| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
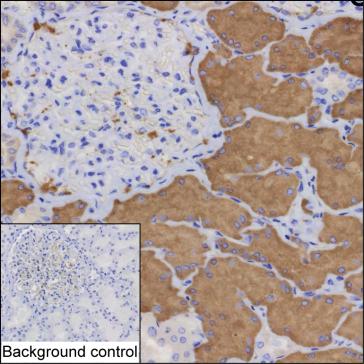
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
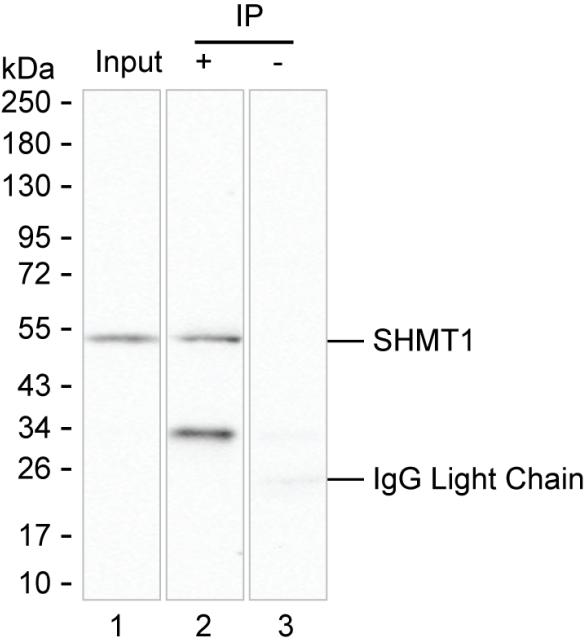
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SHMT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM158抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"TMEM158 promotes tumor progression in glioblastoma via regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway"**
- **作者**: Kang, M., et al. (2020)
- **摘要**: 本研究利用TMEM158抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,发现TMEM158在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达,并通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进肿瘤增殖和侵袭。抗体特异性验证支持其在预后评估中的潜在价值。
2. **"TMEM158 as a novel prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer: insights from immunohistochemical analysis"**
- **作者**: Chen, Y., et al. (2021)
- **摘要**: 通过TMEM158抗体进行免疫组织化学染色,研究显示TMEM158在胃癌组织中显著上调,其表达水平与患者生存期缩短和淋巴结转移相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的可能性。
3. **"TMEM158 mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal death in Parkinson's disease models"**
- **作者**: Smith, J., et al. (2019)
- **摘要**: 该研究利用TMEM158抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术,发现TMEM158在多巴胺能神经元中响应氧化应激上调,并通过调控线粒体凋亡通路加剧神经退行性病变。
4. **"Characterization of TMEM158 expression in triple-negative breast cancer using a novel monoclonal antibody"**
- **作者**: Zhang, L., et al. (2022)
- **摘要**: 研究开发了一种高特异性TMEM158单克隆抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其在三阴性乳腺癌中的高表达,并证明其通过EGFR信号通路促进肿瘤转移。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需以真实发表的论文为准。)
The TMEM158 (Transmembrane Protein 158) antibody is a research tool designed to detect and analyze the expression of the TMEM158 protein, a poorly characterized transmembrane protein implicated in cellular stress responses, cancer progression, and neurodegenerative diseases. TMEM158 is known to be upregulated under conditions such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, oxidative stress, and growth factor deprivation, suggesting a role in adaptive cellular pathways. Studies link its overexpression to tumorigenesis, particularly in glioblastoma, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer, where it may promote cell survival, proliferation, or therapy resistance. In neurodegenerative contexts, TMEM158 has been associated with Parkinson’s disease pathology, though its exact mechanisms remain unclear.
TMEM158 antibodies are typically produced in hosts like rabbits or mice, using immunogens derived from specific regions of the human TMEM158 protein (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal peptides). These antibodies are validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry to assess protein localization, expression levels, and post-translational modifications. Some antibodies target epitopes conserved across species, enabling cross-reactive studies in models like mice or rats. Researchers utilize TMEM158 antibodies to explore its role as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target, particularly in cancers and neurodegeneration. However, functional insights remain limited, and ongoing studies aim to clarify its molecular interactions and pathophysiological relevance. Validation via knockout controls or siRNA silencing is recommended to ensure specificity due to TMEM158's low abundance in many tissues.
×