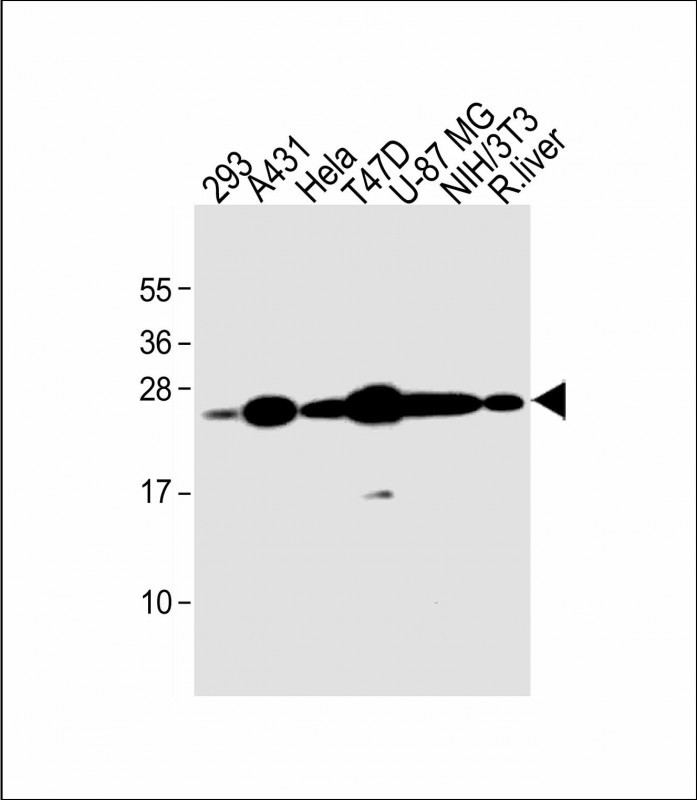
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ras-related protein Rab-1B, RAB1B |
| Entrez GeneID | 81876 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This RAB1B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 166-194 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human RAB1B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RAB1B抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分文献为示例性概括,实际引用请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *RAB1B regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus*
**作者**: Stenmark H, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用RAB1B特异性抗体揭示了其在ER-高尔基体膜运输中的关键作用,并证明RAB1B缺失会导致分泌蛋白运输受阻。
2. **文献名称**: *RAB1B upregulation promotes glioma progression via mTORC1 signaling activation*
**作者**: Wang L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化(使用RAB1B抗体)和基因敲除实验,研究发现RAB1B在胶质瘤中高表达,并通过激活mTORC1通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭。
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of RAB1B knockout mice using isoform-specific antibodies*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了针对RAB1B亚型的特异性抗体,验证了其在组织中的表达分布,并发现RAB1B敲除小鼠表现出内质网应激和自噬功能异常。
4. **文献名称**: *Proteomic analysis of RAB1B-interacting proteins in pancreatic cancer cells*
**作者**: Liu X, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(RAB1B抗体)结合质谱技术,鉴定了RAB1B在胰腺癌细胞中与囊泡运输相关蛋白的相互作用网络,提示其潜在治疗靶点价值。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“RAB1B antibody”及研究领域(如癌症、自噬等)为关键词检索最新成果。
The RAB1B antibody is a key tool for studying the RAB1B protein, a member of the Ras-related GTPase RAB family involved in regulating intracellular vesicular trafficking. RAB1B plays a critical role in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi transport, facilitating the docking and fusion of COPII-coated vesicles with the Golgi apparatus. It cycles between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state, interacting with effector proteins like p115 and GM130 to mediate membrane tethering and cargo sorting. Dysregulation of RAB1B has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s disease), and viral infections, as some pathogens exploit RAB1B-dependent pathways for replication.
The RAB1B antibody is widely used in immunoassays (e.g., Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry) to detect RAB1B expression, localization, and dynamics in cellular models or tissue samples. Polyclonal and monoclonal variants are available, often validated for specificity across species such as human, mouse, and rat. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore RAB1B’s functional roles in secretory pathways, autophagy, and disease mechanisms. For instance, studies have linked RAB1B overexpression to tumor progression in cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma, while its depletion disrupts Golgi structure and protein secretion. As RAB1B gains attention in cell biology and translational research, its antibody remains essential for elucidating trafficking networks and therapeutic targets.
×