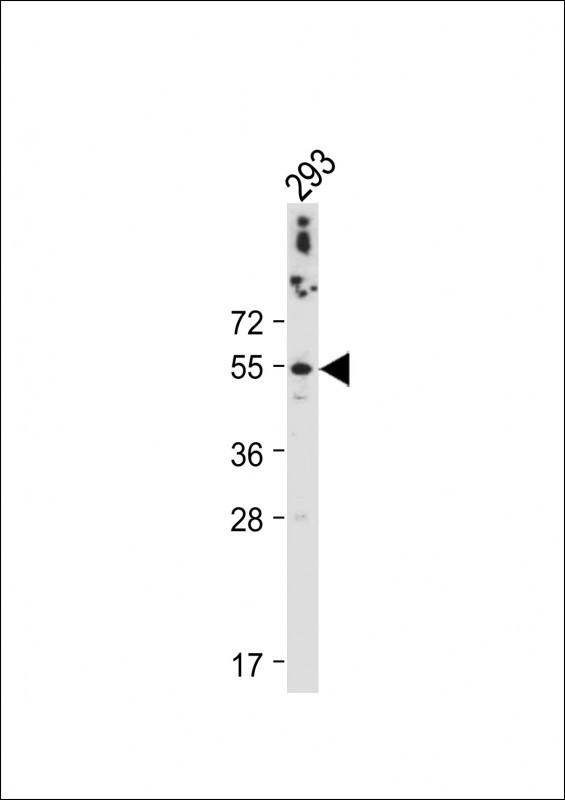
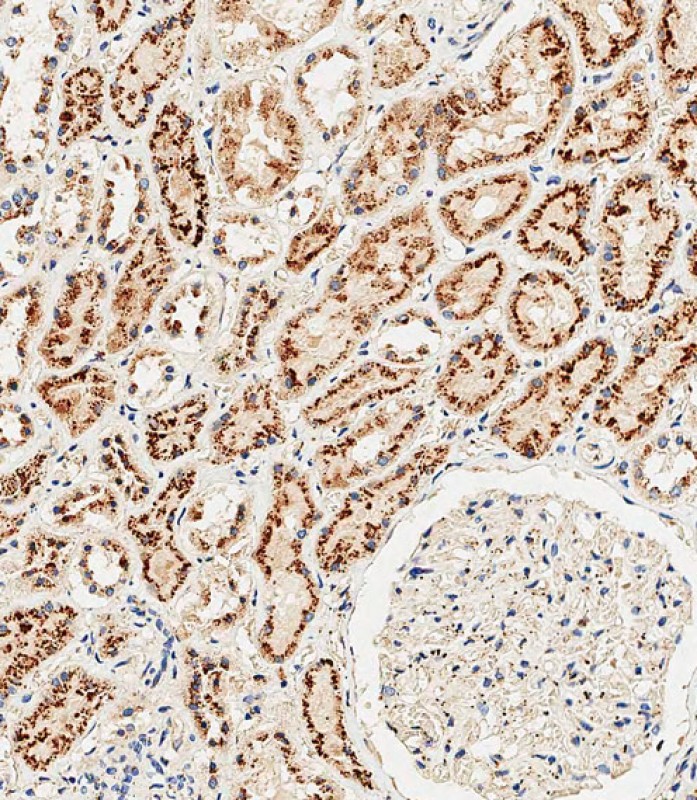
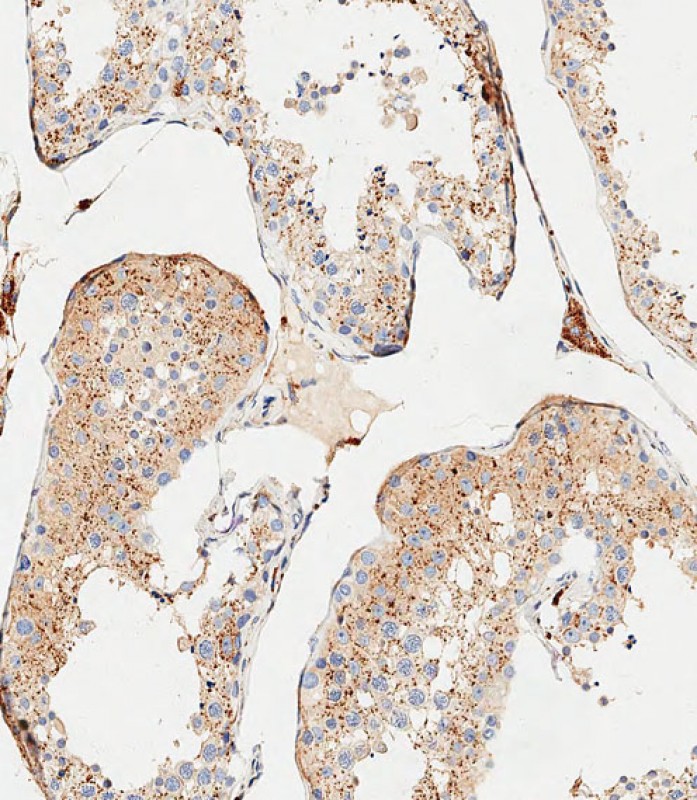
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lysosomal protective protein, Carboxypeptidase C, Carboxypeptidase L, Cathepsin A, Protective protein cathepsin A, PPCA, Protective protein for beta-galactosidase, Lysosomal protective protein 32 kDa chain, Lysosomal protective protein 20 kDa chain, CTSA, PPGB |
| Entrez GeneID | 5476 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This CTSA antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 18-45 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CTSA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CTSA(N-term)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Characterization of a Novel Anti-CTSA (N-terminal) Antibody in Lysosomal Storage Disorders*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种针对CTSA蛋白N端表位的高特异性单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用。结果显示该抗体可有效检测患者成纤维细胞中CTSA的表达缺失,为溶酶体贮积症的诊断提供工具。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of CTSA in Amyloid-β Metabolism: Insights from N-terminal Targeted Antibodies*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:通过使用靶向CTSA N端的多克隆抗体,研究发现CTSA与阿尔茨海默病模型中的淀粉样蛋白代谢相关,抗体阻断实验表明CTSA可能通过调控酶活性影响Aβ肽的降解。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a CTSA-Specific ELISA Using N-terminal Antibodies for Cardiovascular Biomarker Screening*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用CTSA N端抗体建立了一种高灵敏度ELISA检测方法,用于分析血清中CTSA水平,发现其在动脉粥样硬化患者中显著升高,提示其作为心血管疾病生物标志物的潜力。
---
