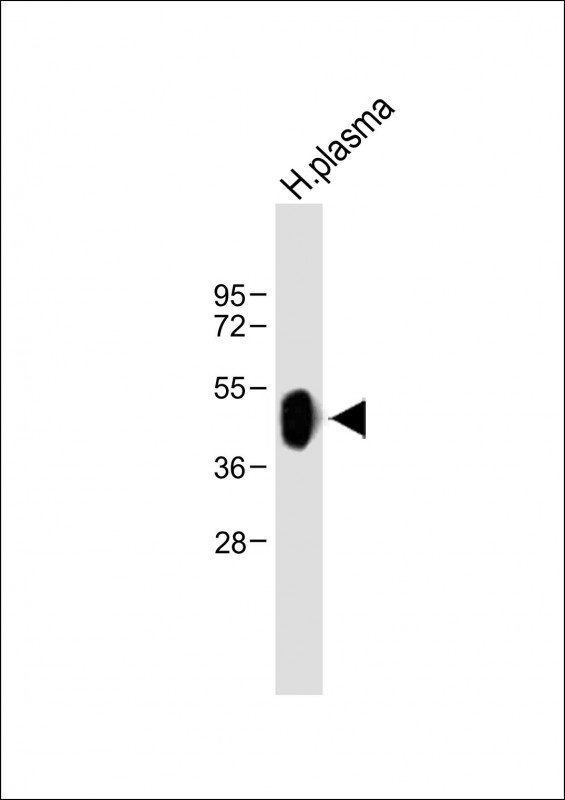
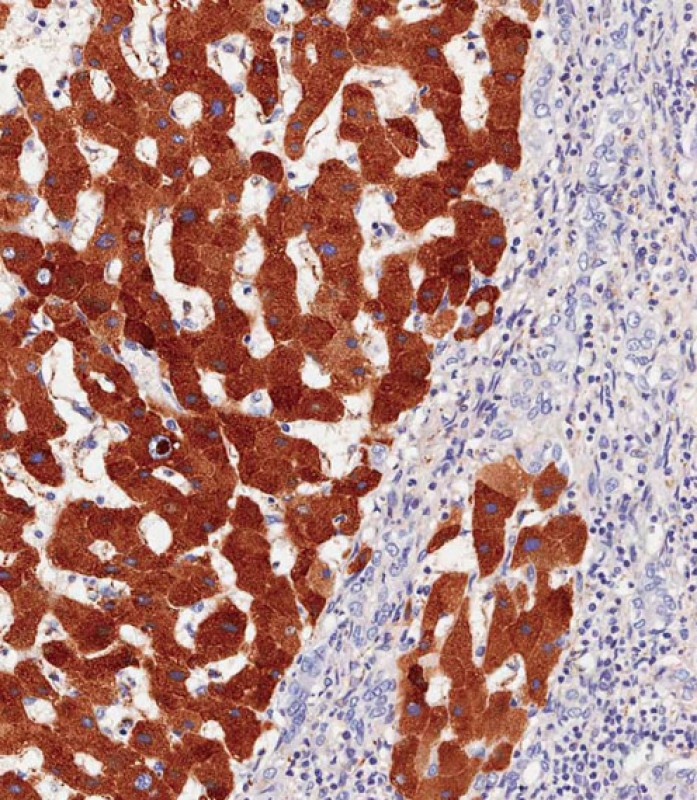
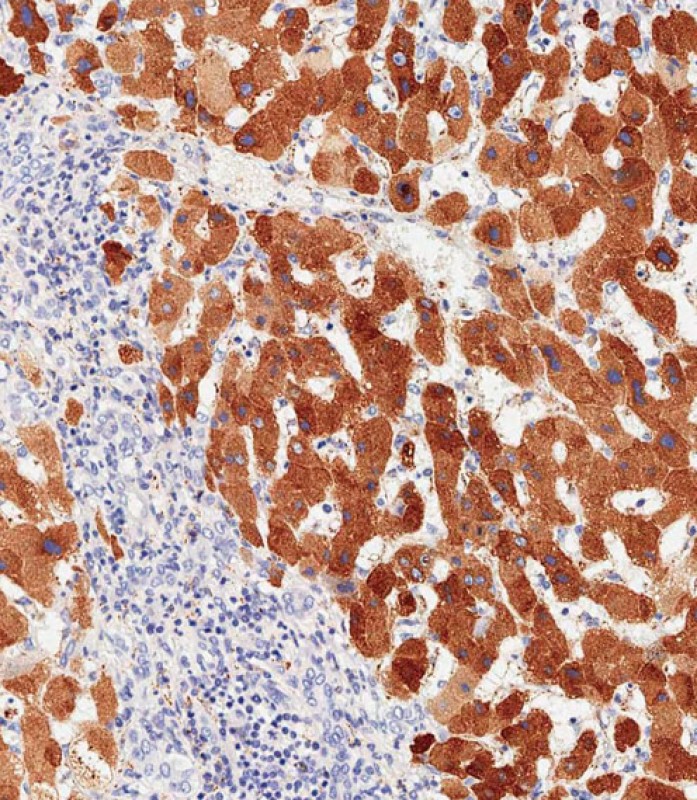
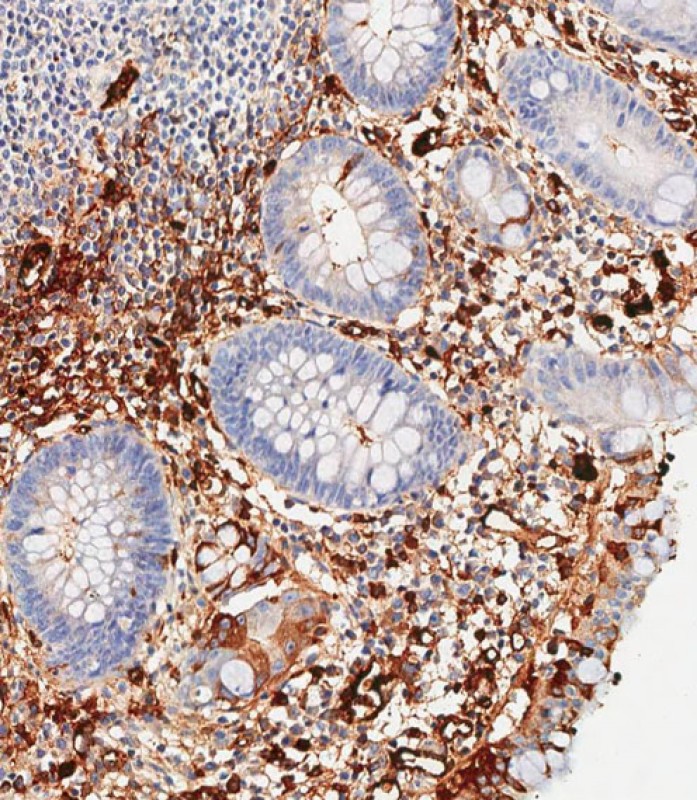
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Haptoglobin, Zonulin, Haptoglobin alpha chain, Haptoglobin beta chain, HP |
| Entrez GeneID | 3240 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This HP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 296-322 amino acids from the Central region of human HP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于幽门螺杆菌(HP)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection using serum antibody measurements"*
**作者**:Pérez-Pérez GI, Blaser MJ
**摘要**:研究评估了血清中抗HP IgG抗体的检测在诊断幽门螺杆菌感染中的敏感性和特异性,提出该方法可作为非侵入性筛查工具,尤其适用于流行病学调查和初次诊断。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Helicobacter pylori antibodies and gastric cancer risk: a prospective study"*
**作者**:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Working Group
**摘要**:通过大规模队列研究分析HP抗体阳性与胃癌风险的关系,发现长期HP感染者的血清抗体水平与胃癌发病率显著相关,支持HP感染作为胃癌的重要危险因素。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Decline in Helicobacter pylori IgG antibodies after eradication therapy: implications for monitoring treatment success"*
**作者**:Kosunen TU, Seppälä K
**摘要**:追踪患者接受HP根除治疗后血清IgG抗体的动态变化,发现抗体滴度在治疗后6-12个月内显著下降,提示血清学检测可用于间接评估治疗效果。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Helicobacter pylori infection in children: detection of specific antibodies in saliva and serum"*
**作者**:Thomas JE, Dale A
**摘要**:比较儿童唾液和血清中HP抗体的检测效能,发现唾液抗体检测的敏感度较低,但结合血清学结果可提高儿童HP感染诊断的准确性,为无创检测提供新方向。
---
以上文献涵盖了HP抗体在诊断、疾病关联、治疗监测及儿童感染中的应用,均为该领域的经典研究方向。如需具体文献来源,可进一步通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索标题及作者获取全文。
**Background of *Helicobacter pylori* (HP) Antibodies**
*Helicobacter pylori* (HP), a Gram-negative bacterium colonizing the human gastric mucosa, is a major cause of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. HP infection triggers both innate and adaptive immune responses, leading to the production of specific antibodies, primarily IgG and IgA, detectable in serum. These antibodies serve as biomarkers for diagnosing HP infection, especially in non-invasive testing.
Serological tests for HP antibodies are widely used due to their convenience and cost-effectiveness. However, they have limitations: antibodies may persist long after infection resolution, leading to false-positive results, and they cannot distinguish between active or past infections. Thus, serology is often combined with other methods (e.g., urea breath test, stool antigen test) for accurate diagnosis.
Epidemiologically, HP infection affects over 50% of the global population, with higher prevalence in developing regions. Antibody studies also contribute to understanding host-pathogen interactions, virulence factors (e.g., CagA, VacA), and vaccine development efforts. Despite advancements, challenges remain in linking antibody profiles to disease outcomes, emphasizing the need for nuanced interpretation in clinical and research settings.
×