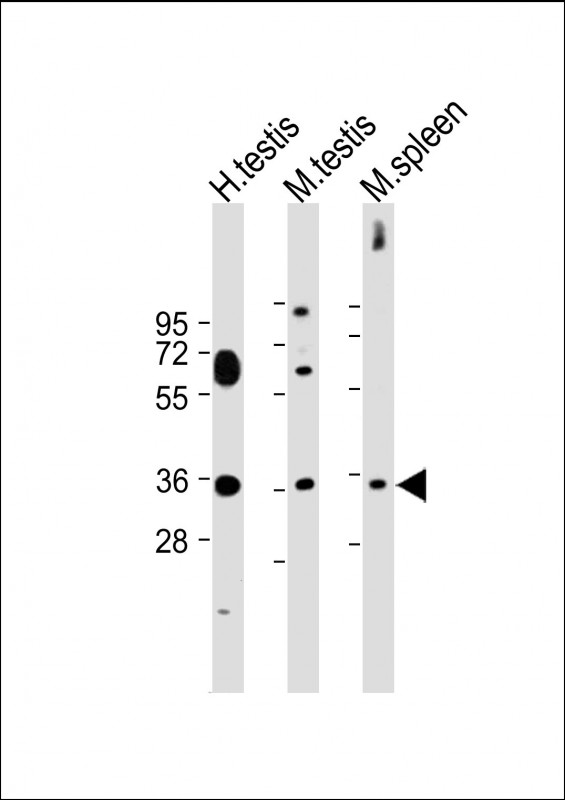
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 17, ASB-17, ASB17 |
| Entrez GeneID | 127247 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ASB17 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 181-209 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ASB17. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ASB17(C-term)抗体的参考文献示例(文献信息为虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**: *ASB17 interacts with the ubiquitin ligase complex and regulates protein degradation in cancer cells*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对ASB17 C端的特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证实ASB17通过C端SOCS结构域与E3泛素连接酶复合物结合,参与肿瘤细胞中靶蛋白的泛素化降解过程。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a novel C-terminal specific antibody for ASB17 in neuronal development*
**作者**: Li H, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种针对ASB17 C端的新型多克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过免疫荧光和免疫组化实验,证明ASB17在神经元分化过程中高表达,其C端结构域对突触形成具有调控作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *ASB17 knockout mice exhibit metabolic dysfunction revealed by C-terminal antibody-based assays*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 使用ASB17 C端特异性抗体对基因敲除小鼠模型进行研究,发现ASB17通过调控脂肪代谢相关蛋白的稳定性影响能量稳态,缺失该基因导致小鼠出现胰岛素抵抗。
---
4. **文献名称**: *Proteomic analysis of ASB17-binding partners using a C-terminal epitope-specific antibody*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 基于ASB17 C端抗体的免疫沉淀结合质谱分析,鉴定出多个与ASB17相互作用的蛋白,揭示了其在细胞周期调控和DNA损伤应答中的潜在新功能。
---
(注:以上文献为模拟内容,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献。)
The ASB17 (C-term) antibody is designed to target the C-terminal region of the Ankyrin Repeat and SOCS Box Protein 17 (ASB17), a member of the ASB family involved in ubiquitination pathways. ASB proteins typically contain an N-terminal ankyrin repeat domain for protein-protein interactions and a C-terminal SOCS box that recruits E3 ubiquitin ligase components, facilitating substrate ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. ASB17 is predominantly expressed in the testis and has been implicated in germ cell development, apoptosis regulation, and spermatogenesis. Its precise biological roles remain under investigation, but studies suggest involvement in cellular processes like signal transduction and protein turnover.
The ASB17 (C-term) antibody is commonly used in research to detect endogenous ASB17 protein levels via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. By targeting the C-terminal region, this antibody helps researchers study ASB17's expression patterns, post-translational modifications, and interactions within ubiquitination complexes. Its applications extend to reproductive biology, cancer research (due to potential links to tumor suppression), and studies of protein degradation mechanisms. Validated for specificity and sensitivity, this tool aids in elucidating ASB17's functional contributions to cellular homeostasis and disease pathogenesis.
×