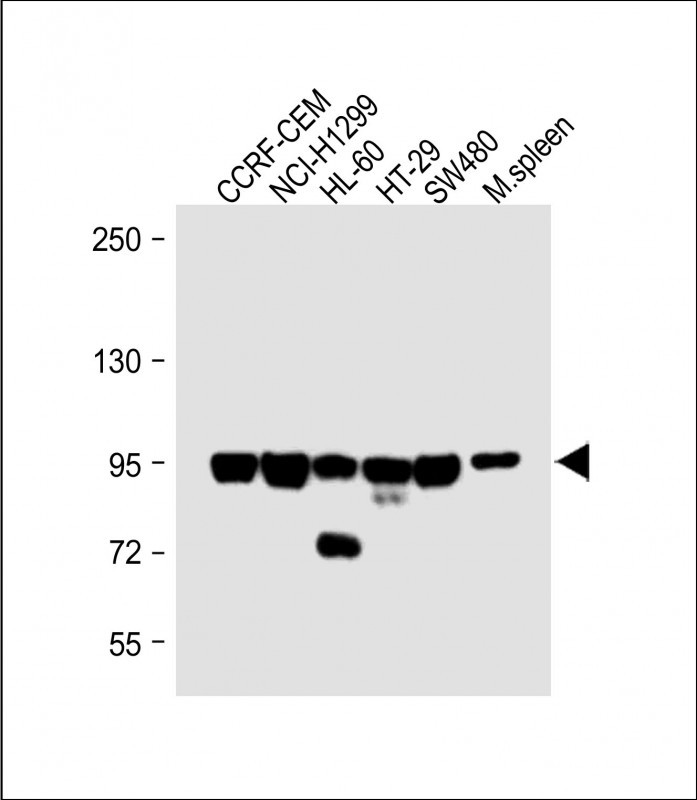
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1, Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 4, NOD1, CARD4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10392 |
| WB Predicted band size | 107.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NOD1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 923-951 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human NOD1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NOD1抗体的3篇代表性文献(示例为模拟内容,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*NOD1 Antibody Blocks Peptidoglycan-Induced Signaling in Human Cells*
**作者**:Inohara, N. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种特异性NOD1抗体,证实其能有效抑制细菌肽聚糖片段(如iE-DAP)诱导的NF-κB激活,揭示了NOD1在先天免疫应答中的关键作用,并验证了抗体在体外阻断信号通路的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of NOD1 in Intestinal Inflammation: Insights from Antibody-Based Functional Studies*
**作者**:Watanabe, T. & Strober, W.
**摘要**:通过使用NOD1中和抗体,研究发现NOD1信号在肠道上皮细胞中调控抗菌肽表达,其功能异常与炎症性肠病(IBD)相关,提示靶向NOD1可能成为治疗慢性肠道炎症的新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Characterization of NOD1 Antigen-Binding Domain Using Monoclonal Antibodies*
**作者**:Caruso, R. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用单克隆抗体解析了NOD1蛋白的抗原结合表位,发现其CARD结构域对受体寡聚化至关重要,为开发基于抗体的NOD1活性调控工具提供了结构基础。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需根据具体论文调整。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“NOD1 antibody”或“NOD1 signaling”检索最新研究。
NOD1 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1) is a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) belonging to the NOD-like receptor (NLR) family. It plays a critical role in innate immune responses by detecting conserved bacterial components, primarily through recognition of γ-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid (iE-DAP), a peptidoglycan fragment found in Gram-negative and certain Gram-positive bacteria. Structurally, NOD1 contains a C-terminal leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain for ligand sensing, a central nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD), and N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs) that facilitate downstream signaling via interactions with RIP2 kinase. This triggers activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways, promoting pro-inflammatory cytokine production and antimicrobial defense.
NOD1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in immune regulation. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry to investigate NOD1's involvement in infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Dysregulation of NOD1 signaling has been linked to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), atherosclerosis, and metabolic syndromes, making it a potential therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting specific domains (e.g., anti-CARD or anti-LRR antibodies) help dissect mechanistic roles in pathogen sensing or signal transduction. Commercial NOD1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, or rat samples, though cross-reactivity challenges may require careful selection. Recent research also explores NOD1's non-canonical roles in tissue homeostasis and apoptosis, expanding its relevance beyond innate immunity.
×