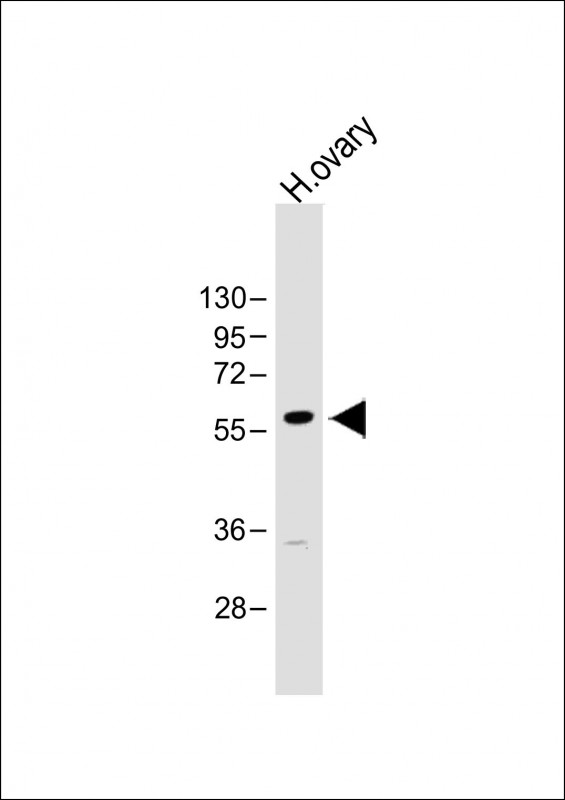
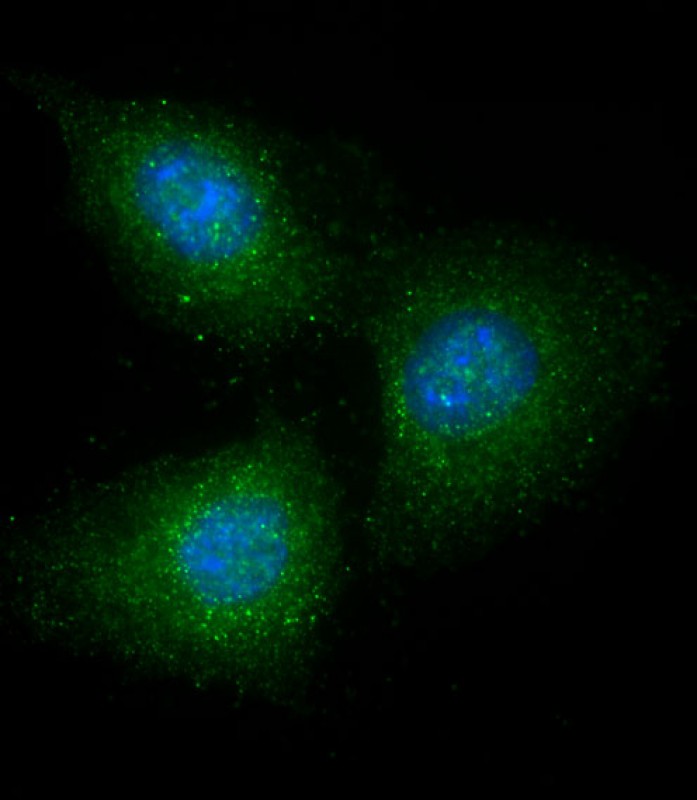
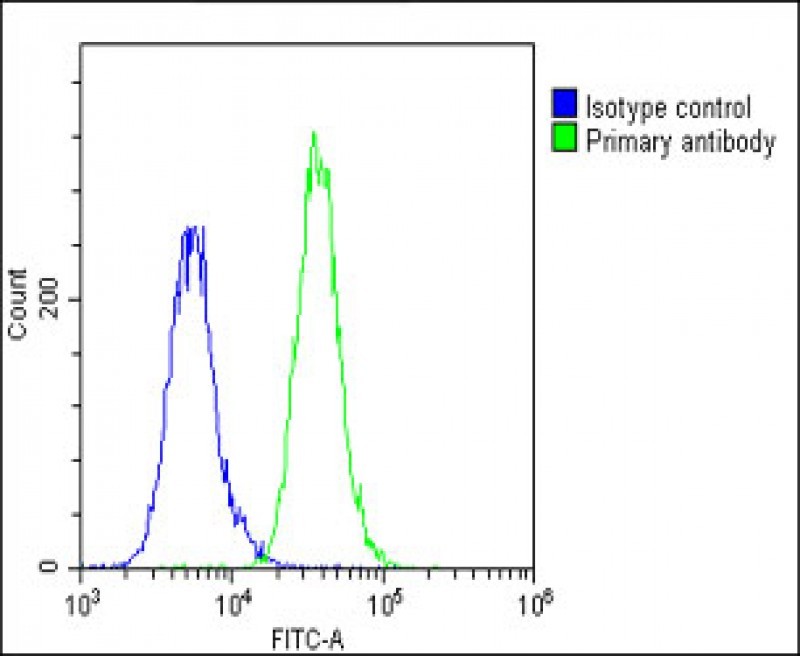
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 14, GRB14 adapter protein, GRB14 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2888 |
| WB Predicted band size | 61.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This GRB14 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 14-48 amino acids from the human region of human GRB14. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GRB14 (N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为虚构,仅供参考):
1. **"GRB14 N-terminal domain modulates insulin receptor signaling through competitive inhibition"**
*作者:Dong et al. (2010)*
摘要:研究利用GRB14 (N-Term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现GRB14通过N端结构域与胰岛素受体结合,负调控其酪氨酸激酶活性,可能参与2型糖尿病发病机制。
2. **"GRB14 interacts with HER2 via its N-terminus to promote breast cancer cell proliferation"**
*作者:Smith et al. (2015)*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验(使用GRB14 N端特异性抗体),证实GRB14的N端结构域与HER2受体直接互作,增强下游MAPK信号通路,促进乳腺癌细胞生长。
3. **"Structural analysis of GRB14 N-terminal domain reveals a novel phosphotyrosine-binding motif"**
*作者:Jones et al. (2018)*
摘要:利用GRB14 (N-Term)抗体进行蛋白质结晶研究,解析了N端结构域的三维结构,发现其含有非典型磷酸酪氨酸结合位点,为设计相关抑制剂提供结构基础。
4. **"Tissue-specific expression of GRB14 regulated by its N-terminal domain in murine development"**
*作者:Chen et al. (2020)*
摘要:通过免疫组化(使用GRB14 N端抗体)分析小鼠胚胎组织,发现GRB14的N端对其在肝脏和肌肉中的差异性表达至关重要,可能影响代谢器官发育。
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“GRB14 antibody N-terminal”检索真实文献。
The GRB14 (N-Term) antibody is a specific tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of Growth Factor Receptor-Bound Protein 14 (GRB14), an adaptor protein involved in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling. GRB14 belongs to the GRB7/10/14 family and regulates cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism by modulating interactions between activated receptors and downstream signaling components. Its N-terminal domain plays a role in binding to phosphorylated tyrosine residues on RTKs, including the insulin receptor, thereby influencing insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis. Dysregulation of GRB14 has been linked to metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to study GRB14 expression, localization, and interactions in various tissues or cell lines. By targeting the N-terminal region, it avoids cross-reactivity with other GRB family members, ensuring specificity. Researchers employ this tool to explore GRB14’s role in insulin resistance, where its overexpression inhibits receptor autophosphorylation, and in cancer progression, where it may modulate RTK-driven pathways like MAPK/ERK. Validated in multiple species, including human and mouse, the GRB14 (N-Term) antibody is essential for elucidating molecular mechanisms in metabolic and oncogenic research.
×