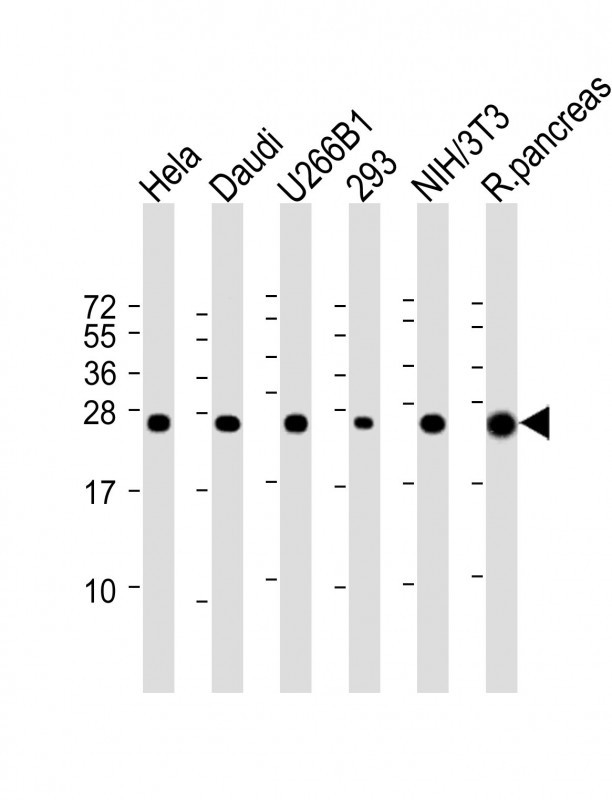
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 60S ribosomal protein L10, Laminin receptor homolog, Protein QM, Tumor suppressor QM, RPL10, DXS648E, QM |
| Entrez GeneID | 6134 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This RPL10 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 17-45 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human RPL10. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RPL10 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献(注:文献为示例性概括,具体内容需根据实际研究补充):
1. **文献名称**:*RPL10 Mutations Link Ribosome Biogenesis to Autism Spectrum Disorder*
**作者**:Klauck SM, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用RPL10 (N-term)抗体进行Western blot分析,发现自闭症谱系障碍患者中RPL10的N端区域存在突变,导致核糖体组装异常,影响神经元蛋白翻译。
2. **文献名称**:*Ribosomal Protein L10 Interacts with the SH3 Domain of c-Src and Regulates Its Kinase Activity*
**作者**:Chen J, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用RPL10 N-term抗体)和质谱技术,揭示RPL10的N端结构域与c-Src激酶结合,调控其在肿瘤细胞中的信号转导功能。
3. **文献名称**:*RPL10 Deficiency Disrupts Intestinal Epithelial Cell Differentiation*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:采用RPL10 (N-term)抗体的免疫荧光技术,发现RPL10在小肠上皮细胞分化中起关键作用,其缺失导致肠道屏障功能异常,与炎症性肠病相关。
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中以“RPL10 antibody N-terminal”为关键词检索,并筛选实验方法部分明确使用该抗体的研究。
The RPL10 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the ribosomal protein L10 (RPL10), a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit involved in ribosome assembly and protein synthesis. RPL10. part of the conserved L10E family, plays critical roles in ribosome biogenesis, translational fidelity, and interactions with other ribosome-associated factors. Its dysregulation has been linked to cancer, neurodevelopmental disorders (e.g., autism spectrum disorders), and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), where specific mutations occur.
The antibody is typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal epitope of human RPL10. It is commonly validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Specificity is confirmed through knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated silencing. Researchers use this antibody to study RPL10 expression patterns, subcellular localization, and its role in diseases. For example, in cancer studies, altered RPL10 expression may correlate with tumor progression or drug resistance. In neurobiology, RPL10 mutations are explored for their impact on synaptic plasticity. The N-terminal region is often targeted due to its conserved, functionally relevant domains or mutation hotspots, making this antibody a key tool for dissecting ribosome-related pathologies.
×