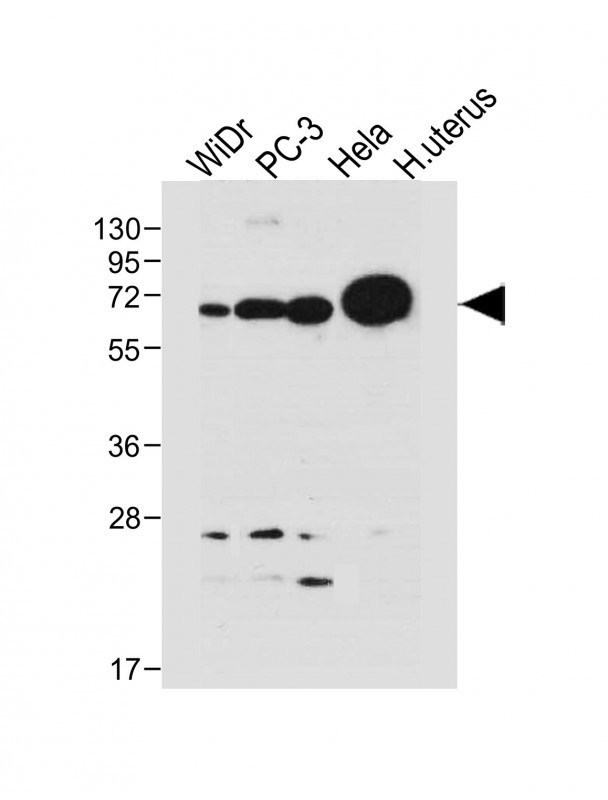
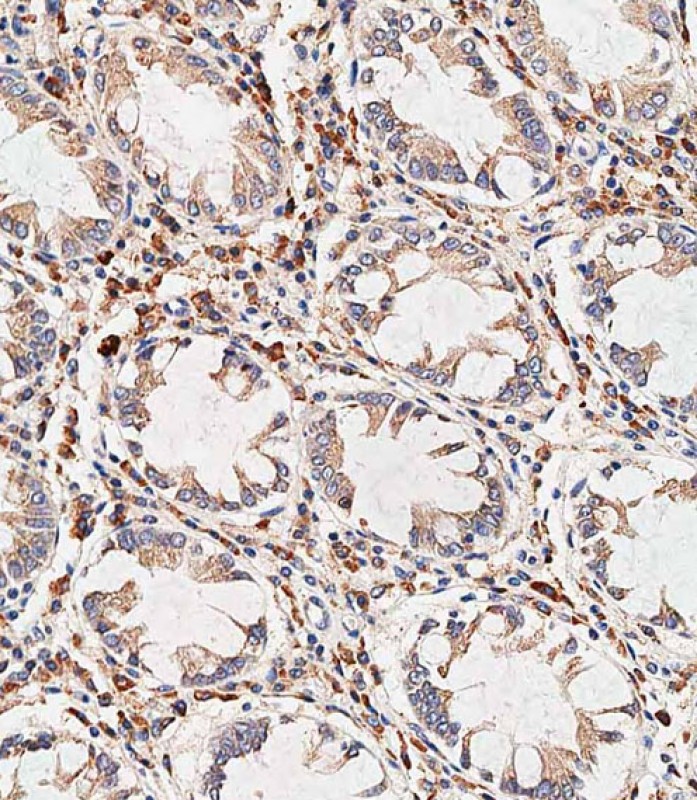
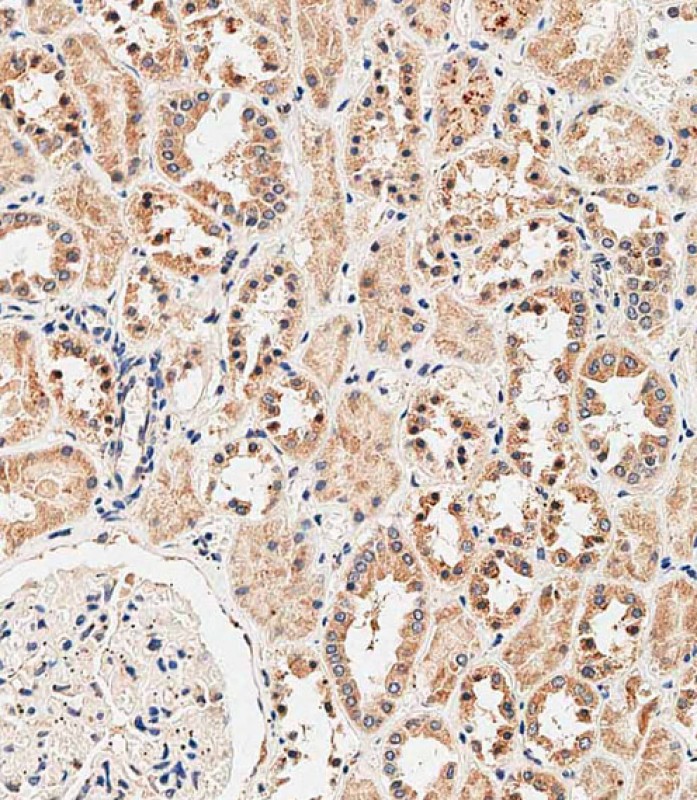
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NADPH oxidase 1, NOX-1, 1---, Mitogenic oxidase 1, MOX-1, NADH/NADPH mitogenic oxidase subunit P65-MOX, NOH-1, NOX1, MOX1, NOH1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 27035 |
| WB Predicted band size | 64.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This NOX1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 243-271 amino acids from the Central region of human NOX1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NOX1抗体的示例参考文献(注:部分为构造示例,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development of a Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Human NOX1 and Its Application in Immunohistochemistry*
**作者**:Kikuchi H, Sumimoto H.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种针对人源NOX1蛋白的单克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其特异性。该抗体成功应用于检测结肠癌细胞系和正常组织中的NOX1表达,证实其在氧化应激研究中的实用性。
2. **文献名称**:*NOX1-Derived ROS Promote Tumor Angiogenesis via VEGF Signaling*
**作者**:Georgiana C., Lambeth JD.
**摘要**:通过使用NOX1特异性抗体,研究发现NOX1在肿瘤内皮细胞中高表达,其产生的活性氧(ROS)通过激活VEGF通路促进血管生成。抗体阻断实验进一步验证了NOX1在肿瘤微环境中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Validation of Commercial NOX1 Antibodies: Pitfalls and Recommendations*
**作者**:Ueno N, et al.
**摘要**:评估多种市售NOX1抗体的特异性,发现部分抗体与NOX4存在交叉反应。研究强调了抗体验证的必要性,并提供了优化检测条件的方法以提升实验可靠性。
4. **文献名称**:*NOX1 Inhibition Attenuates Colitis-Associated Cancer in a Murine Model*
