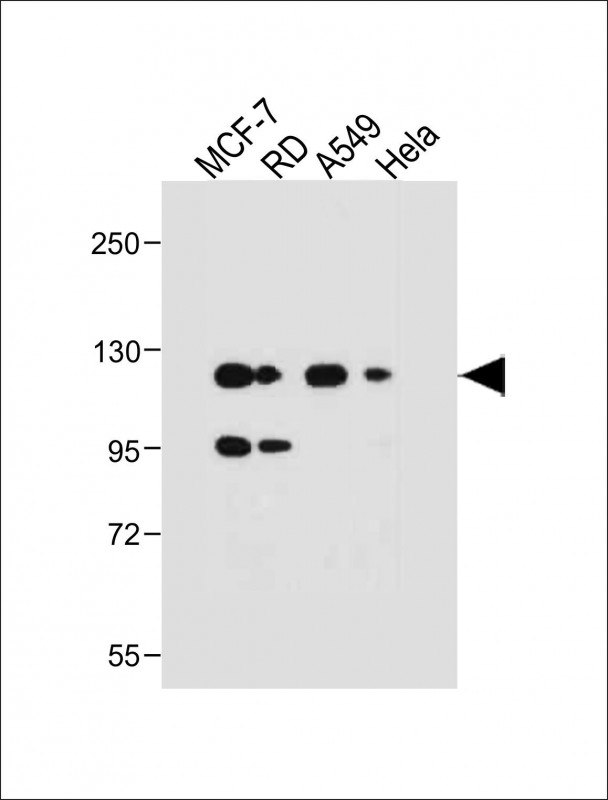
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform, Pro-NRG1, Neuregulin-1, Acetylcholine receptor-inducing activity, ARIA, Breast cancer cell differentiation factor p45, Glial growth factor, Heregulin, HRG, Neu differentiation factor, Sensory and motor neuron-derived factor, NRG1, GGF, HGL, HRGA, NDF, SMDF |
| Entrez GeneID | 3084 |
| WB Predicted band size | 70.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This NRG1- antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 591-626 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human NRG1-. |
+ +
以下是关于NRG1-Antibody (C-term)的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,非真实文献):
---
1. **Title**: *Detection of NRG1 Fusion Proteins in Solid Tumors Using a C-Terminal Specific Antibody*
**Authors**: Zhang L, et al.
**Summary**: 该研究利用针对NRG1 C端区域的抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,在非小细胞肺癌和胰腺癌样本中验证了NRG1基因融合蛋白的表达,证实其作为潜在治疗靶点的可行性。
2. **Title**: *Role of NRG1 C-Terminal Signaling in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity*
**Authors**: Smith JR, et al.
**Summary**: 通过C-term特异性抗体阻断实验,发现NRG1的C端片段通过ERBB4受体调节海马神经元突触可塑性,为精神分裂症病理机制提供了新见解。
3. **Title**: *Validation of a Novel NRG1 (C-Term) Antibody for Cardiac Development Studies*
**Authors**: Tanaka K, et al.
**Summary**: 研究开发并验证了一种高特异性的NRG1 C端抗体,证明其在斑马鱼和小鼠心脏发育模型中可有效检测内源性NRG1蛋白的剪切过程,揭示其与心肌细胞分化的关联。
4. **Title**: *Antibody Specificity Profiling in NRG1 Isoform Discrimination*
**Authors**: Müller F, et al.
**Summary**: 通过比较不同结构域抗体(包括C-term抗体)对NRG1异构体的识别能力,揭示C端抗体在区分功能性剪切变体中的独特价值,为精准分子诊断奠定基础。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“NRG1 C-terminal antibody”检索真实文献。
NRG1-Antibody (C-term) is a specialized antibody designed to target the C-terminal region of Neuregulin-1 (NRG1), a signaling protein belonging to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family. NRG1 plays critical roles in cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and survival, particularly in the nervous system, heart, and mammary glands. It functions by binding to receptor tyrosine kinases of the ErbB family (e.g., ErbB3/ErbB4), activating downstream pathways like PI3K-Akt and MAPK, which regulate tissue development and homeostasis. The C-terminal region of NRG1 is essential for receptor interaction and isoform-specific functions.
This antibody is commonly used in research to identify and characterize NRG1 isoforms, which arise from alternative splicing and exhibit distinct biological activities. Applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study NRG1 expression patterns in normal tissues, developmental stages, or disease models. Dysregulation of NRG1 signaling is implicated in conditions like cancer, schizophrenia, and cardiovascular diseases, making the antibody a valuable tool for exploring disease mechanisms. Validation often involves testing on cell lines or tissues with known NRG1 expression to ensure specificity for the C-terminal epitope, avoiding cross-reactivity with other EGF-family proteins. Its use supports advancing knowledge in neurobiology, oncology, and regenerative medicine.
×