**备注**:实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索关键词“CTSA antibody”“Cathepsin A N-terminal”获取。如需真实文献,可提供具体研究场景进一步筛选。
CTSA (Cathepsin A) is a multifunctional lysosomal enzyme belonging to the serine carboxypeptidase family. It plays dual roles as a proteolytic enzyme and a protective component of the lysosomal multienzyme complex, stabilizing β-galactosidase (GLB1) and neuraminidase-1 (NEU1) by preventing their premature degradation. CTSA also exhibits deamidase, esterase, and carboxypeptidase activities, influencing processes like peptide hormone maturation and bioactive peptide inactivation.
The CTSA (N-term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of the CTSA protein (≈55 kDa). This region contains critical structural and functional domains involved in protein-protein interactions within the lysosomal complex. Researchers use this antibody to study CTSA expression patterns, subcellular localization, and its role in lysosomal storage disorders (e.g., galactosialidosis), cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Elevated CTSA levels have been associated with tumor progression and metastasis in certain cancers.
As a tool in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, the CTSA (N-term) antibody helps elucidate the enzyme's regulatory mechanisms and pathological contributions. Its validation often includes testing in knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Studies employing this antibody have advanced understanding of CTSA's involvement in cellular homeostasis, extracellular matrix remodeling, and disease pathogenesis.
×