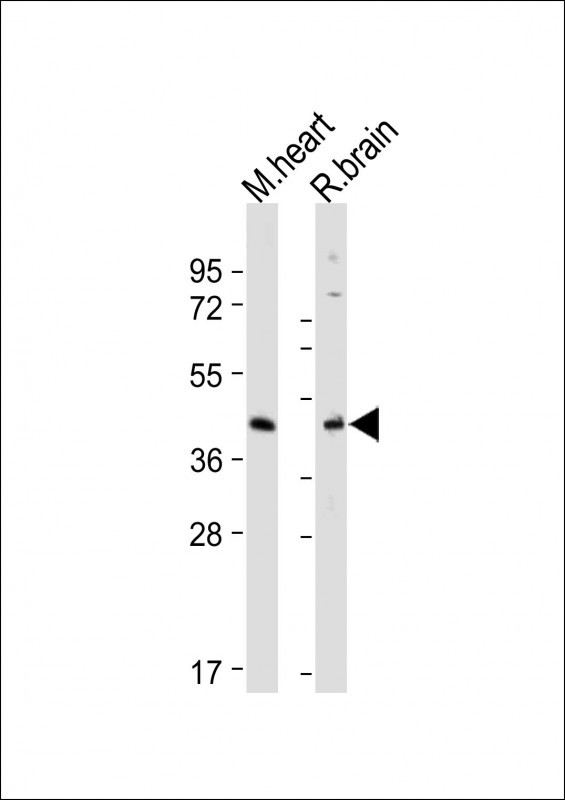
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1, Chemoattractant receptor-like 2, Flow-induced endothelial G-protein coupled receptor 1, FEG-1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1, G-protein coupled receptor 30, GPCR-Br, IL8-related receptor DRY12, Lymphocyte-derived G-protein coupled receptor, LYGPR, Membrane estrogen receptor, mER, GPER1, CEPR, CMKRL2, DRY12, GPER, GPR30 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2852 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This GPER antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 346-375 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human GPER. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GPER抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要总结其研究内容和抗体相关结论:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"GPR30: A G Protein-Coupled Receptor for Estrogen"*
**作者**:Filardo EJ, et al.
**摘要**:早期研究确认GPER(GPR30)作为雌激素膜受体的功能,通过免疫荧光和Western blot验证了GPER抗体的特异性,发现其在乳腺癌细胞中高表达,并介导非基因组雌激素信号通路。
2. **文献名称**:*"Critical evaluation of GPR30 antibody specificity"*
**作者**:Prossnitz ER, et al.
**摘要**:系统评估了多种市售GPER抗体的特异性,发现部分抗体在GPER基因敲除小鼠组织中仍出现非特异性结合,提示需谨慎选择抗体并建议结合基因沉默/过表达实验验证结果。
3. **文献名称**:*"G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor (GPER) Expression in Normal and Pathological Endometrium"*
**作者**:He YY, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析GPER在子宫内膜组织中的分布,使用经肽阻断实验验证抗体的可靠性,发现GPER在子宫内膜癌中表达显著上调,提示其临床相关性。
---
**说明**:上述文献强调抗体验证的重要性,尤其在GPER研究中需结合基因编辑技术(如敲除模型)或竞争性肽段阻断实验排除假阳性。建议优先选择经同行评议验证的抗体或引用方法学严谨的研究。
**Background of GPER Antibodies**
GPER (G-Protein Coupled Estrogen Receptor), also known as GPR30. is a membrane-bound receptor that mediates rapid, non-genomic signaling responses to estrogen. Unlike classical nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα/β), GPER activates intracellular pathways via G-proteins, influencing processes like cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. GPER antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in tissues and cell lines. These antibodies are commonly used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate GPER's role in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders.
However, challenges exist due to historical inconsistencies in antibody specificity, leading to debates about GPER's physiological relevance. Validation via knockout controls or siRNA silencing is essential to confirm antibody reliability. Recent studies highlight GPER's therapeutic potential, particularly in hormone-resistant cancers and cardiovascular protection, driving demand for high-quality reagents. Research also explores GPER's interplay with traditional ERs and its ligand-binding mechanisms, including interactions with synthetic agonists (e.g., G-1) and antagonists (e.g., G15). As interest grows in targeting GPER for disease modulation, optimizing antibody specificity remains pivotal for advancing mechanistic and translational studies.
×