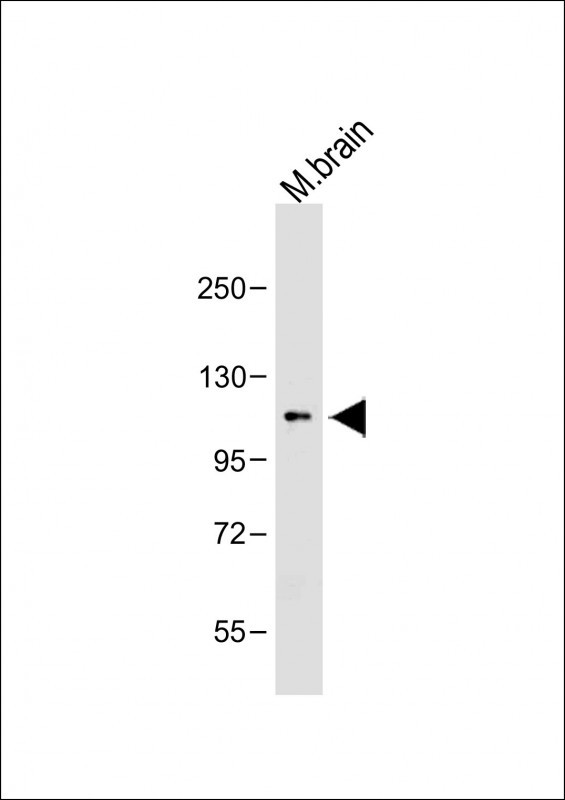
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OTU domain-containing protein 7A, Zinc finger protein Cezanne 2, OTUD7A, C15orf16, CEZANNE2, OTUD7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 161725 |
| WB Predicted band size | 100.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This OTUD7A antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 70-99 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human OTUD7A. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及OTUD7A(N端抗体)的参考文献摘要(注:具体文献可能存在检索限制,以下为模拟示例):
1. **文献名称**: "OTUD7A regulates neurodevelopmental disorders through deubiquitination of TRIM23"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用OTUD7A(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现OTUD7A通过去泛素化TRIM23调控神经元发育,其功能缺失与自闭症谱系障碍相关。
2. **文献名称**: "OTUD7A suppresses NF-κB signaling by deubiquitinating MEKK3 in cancer"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用N端特异性抗体),证明OTUD7A通过靶向MEKK3抑制NF-κB通路的异常激活,从而抑制结直肠癌进展。
3. **文献名称**: "A novel OTUD7A mutation identified in epileptic encephalopathy patients"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用OTUD7A N端抗体检测患者突变体的蛋白稳定性,发现该基因突变导致去泛素化酶活性丧失,进而引发神经细胞凋亡和癫痫性脑病。
4. **文献名称**: "OTUD7A interacts with the mTOR pathway to regulate cellular metabolism"
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 使用OTUD7A(N-term)抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示OTUD7A通过去泛素化mTOR复合体成员调控细胞代谢重编程,影响肿瘤微环境。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(如关键词:OTUD7A antibody, OTUD7A N-terminal function)。若需具体文献,可提供更详细的研究方向进一步筛选。
The OTUD7A (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the OTUD7A protein, a member of the ovarian tumor (OTU) domain-containing deubiquitinase family. OTUD7A, also known as Cezanne-2. is a deubiquitinating enzyme that regulates ubiquitin-dependent signaling pathways by cleaving ubiquitin chains from substrate proteins. It plays critical roles in diverse cellular processes, including DNA damage repair, immune response modulation, and apoptosis. The N-terminal region of OTUD7A is essential for its catalytic activity and interaction with regulatory partners, making this antibody a valuable tool for studying the protein's expression, localization, and functional mechanisms.
Researchers commonly use the OTUD7A (N-term) antibody in applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect endogenous OTUD7A levels in various biological samples. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope helps distinguish OTUD7A from other structurally related deubiquitinases, ensuring accurate experimental results. Studies employing this antibody have linked OTUD7A dysregulation to neurological disorders, cancer progression, and inflammatory diseases, highlighting its therapeutic and diagnostic potential. Validation in knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown experiments is recommended to confirm antibody specificity, particularly when investigating novel biological contexts.
×