

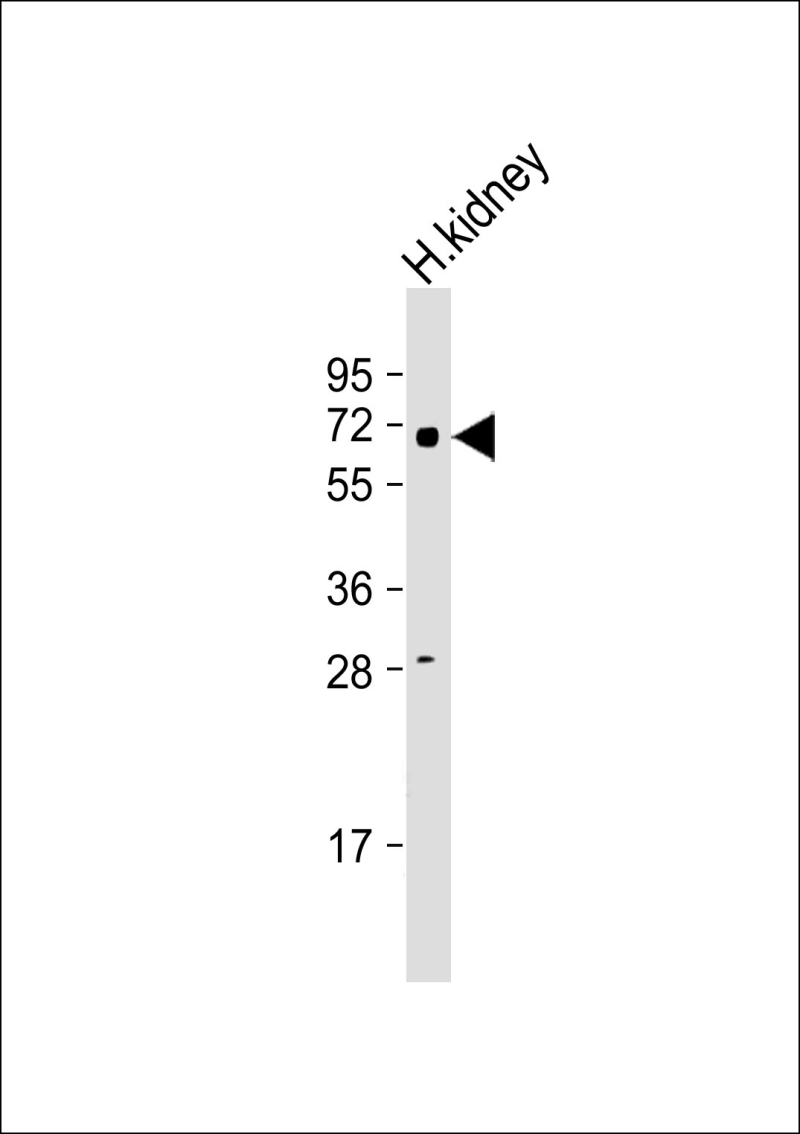

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HERV-H LTR-associating protein 2, Human endogenous retrovirus-H long terminal repeat-associating protein 2, HHLA2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 11148 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This HHLA2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 58-87 amino acids of human HHLA2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下为3篇涉及HHLA2(N-term)抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **"HHLA2. a New Immune Checkpoint Member of the B7 Family, Is Widely Expressed in Human Lung Cancer and Associated with Mutational Status"**
- **作者**: Zhu Y. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了HHLA2在非小细胞肺癌中的高表达及其与EGFR/KRAS突变的相关性,利用N端特异性抗体验证了其在肿瘤细胞膜和胞质的定位,提示其作为免疫治疗新靶点的潜力。
2. **"Characterization of HHLA2 Antibodies for Immunohistochemical Analysis in Multiple Cancer Types"**
- **作者**: Cheng H. et al.
- **摘要**: 开发并验证了针对HHLA2 N端的单克隆抗体,通过IHC证实其在结直肠癌、乳腺癌等多种实体瘤中的差异表达,强调该抗体在临床病理检测中的可靠性。
3. **"HHLA2 Immune Regulatory Function in the Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Antibody Development"**
- **作者**: Janakiram M. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用N端特异性抗体阻断HHLA2与受体相互作用,发现其可增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,为开发靶向HHLA2的免疫检查点抑制剂提供实验依据。
备注:具体文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认,部分研究可能聚焦于HHLA2功能而非抗体本身。若需实验用抗体文献,建议补充供应商(如CST、Abcam)的技术文档作为参考。
The HHLA2 (N-term) antibody is a reagent designed to detect the N-terminal region of human HHLA2 (Human Endogenous Retrovirus-H Long Terminal Repeat-Associating Protein 2), a member of the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. HHLA2 is a transmembrane protein expressed in various tissues and has gained attention for its dual roles in immune modulation, particularly within the tumor microenvironment. Unlike classical B7 ligands, HHLA2 interacts with multiple receptors, including TMIGD2 and KIR3DL3. and exhibits context-dependent co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory functions. Its overexpression in cancers such as melanoma, lung, and breast cancer correlates with immune evasion and poor prognosis, positioning it as a potential immune checkpoint target.
The HHLA2 (N-term) antibody specifically targets epitopes near the protein’s extracellular N-terminal domain, enabling applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to study HHLA2 expression and localization. Research using this antibody has highlighted HHLA2’s role in suppressing T-cell activation, promoting tumor progression, and contributing to resistance against anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies. Its development supports ongoing investigations into HHLA2’s therapeutic relevance, including efforts to design blocking antibodies or fusion proteins to disrupt HHLA2-mediated immunosuppression. This tool is critical for advancing understanding of HHLA2 biology and its implications in cancer immunotherapy.
×