADAMTS13 proteolytic activity or accelerate its clearance. This results in accumulation of ultra-large VWF multimers, promoting platelet aggregation and microthrombi formation that cause organ ischemia and thrombocytopenia.
Most anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies are neutralizing, targeting critical functional domains like the spacer region or cysteine-rich domains. Non-neutralizing antibodies may also contribute by forming immune complexes. Their development is associated with HLA-DRB1*11 and other genetic factors, though triggers remain unclear in many cases. Diagnosis relies on demonstrating severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (<10% activity) with detectable inhibitors via functional assays (e.g., FRET-VWF73) and antibody detection methods (ELISA).
Treatment involves urgent plasma exchange to remove antibodies and replenish ADAMTS13. combined with immunosuppressants (e.g., corticosteroids, rituximab). Persistent antibodies correlate with relapse risk, necessitating long-term monitoring. Research continues to clarify epitope specificity and develop targeted therapies like caplacizumab and recombinant ADAMTS13.
×