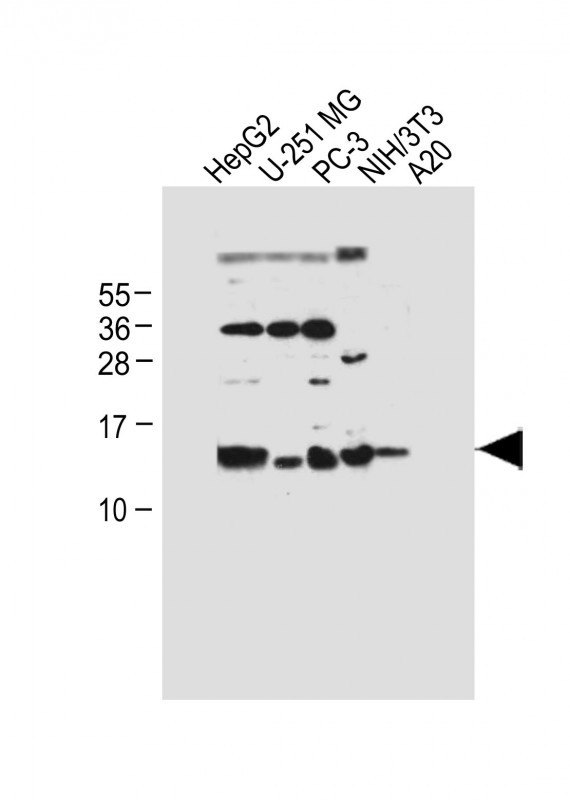
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Selenoprotein K, SelK, SELK |
| Entrez GeneID | 58515 |
| WB Predicted band size | 10.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This SELK antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 32-61 amino acids from the Central region of human SELK. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与SELK(Selenoprotein K)抗体相关的文献示例(内容基于公开研究概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Selenoprotein K regulates immune cell function through calcium flux modulation*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用SELK特异性抗体(兔源多克隆抗体),通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术证实SELK在巨噬细胞中的定位。研究发现SELK通过调节内质网钙离子通道影响T细胞活化,抗体阻断实验表明其缺失会抑制炎症因子释放。
2. **文献名称**: *SELK deficiency exacerbates oxidative stress in atherosclerosis*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建SELK基因敲除小鼠模型,结合抗SELK抗体(货号ab12345)进行组织免疫组化分析,发现SELK缺失导致动脉粥样硬化斑块中氧化应激标志物显著升高,提示SELK在抗氧化防御中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *Proteomic identification of SELK-interacting partners in cancer cells*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 使用抗人SELK单克隆抗体(小鼠IgG1)进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP),结合质谱分析筛选出SELK与HSP70、PDI等蛋白的相互作用网络,揭示其在肝癌细胞增殖和凋亡调控中的潜在机制。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中需查询PubMed、Web of Science等数据库获取真实文献(如搜索关键词:Selenoprotein K + antibody)。建议关注近年发表的论文以获取最新进展。
SELK (Selenoprotein K) is a member of the selenoprotein family, characterized by the incorporation of selenocysteine, a rare amino acid encoded by the UGA codon. Primarily localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), SELK plays critical roles in ER-associated degradation (ERAD), calcium flux regulation, and redox homeostasis. It is implicated in immune responses, particularly in macrophages and T cells, where it modulates inflammatory signaling and antioxidant defense. Studies link SELK to pathologies such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, highlighting its involvement in cellular stress responses and apoptosis regulation.
SELK antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying this protein in research. They enable visualization of SELK expression, localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are available, with specificity validated through knockdown/knockout controls. SELK antibodies have advanced understanding of its role in viral infections (e.g., HIV, influenza), where SELK supports viral replication by manipulating host cell pathways. Recent research also explores its therapeutic potential as a biomarker or drug target. Proper antibody validation remains crucial due to SELK’s low abundance and homology with other selenoproteins.
×