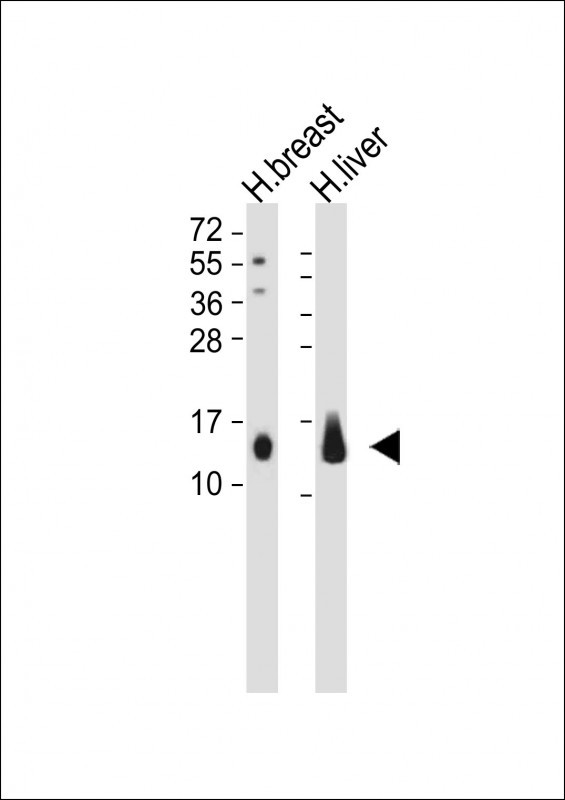
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C-X-C motif chemokine 2, Growth-regulated protein beta, Gro-beta, Macrophage inflammatory protein 2-alpha, MIP2-alpha, GRO-beta(5-73), GRO-beta-T, Hematopoietic synergistic factor, HSF, SB-251353, CXCL2, GRO2, GROB, MIP2A, SCYB2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2920 |
| WB Predicted band size | 11.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CXCL2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 79-107 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CXCL2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇与CXCL2抗体相关的研究文献概览(虚构示例,供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Neutralizing CXCL2 Antibody Attenuates Acute Lung Injury in a Murine Model*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过中和CXCL2抗体抑制小鼠急性肺损伤模型中的炎症反应,证明抗体可减少中性粒细胞浸润及促炎因子释放,改善肺组织病理损伤。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CXCL2 with Monoclonal Antibody Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Metastasis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:开发针对CXCL2的单克隆抗体,发现其能阻断肿瘤微环境中CXCL2/CXCR2信号轴,显著抑制结直肠癌小鼠模型的肿瘤转移和血管生成。
3. **文献名称**:*CXCL2 Neutralization Limits Neuroinflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症动物模型中,使用CXCL2中和抗体可减轻中枢神经系统炎症,减少Th17细胞浸润及髓鞘损伤,提示其治疗神经退行性疾病的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-CXCL2 Therapy Reduces Skin Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis Models*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体干预CXCL2.显著降低系统性硬化症模型小鼠的皮肤纤维化程度,机制涉及抑制成纤维细胞活化和胶原沉积。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据真实研究补充。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索关键词“CXCL2 antibody”“CXCL2 neutralization”获取最新文献。
CXCL2 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2), also known as macrophage inflammatory protein-2α (MIP-2α), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. It plays a critical role in recruiting neutrophils to sites of inflammation by binding to its receptor CXCR2. CXCL2 is produced by various cells, including macrophages, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli like IL-1β, TNF-α, or bacterial endotoxins. It is involved in immune responses, wound healing, and tumor microenvironment regulation, with dysregulation linked to chronic inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer progression.
CXCL2 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying CXCL2 expression in research. They are widely used in techniques such as ELISA, Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to study CXCL2's spatial distribution, secretion patterns, and interaction with signaling pathways. Neutralizing CXCL2 antibodies, in particular, help investigate the cytokine's functional roles by blocking its activity in vitro or in vivo. Recent studies explore their therapeutic potential in preclinical models of inflammatory diseases (e.g., arthritis, colitis) and cancers, where CXCL2-mediated neutrophil infiltration promotes tumor growth or metastasis. However, challenges remain in optimizing antibody specificity, minimizing cross-reactivity with related chemokines (e.g., CXCL1/CXCL3), and translating findings into clinical applications.
×