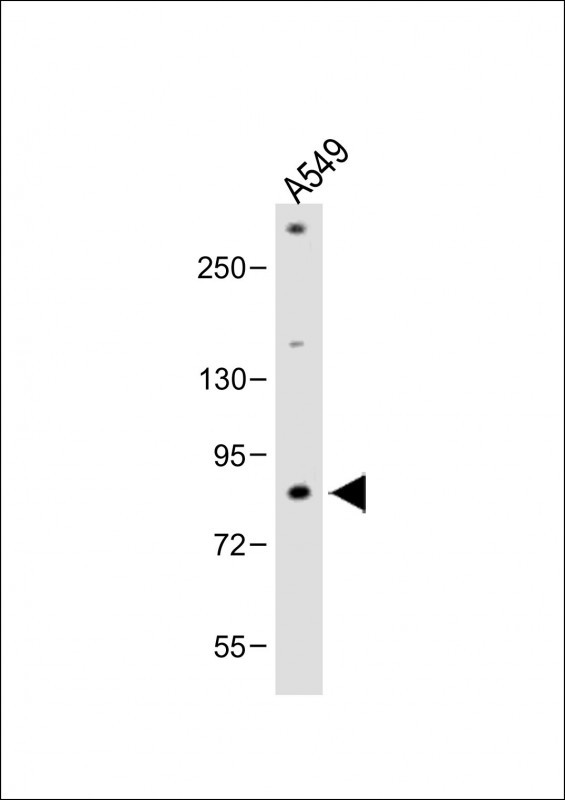
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 19, F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 19, FBXL19, FBL19 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54620 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This FBXL19 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 543-570 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human FBXL19. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于FBXL19抗体的3篇参考文献概览(文献名称、作者及简要摘要):
---
1. **文献名称**: *FBXL19 regulates BMP signaling by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of Smad1*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用FBXL19特异性抗体,发现FBXL19通过介导Smad1的泛素化降解负调控BMP信号通路,影响胚胎发育和细胞分化。
---
2. **文献名称**: *F-box protein FBXL19-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC3 promotes tumor metastasis*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过FBXL19抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示FBXL19通过降解组蛋白去乙酰化酶HDAC3促进肿瘤转移,为癌症治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *FBXL19 interacts with the NLRP3 inflammasome and modulates its activity in macrophages*
**作者**: Wang X, et al.
**摘要**: 使用FBXL19抗体进行蛋白质组学分析,发现FBXL19通过与NLRP3炎性小体结合调控炎症反应,在自身免疫性疾病中发挥重要作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对真实文献信息(可通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索“FBXL19 antibody”或“FBXL19 function”获取最新研究)。
FBXL19 (F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 19) is a substrate-recognition component of the Skp1-Cullin-F-box (SCF) ubiquitin ligase complex, which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of specific target proteins. As an F-box protein, FBXL19 contains a conserved F-box domain that facilitates interactions with Skp1. anchoring it to the core SCF complex. It also harbors leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) at its C-terminus, which are critical for substrate recognition.
FBXL19 has been implicated in diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, inflammatory responses, and autophagy. Studies suggest it regulates skin homeostasis by targeting specific proteins for degradation, such as c-Jun, a component of the AP-1 transcription factor involved in epidermal differentiation and inflammation. Dysregulation of FBXL19 has been linked to pathological conditions, particularly psoriasis, where reduced FBXL19 expression correlates with hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and impaired skin barrier function.
Antibodies against FBXL19 are essential tools for investigating its expression patterns, protein interactions, and mechanistic roles in both physiological and disease contexts. These antibodies are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Validation typically includes testing in FBXL19-knockout models to confirm specificity. Research utilizing FBXL19 antibodies continues to explore its potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in inflammatory skin disorders and cancers where SCF complex activity is altered.
×