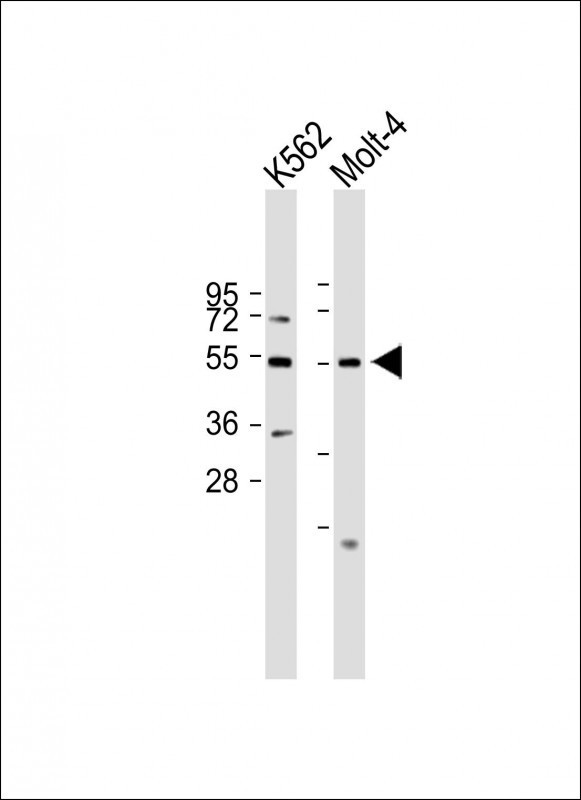
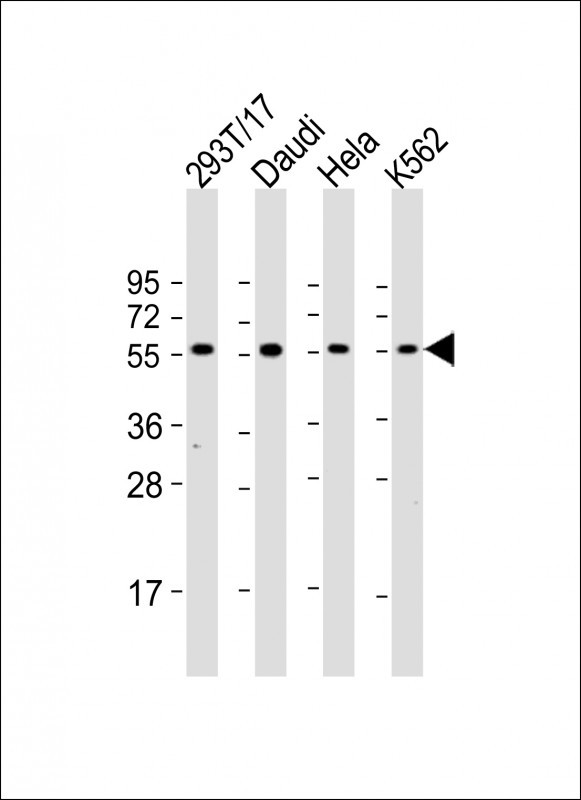
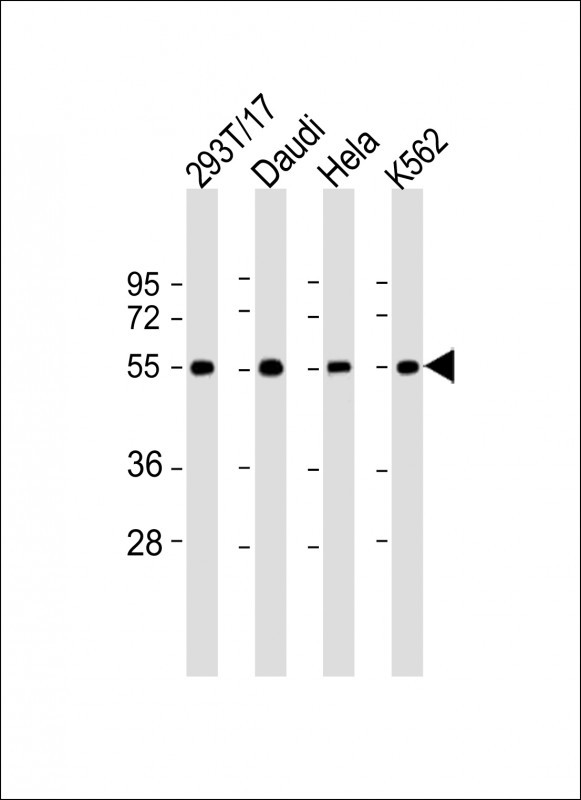
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 ligand 1, B7 homolog 6, B7-H6, NCR3LG1, B7H6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 374383 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This B7H6 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 389-415 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human B7H6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于B7H6抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**:*B7-H6-mediated NK cell targeting in human tumors: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential*
**作者**:Brandt CS, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了B7H6在多种实体瘤中的高表达及其通过结合NK细胞表面受体NKp30介导免疫逃逸的机制。作者开发了一种抗B7H6单克隆抗体,证实其可阻断B7H6-NKp30相互作用,增强NK细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤活性,并在小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A humanized anti-B7-H6 antibody induces potent antitumor immunity in preclinical models*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究报道了一种人源化抗B7H6抗体的开发与功能验证。通过结构优化,该抗体对B7H6具有高亲和力和特异性,在体外实验中有效促进NK细胞和T细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤。动物实验进一步显示,抗体单药或联合化疗可显著抑制卵巢癌和结直肠癌模型中的肿瘤进展。
---
3. **文献名称**:*B7-H6 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in hematologic malignancies*
**作者**:Chen X, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道B7H6在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞表面异常高表达。通过抗B7H6抗体联合CAR-NK细胞治疗,研究者观察到AML细胞凋亡显著增加,且抗体可逆转肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制状态,为血液肿瘤的免疫治疗提供了新策略。
---
**备注**:B7H6(又称NCR3LG1)是一种肿瘤相关免疫调节蛋白,靶向其的抗体研究多聚焦于增强天然免疫(如NK细胞)的抗肿瘤活性。以上文献涵盖了机制探索、抗体开发及联合治疗等方向,可作为该领域的核心参考。
B7H6 (B7 homolog 6), also known as CD276. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules. It functions as a ligand for natural killer (NK) cell receptor NKp30. playing a dual role in immune regulation. Unlike other B7 family members, B7H6 is rarely expressed in normal tissues but is frequently overexpressed in various malignancies, including solid tumors and hematological cancers. Its expression correlates with tumor progression, immune evasion, and poor prognosis.
Structurally, B7H6 contains immunoglobulin-like domains and binds to NKp30 to activate NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production. However, tumors exploit this interaction to create immunosuppressive effects by inducing NKp30 internalization or secreting soluble B7H6. thereby dampening NK cell responses. This dual immunoregulatory mechanism makes B7H6 a compelling therapeutic target.
Antibodies targeting B7H6 are being developed to block its immunosuppressive functions or deliver cytotoxic payloads. Preclinical studies show that anti-B7H6 monoclonal antibodies enhance NK-mediated tumor cell lysis and synergize with checkpoint inhibitors. Bispecific antibodies and CAR-T/NK cell therapies incorporating B7H6-specific binding domains are also under investigation. Challenges include optimizing specificity to minimize off-target effects and addressing tumor heterogeneity. Current research focuses on elucidating B7H6’s role in the tumor microenvironment and advancing antibody-based strategies into clinical trials.
×