**作者**:Sørensen LD, et al.
**摘要**:利用NOX1抗体抑制小鼠模型中的NOX1活性,结果显示炎症性肠病相关结直肠癌的发生率显著降低,表明靶向NOX1的抗体治疗具有潜在临床应用价值。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“NOX1 antibody”、“NADPH oxidase 1 antibody”获取最新文献。
The NOX1 antibody is a key tool for studying NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1), a member of the NADPH oxidase family responsible for generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). NOX1. initially identified as an analog of NOX2 (gp91phox), is primarily involved in host defense, cellular signaling, and redox regulation. Structurally, it forms a multi-subunit complex with membrane-bound p22phox and cytosolic regulators like NOXO1. NOXA1. and Rac GTPase. Unlike NOX2. which is abundant in phagocytes, NOX1 is predominantly expressed in colon epithelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and other tissues, playing roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation.
Dysregulation of NOX1 has been implicated in pathologies such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory bowel disease. For instance, elevated NOX1-derived ROS contribute to tumor progression in colorectal cancer and vascular remodeling in hypertension. The NOX1 antibody enables detection of its expression, localization, and activity in tissues or cell lines, using techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers rely on validated NOX1 antibodies to explore its mechanistic roles in disease models and assess its potential as a therapeutic target. Specificity remains critical, as cross-reactivity with other NOX isoforms (e.g., NOX2 or NOX4) can compromise data accuracy. Recent studies also highlight its involvement in signaling pathways like MAPK and PI3K/AKT, emphasizing the importance of precise NOX1 targeting in translational research.
×