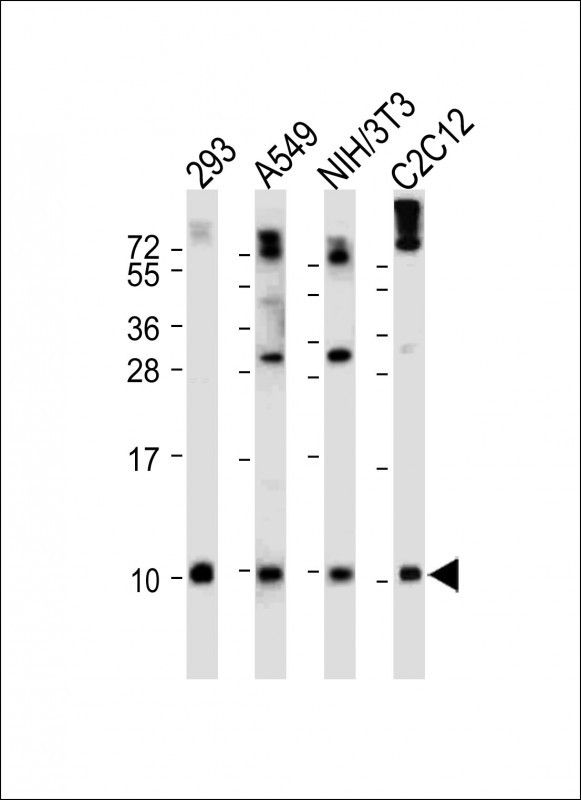
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Polyubiquitin-C, Ubiquitin, UBC |
| Entrez GeneID | 7316 |
| WB Predicted band size | 77.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This Ubiquitin antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-32 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human Ubiquitin. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于Ubiquitin (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(仅供参考,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"A monoclonal antibody targeting the N-terminus of ubiquitin reveals distinct cellular pools of free ubiquitin"*
**作者**: Tanaka, K. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种特异性识别Ubiquitin N端表位的单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用。该抗体能有效区分游离Ubiquitin与多聚泛素链或底物结合形式,为研究泛素动态分布提供了工具。
2. **文献名称**: *"N-terminal ubiquitin-specific antibodies in the analysis of proteasomal degradation"*
**作者**: Finley, D. & Peng, T.
**摘要**: 文章利用N端Ubiquitin抗体追踪蛋白酶体依赖的蛋白质降解过程,揭示了底物泛素化位点对其降解效率的影响,并验证了抗体在体外泛素化体系中的特异性。
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural characterization of an anti-ubiquitin N-terminus antibody and its use in Parkinson’s disease models"*
**作者**: Lee, S. et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析了抗体与Ubiquitin N端的结合模式,并应用该抗体在帕金森病模型中检测到异常聚集的游离泛素,提示其与神经元退行性变的潜在关联。
4. **文献名称**: *"Comparative study of ubiquitin N-terminal antibodies in detecting oxidative stress-induced protein damage"*
**作者**: Chen, X. et al.
**摘要**: 比较了多种商业N端Ubiquitin抗体在氧化应激条件下的灵敏度,筛选出适用于组织切片的高特异性抗体,为病理状态下泛素化调控研究提供了方法学支持。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词 **"ubiquitin N-terminal antibody"** 或 **"anti-ubiquitin (N-term)"**,并筛选近年的应用或开发类研究。
Ubiquitin (N-term) antibodies are essential tools for studying ubiquitination, a post-translational modification critical for regulating protein degradation, cellular signaling, and stress responses. Ubiquitin, a highly conserved 76-amino-acid protein, is covalently attached to substrate proteins via its C-terminal glycine, typically forming isopeptide bonds with lysine residues on targets. However, ubiquitin can also link to substrates through its N-terminal methionine (M1) or other non-canonical sites, a process termed "linear ubiquitination" or N-terminal ubiquitination. Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region of ubiquitin (residues 1-10 or similar epitopes) specifically recognize this modification pattern, distinguishing it from C-terminal-linked polyubiquitin chains or free ubiquitin.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate diseases associated with dysregulated ubiquitination, such as neurodegeneration, cancer, and immune disorders. They help identify substrates undergoing N-terminal ubiquitination, which is implicated in NF-κB signaling, inflammation, and proteasomal degradation. However, their specificity requires validation, as cross-reactivity with free ubiquitin or other ubiquitin-like proteins (e.g., SUMO or NEDD8) may occur. Researchers often pair them with pan-ubiquitin antibodies or ubiquitin remnant motif antibodies (e.g., K-ε-GG) to confirm ubiquitination context. Proper sample preparation, including protease/ubiquitinase inhibition, ensures accurate detection of this dynamic, reversible modification.
×