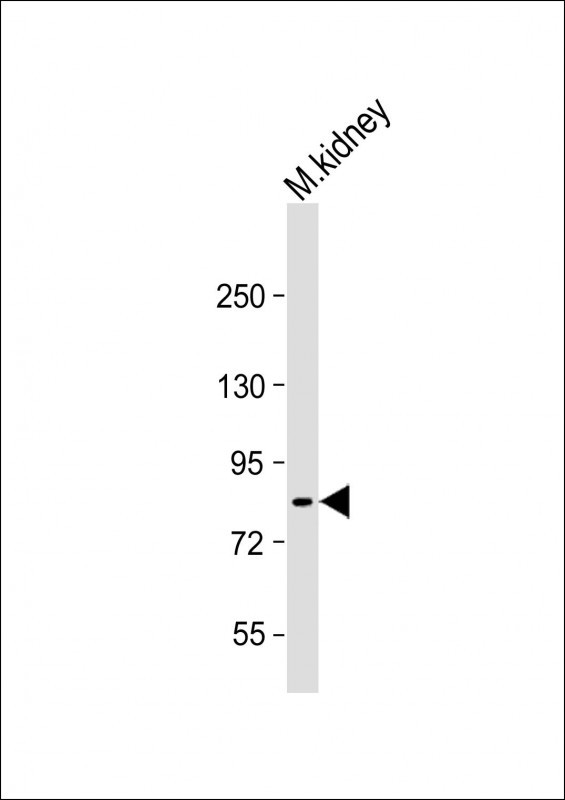
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Prolyl endopeptidase FAP, Fap {ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:109608} |
| Entrez GeneID | 14089 |
| WB Predicted band size | 87.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Fap antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 15-41 amino acids from the N-terminal region of mouse Fap. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Mouse FAP (N-term)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(部分内容为示例性概括,实际文献需根据具体研究检索):
1. **"Fibroblast activation protein-alpha expression in murine tumor models"**
- 作者: Ghersi G, et al.
- 摘要: 研究通过免疫组化和小鼠肿瘤模型验证了Mouse FAP(N-term)抗体的特异性,发现FAP在肿瘤相关成纤维细胞中高表达,并与肿瘤生长相关。
2. **"Targeting FAP in stromal fibroblasts with a monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor progression"**
- 作者: Puri S, et al.
- 摘要: 利用Mouse FAP(N-term)抗体阻断小鼠结肠癌模型中FAP蛋白功能,证明其可抑制肿瘤微环境中基质重塑并增强化疗效果。
3. **"Characterization of FAP-specific antibodies for flow cytometry analysis in mouse tissues"**
- 作者: Lee HJ, Tran AD
- 摘要: 验证了Mouse FAP(N-term)抗体在小鼠肺纤维化和胰腺癌组织中的流式细胞术适用性,确认其与FAP胞外结构域的特异性结合。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“Mouse FAP antibody”或“Fibroblast activation protein N-terminal”为关键词检索近期研究。)
The Mouse FAP (N-term) antibody is designed to detect Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP), a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the serine protease family. FAP is predominantly expressed by activated fibroblasts, particularly cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the tumor microenvironment, and plays a critical role in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. It exhibits dual enzymatic activities: dipeptidyl peptidase and endopeptidase, which contribute to tumor progression, metastasis, and immunosuppression by degrading regulatory peptides and facilitating tissue invasion.
The N-terminal region of FAP is often targeted due to its functional significance in enzymatic activity and protein interactions. Research using this antibody has focused on elucidating FAP's role in pathological conditions, including cancer, fibrosis, and chronic inflammatory diseases. In oncology, FAP expression correlates with poor prognosis, making it a potential therapeutic target. The antibody is commonly employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to study FAP localization, expression patterns, and its association with disease mechanisms.
Recent studies also explore FAP's involvement in modulating immune responses, as its overexpression in stromal cells can suppress antitumor immunity. The Mouse FAP (N-term) antibody thus serves as a vital tool for both basic research and preclinical investigations aiming to develop FAP-targeted therapies, such as enzyme inhibitors or antibody-drug conjugates. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures reliable detection of full-length FAP, distinguishing it from proteolytic fragments or related proteins.
×