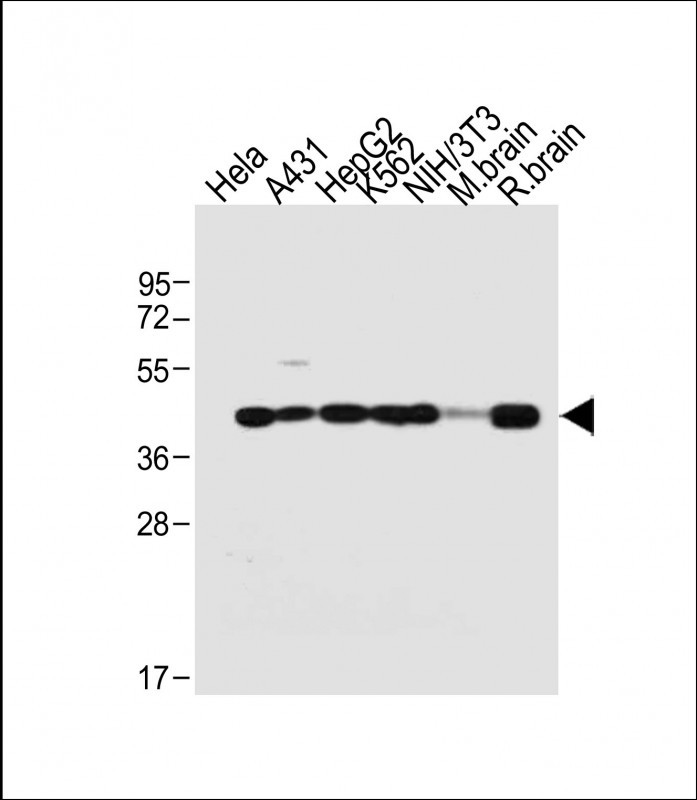
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
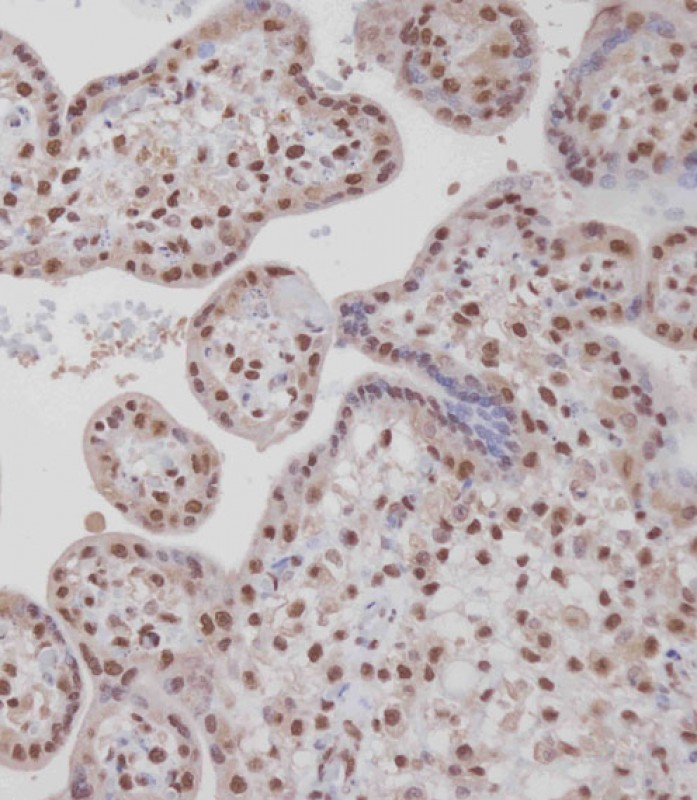
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TAR DNA-binding protein 43, TDP-43, TARDBP, TDP43 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23435 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This TARDBP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human TARDBP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TARDBP (N-term)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis"**
- **作者**: Neumann, M., et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究首次报道TDP-43在FTLD和ALS患者神经元中的异常聚集,并利用针对TDP-43 N端的抗体(如兔多克隆抗体)通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其在病理包涵体中的特异性标记,揭示了TDP-43蛋白病变与神经退行性疾病的相关性。
2. **"Characterization of antibodies phosphorylated neurofilament and TDP-43 in neurodegenerative diseases"**
- **作者**: Zhang, Y.J., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究系统评估了多种TDP-43抗体(包括N端抗体)的特异性,证明其在人脑组织及细胞模型中能有效识别全长TDP-43蛋白,但对C端片段无交叉反应,为病理诊断和机制研究提供了可靠工具。
3. **"Dysregulation of TDP-43 intracellular localization and early onset ALS caused by TARDBP mutations"**
- **作者**: Igaz, L.M., et al.
- **摘要**: 通过N端特异性抗体,研究发现TARDBP基因突变导致TDP-43从细胞核错误定位至胞质,并形成不溶性聚集体,揭示了突变如何通过影响TDP-43的正常功能参与ALS发病机制。
4. **"TDP-43 is deposited in the Guam parkinsonism-dementia complex brains"**
- **作者**: Hasegawa, M., et al.
- **摘要**: 利用TDP-43 N端抗体,研究证实关岛型帕金森-痴呆综合征患者脑内存在TDP-43阳性包涵体,提示其病理过程与TDP-43蛋白异常加工相关,拓展了TDP-43蛋白病的疾病谱。
这些文献涵盖了抗体在疾病机制、诊断工具开发和病理标记物验证中的应用,均强调N端抗体在检测全长TDP-43及其异常聚集中的关键作用。
The TARDBP (N-term) antibody is a tool used to detect the N-terminal region of TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43), encoded by the TARDBP gene. TDP-43 is a ubiquitously expressed RNA/DNA-binding protein involved in transcriptional regulation, RNA splicing, and mRNA stability. Structurally, TDP-43 contains two N-terminal RNA recognition motifs (RRM1 and RRM2) and a C-terminal disordered region. The N-terminal domain is critical for protein homodimerization and interactions with other molecules, playing a role in maintaining TDP-43’s solubility and nuclear localization.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region are particularly valuable in studying TDP-43 pathology, as neurodegenerative diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) are characterized by cytoplasmic mislocalization, aggregation, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, cleavage) of TDP-43. Unlike C-terminal epitopes, which may be obscured by disease-associated modifications, the N-terminal region remains more accessible, making this antibody reliable for detecting both normal and pathological TDP-43 forms in techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence.
Research using this antibody has contributed to understanding TDP-43’s role in disease mechanisms, including stress granule dynamics, proteostasis, and neuronal toxicity. It also helps differentiate TDP-43 pathology from other proteinopathies (e.g., tau, α-synuclein) in diagnostic applications.
×