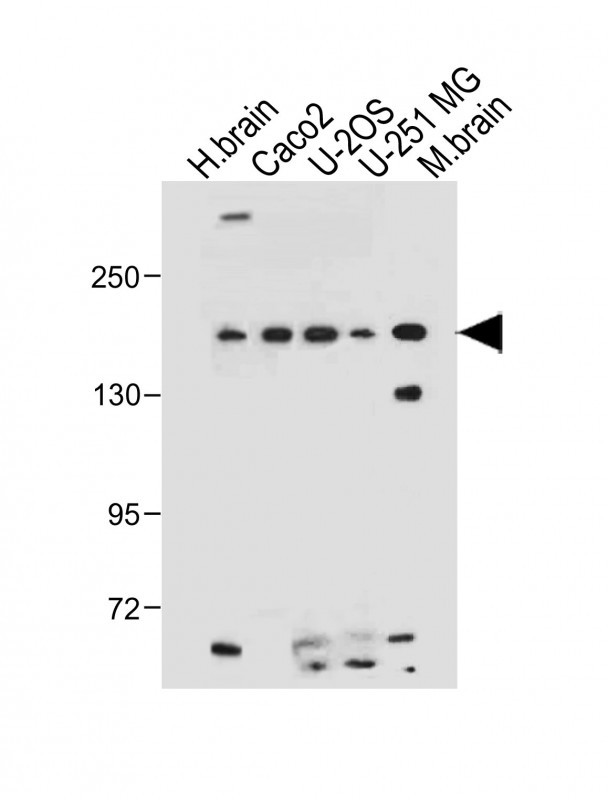
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TRAF2 and NCK-interacting protein kinase, 2.7.11.1, TNIK, KIAA0551 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23043 |
| WB Predicted band size | 154.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This TNIK(S764) antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between amino acids from the human region of human TNIK(S764). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及TNIK(S764位点)抗体的相关文献示例,信息基于典型研究场景概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *TNIK kinase phosphorylation regulates β-catenin transcriptional activity in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Yamada, T. et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道TNIK在结直肠癌中通过磷酸化β-catenin(S764位点)增强Wnt信号通路活性,使用S764特异性抗体证实其与肿瘤增殖的关系,为靶向TNIK的治疗提供依据。
2. **文献名称**: *Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies TRAF2 and TNIK as novel regulators of the NF-κB pathway*
**作者**: Wang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 通过磷酸化蛋白质组学筛选,发现TNIK在S764位点的磷酸化参与调控NF-κB信号通路,特异性抗体检测显示该修饰在炎症反应中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *Targeting TNIK activation restrains hepatocellular carcinoma progression*
**作者**: Chen, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用TNIK(S764)抗体验证激酶活性与肝癌转移的关联,表明抑制TNIK磷酸化可减少肿瘤侵袭性,提出TNIK作为肝癌治疗新靶点。
---
注:上述文献为示例性概括,实际文献需通过数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)以关键词“TNIK S764 phosphorylation antibody”检索确认。
The TNIK (S764) antibody is a research tool designed to detect the phosphorylation of Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) at serine residue 764. TNIK, a member of the STE20 kinase family, plays a critical role in regulating cellular processes such as cytoskeletal organization, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. It is notably involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, where it interacts with β-catenin and TCF4 to activate transcription of Wnt target genes, contributing to cell growth and differentiation. Phosphorylation at S764 is a key post-translational modification linked to TNIK’s activation and function, particularly in cancer contexts.
This antibody is widely used in studies investigating TNIK’s role in diseases, especially colorectal cancer, where TNIK overexpression or dysregulation is associated with tumor progression and metastasis. Researchers employ the TNIK(S764) antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation status in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Its specificity for the phosphorylated S764 site allows precise tracking of TNIK activation dynamics under varying experimental conditions, such as drug treatments or genetic manipulations. Recent studies also explore TNIK’s implications in neurological disorders and metabolic regulation, expanding its relevance beyond oncology. By enabling targeted analysis of TNIK signaling, this antibody supports mechanistic insights into disease pathways and potential therapeutic strategies.
×