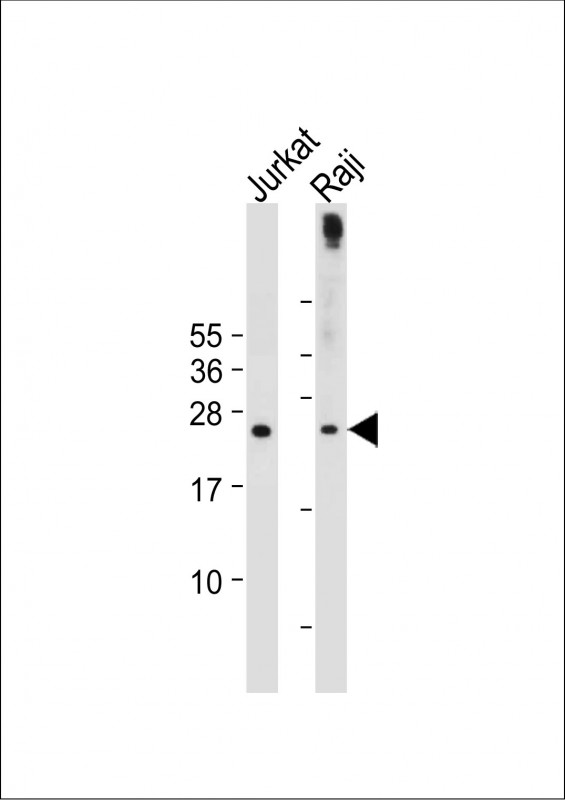
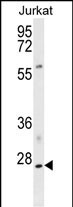
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
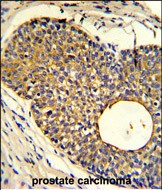
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DNA dC->dU-editing enzyme APOBEC-3A, A3A, 354-, Phorbolin-1, APOBEC3A |
| Entrez GeneID | 100913187;200315 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PHO1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PHO1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于PHO1(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*PHO1 participates in phosphate loading to the xylem in Arabidopsis*
**作者**:Poirier Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过PHO1(N-term)抗体的免疫定位实验,揭示了PHO1蛋白在拟南芥根中柱细胞中的表达模式,证明其参与磷酸盐向木质部的装载过程,并分析了pho1突变体中磷酸盐转运缺陷的机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The role of PHO1 in phosphate homeostasis and root development in rice*
**作者**:Secco D, et al.
**摘要**:利用PHO1(N-term)抗体进行Western blot分析,发现水稻PHO1蛋白在低磷胁迫下表达上调,并调控根系构型以增强磷吸收。研究还表明PHO1通过影响生长素信号通路调节根毛发育。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Interaction between PHO1 and SYG1 proteins modulates phosphate distribution in plants*
**作者**:Wege S, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用PHO1 N-term抗体)和荧光共定位技术,揭示了PHO1与SYG1蛋白的互作关系,表明两者共同调控细胞内磷酸盐的区隔化运输,影响植物整体磷稳态。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究补充详细信息(如期刊、年份)。若需进一步检索,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中以关键词“PHO1 antibody N-terminal”或“PHO1 phosphorylation transport”进行精准查询。
The PHO1 (N-term) antibody is a polyclonal or monoclonal antibody specifically designed to target the N-terminal region of the PHO1 protein, a key player in phosphate homeostasis. PHO1. primarily studied in plants like *Arabidopsis thaliana*, functions as a phosphate transporter involved in loading inorganic phosphate (Pi) from root cells into the xylem for distribution to aerial tissues. It is critical for maintaining Pi balance, particularly under low-phosphate conditions, and influences root development and stress responses. The N-terminal domain of PHO1 is believed to mediate protein-protein interactions or regulatory functions, though its exact role remains under investigation.
The PHO1 (N-term) antibody is widely used in plant biology research to detect PHO1 expression levels, localization, and post-translational modifications via techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. It has been instrumental in elucidating PHO1's role in phosphate signaling and its interaction with other proteins, such as PHO2. which regulates Pi transport through ubiquitination. Researchers also employ this antibody to study PHO1 dysfunction in mutants, which typically exhibit phosphate deficiency symptoms, including stunted growth and altered root architecture.
Produced using recombinant PHO1 N-terminal fragments or synthetic peptides, the antibody’s specificity is validated through knockout controls. Its applications extend to agricultural studies aiming to improve crop phosphate-use efficiency, a key trait for sustainable agriculture. Commercial suppliers often provide detailed validation data, ensuring reliability across experimental setups.
×