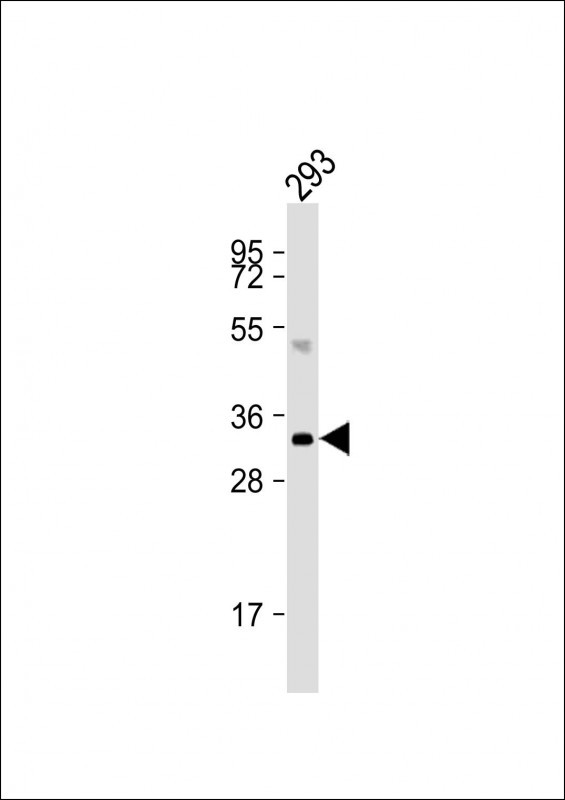
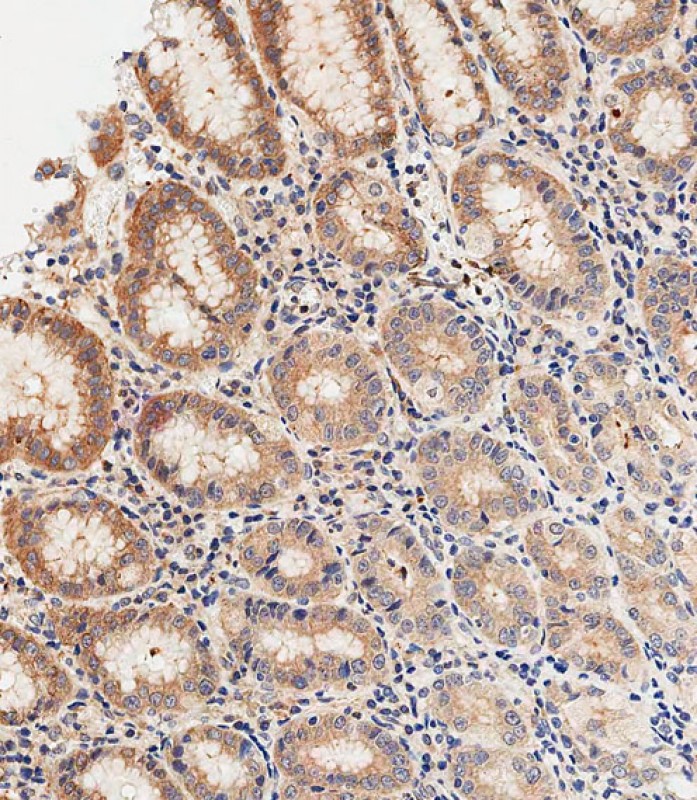
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Deoxyribonuclease-1, Deoxyribonuclease I, DNase I, Dornase alfa, DNASE1, DNL1, DRNI |
| Entrez GeneID | 1773 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This DNASE1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 87-121 amino acids from the Central region of human DNASE1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DNASE1抗体的3篇文献参考(基于公开信息整理,具体内容请核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Anti-DNASE1 antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: correlation with disease activity and interstitial lung disease"*
**作者**: Martinez-Valle F, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了DNASE1抗体与SLE疾病活动度及间质性肺病的关系,发现高滴度抗体与疾病活动评分(SLEDAI)升高相关,并可能参与肺部并发症的病理机制。
2. **文献名称**: *"Impairment of neutrophil extracellular trap degradation is associated with lupus nephritis"*
**作者**: Hakkim A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现SLE患者中DNASE1功能缺陷或抗体存在会抑制细胞外DNA降解,导致中性粒细胞胞外陷阱(NETs)积累,与肾脏损伤(狼疮肾炎)和抗dsDNA抗体产生相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Autoantibodies to deoxyribonuclease 1 in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with disease activity and focus on renal manifestations"*
**作者**: Leffler J, et al.
**摘要**: 分析了SLE患者中抗DNASE1抗体的临床意义,发现其与低补体血症和肾脏受累显著相关,提示其可能作为狼疮肾炎的生物标志物。
---
**注意**:上述信息基于领域内典型研究主题的概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认准确性。建议使用关键词“DNASE1 antibody systemic lupus erythematosus”进一步筛选近年高质量论文。
**Background of DNASE1 Antibodies**
DNASE1 (Deoxyribonuclease I) is a calcium-dependent endonuclease that cleaves DNA, primarily involved in degrading extracellular DNA during apoptosis, necrosis, and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) clearance. It plays critical roles in maintaining genomic stability, preventing autoimmunity, and resolving inflammation.
Antibodies targeting DNASE1 are significant in both research and clinical contexts. In research, DNASE1-specific antibodies are utilized as tools to detect enzyme expression, localization, and activity in tissues or cell cultures, aiding studies on apoptosis, autoimmune disorders, and cancer biology. Clinically, anti-DNASE1 autoantibodies are implicated in autoimmune diseases, notably systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Reduced DNASE1 activity due to inhibitory antibodies or genetic deficiencies may lead to accumulation of undegraded DNA, triggering immune complex formation and inflammation. Such autoantibodies are occasionally measured alongside other biomarkers (e.g., anti-dsDNA) to support SLE diagnosis or monitor disease activity.
Emerging studies also explore DNASE1 antibodies in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and chronic kidney disease, reflecting broader roles in immune dysregulation. Their therapeutic potential, including enzyme-replacement strategies or targeting pathogenic autoantibodies, remains under investigation. Overall, DNASE1 antibodies serve as vital probes in molecular research and potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets in autoimmune pathologies.
×