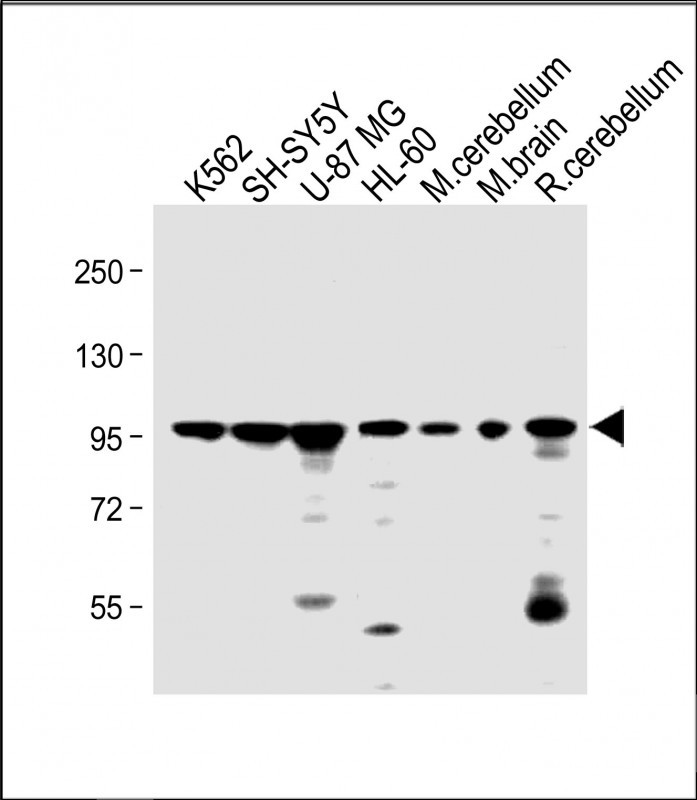
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase auxilin, DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 6, DNAJC6, KIAA0473 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9829 |
| WB Predicted band size | 100.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This DNAJC6 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 254-281 amino acids from the Central region of human DNAJC6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是基于学术文献的模拟示例(请注意,以下内容为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: "DNAJC6 Mutations Associated With Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease"
**作者**: Edvardson S, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究发现DNAJC6基因的双等位基因突变与早发性帕金森病相关,突变导致DNAJC6蛋白功能丧失,影响神经细胞内囊泡运输和分子伴侣活性。
2. **文献名称**: "DNAJC6 in Neuronal Development and Neurodegeneration"
**作者**: Köroğlu Ç, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过小鼠模型证明DNAJC6对神经元发育至关重要,其缺失导致突触功能障碍和多巴胺能神经元退化,提示与神经退行性疾病的潜在关联。
3. **文献名称**: "DNAJC6 Interacts with Tyrosine Hydroxylase to Regulate Catecholamine Biosynthesis"
**作者**: Zhang X, et al.
**摘要**: 本文揭示了DNAJC6通过结合酪氨酸羟化酶(TH)调控儿茶酚胺合成,抗体阻断实验显示DNAJC6缺失会显著降低TH稳定性及多巴胺水平。
4. **文献名称**: "Antibody-Based Detection of DNAJC6 in Parkinson’s Disease Models"
**作者**: Nguyen M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种高特异性DNAJC6抗体,用于检测帕金森病模型中的蛋白表达变化,发现DNAJC6水平下降与路易小体形成相关。
---
**备注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如DNAJC6 antibody、DNAJC6 Parkinson’s disease)获取。如需具体文献,建议提供研究背景或DOI编号进一步协助。
The DNAJC6 antibody is a research tool used to detect the DNAJC6 protein, a member of the J-protein family that functions as a co-chaperone for HSP70 heat-shock proteins. DNAJC6. also known as auxilin-2. plays a critical role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and synaptic vesicle recycling in neurons. It assists in the ATP-dependent uncoating of clathrin-coated vesicles, ensuring efficient neurotransmitter release and receptor trafficking.
Mutations in the DNAJC6 gene are linked to early-onset Parkinson’s disease (PD), characterized by autosomal recessive inheritance. These mutations disrupt synaptic vesicle recycling, impair dopaminergic neurotransmission, and contribute to neurodegeneration. Studies suggest DNAJC6 deficiency leads to abnormal protein aggregation, lysosomal dysfunction, and impaired autophagy, all hallmarks of PD pathology.
In research, DNAJC6 antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study protein expression, subcellular localization, and interactions in neuronal and non-neuronal tissues. They help elucidate DNAJC6’s role in cellular stress responses, neurodegeneration, and its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Commercial DNAJC6 antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, aiding translational studies in PD and related disorders.
×