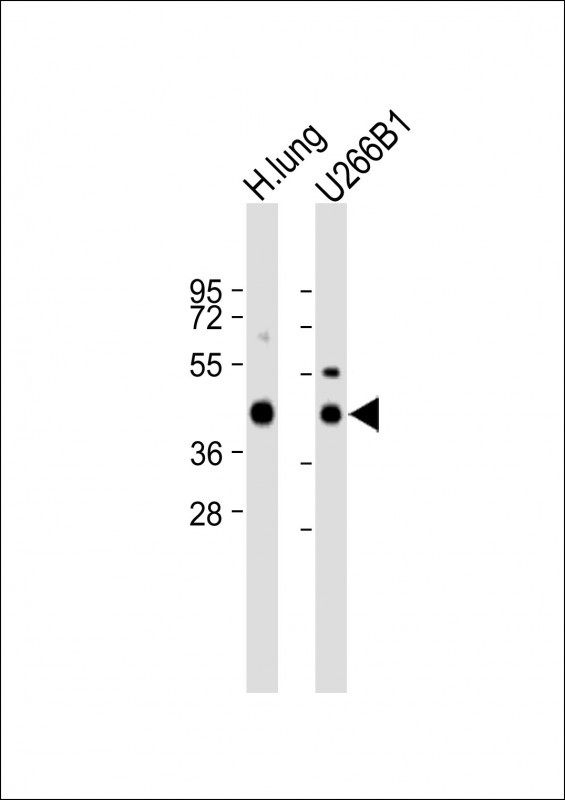
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain F, CDA12, HLA F antigen, Leukocyte antigen F, MHC class I antigen F, HLA-F, HLA-54, HLAF |
| Entrez GeneID | 3134 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This HLA-F antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 172-198 amino acids from the Central region of human HLA-F. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于HLA-F抗体的相关文献摘要概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"HLA-F: A New Kid in Immune Tolerance"*
**作者**: Goodridge, J.P. et al.
**摘要**: 探讨HLA-F在免疫耐受中的作用,发现其通过与NK细胞表面的KIR3DS1受体结合,调控母胎界面和器官移植中的免疫应答,提示HLA-F抗体可能用于监测移植排斥或妊娠并发症。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"HLA-F and Immune Evasion in Viral Infections"*
**作者**: Burrows, S.R. et al.
**摘要**: 研究HLA-F在病毒感染中的表达模式,发现HIV和EBV等病毒可能通过上调HLA-F抑制细胞毒性T细胞活性,HLA-F抗体或可作为阻断病毒免疫逃逸的治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"HLA-F Antibodies in Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review"*
**作者**: Ishtaiq, A. et al.
**摘要**: 综述HLA-F抗体在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿性关节炎中的检测意义,指出其与疾病活动度相关,可能作为潜在生物标志物或治疗干预目标。
---
**备注**:若需获取全文或具体实验细节,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar或高校数据库检索以上标题或作者。HLA-F研究尚处发展阶段,近年文献多聚焦其非经典MHC-I功能及治疗潜力。
HLA-F, a non-classical HLA class I molecule, plays distinct roles in immune regulation compared to classical HLA-A, -B, and -C proteins. Unlike its counterparts, HLA-F exhibits limited polymorphism and preferentially presents peptides in specific contexts, such as during cellular stress or viral infection. It interacts with inhibitory receptors (e.g., KIR3DS1 on NK cells, LILRB1/2 on myeloid cells) to modulate immune tolerance, particularly at maternal-fetal interfaces, transplant sites, and tumor microenvironments. HLA-F expression increases during pregnancy, allograft rejection, and in certain cancers, suggesting its involvement in immune evasion.
Antibodies targeting HLA-F remain understudied but hold clinical interest. While classical HLA antibodies drive transplant rejection, HLA-F antibodies are detected in some transplant recipients and autoimmune patients, though their pathogenicity is unclear. Emerging evidence suggests anti-HLA-F antibodies might influence immune cell function by blocking HLA-F/receptor interactions, potentially altering NK-mediated cytotoxicity or T-cell responses. Commercial ELISA kits now enable HLA-F antibody detection, yet standardized clinical correlations are lacking. Research gaps persist in understanding their role in pregnancy complications, graft survival, and cancer immunotherapy. Current studies focus on whether HLA-F antibodies could serve as biomarkers or therapeutic targets, necessitating deeper mechanistic investigations.
×