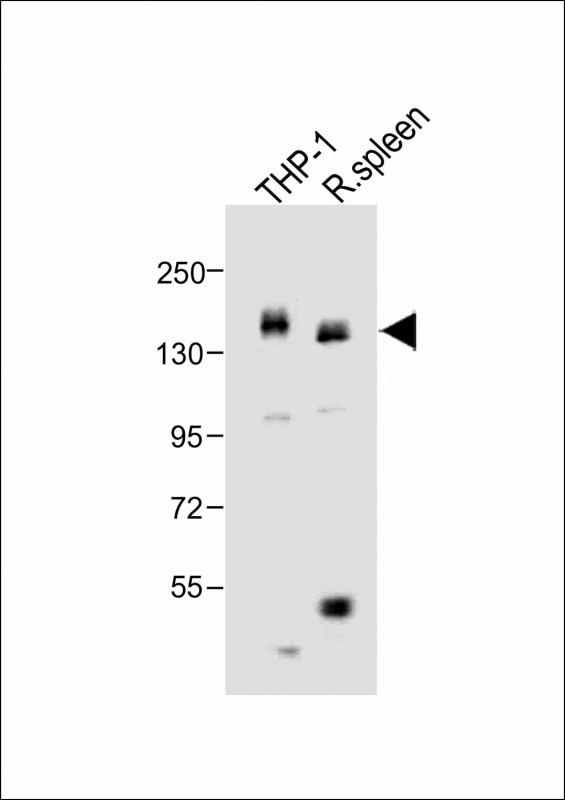
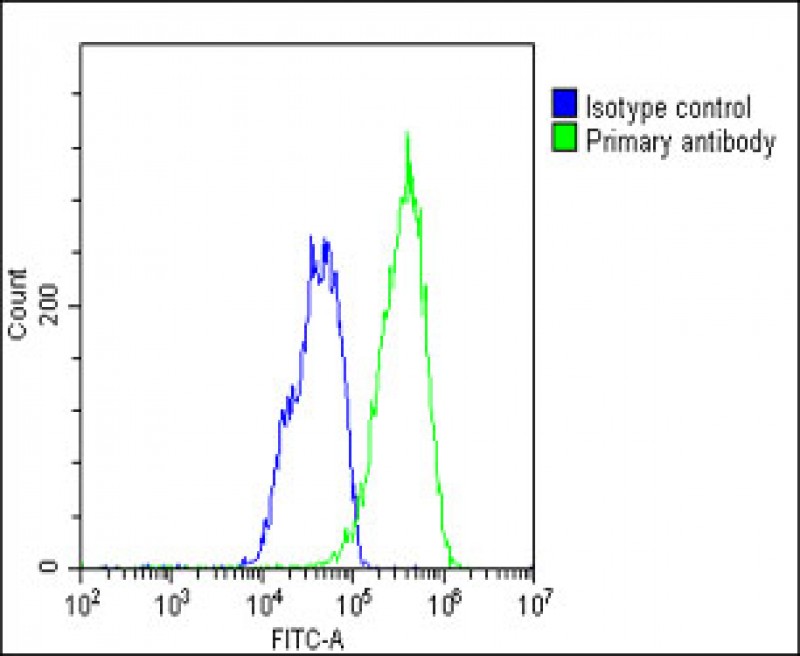
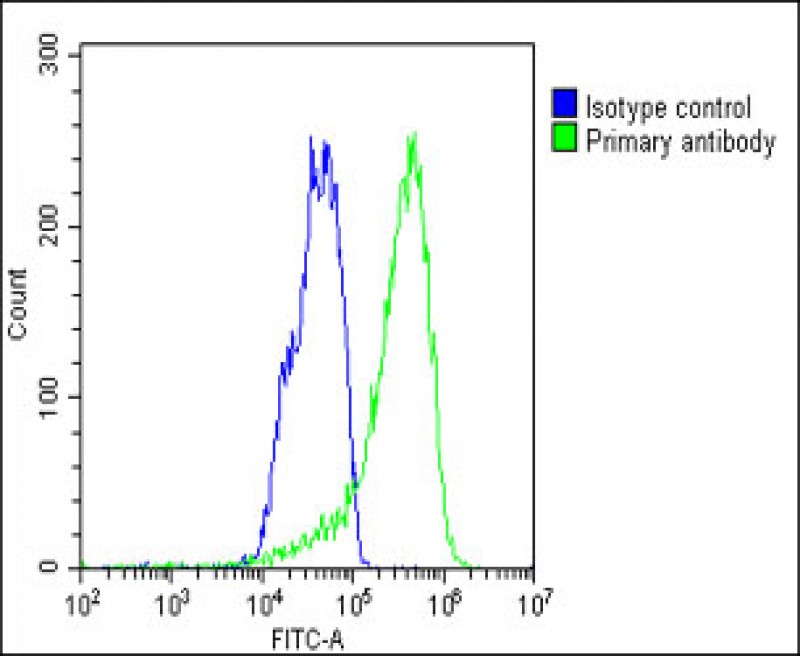
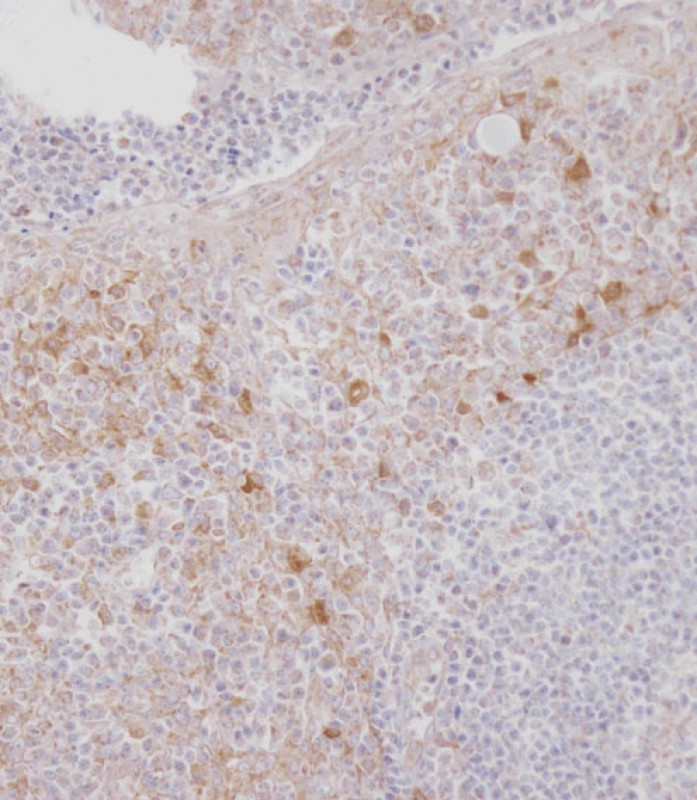
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, CSF-1 receptor, CSF-1-R, CSF-1R, M-CSF-R, Proto-oncogene c-Fms, CD115, CSF1R, FMS |
| Entrez GeneID | 1436 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This MCSF Receptor (CSF1R) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 940-971 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MCSF Receptor (CSF1R). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下为3篇关于CSF1R抗体的文献摘要概述:
1. **文献名称**: *"CSF1R inhibition with emactuzumab depletes tumor-associated macrophages and slows tumor growth in a canine solid tumor model"*
**作者**: Ma et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究使用抗CSF1R单克隆抗体(emactuzumab)阻断肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)的招募,通过抑制CSF1/CSF1R信号通路减少TAMs数量,从而延缓犬类实体瘤生长,验证了该抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *"Targeting tumor-associated macrophages with anti-CSF-1R antibody reveals a strategy for cancer therapy"*
**作者**: Pyonteck et al. (2013)
**摘要**: 该研究通过抗CSF1R抗体(如RG7155)选择性清除肿瘤微环境中的巨噬细胞,证明其在多种小鼠肿瘤模型中显著抑制肿瘤进展,为靶向TAMs的癌症治疗提供实验依据。
3. **文献名称**: *"CSF1/CSF1R signaling is a critical driver of myeloid cell recruitment and polarization in tumor microenvironments"*
**作者**: DeNardo et al. (2011)
**摘要**: 通过特异性抗CSF1R抗体阻断小鼠模型中的CSF1R信号,发现其显著减少肿瘤内M2型巨噬细胞浸润,并抑制血管生成和肿瘤转移,揭示该抗体在调控免疫微环境中的作用。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议核对最新文献及具体内容。)
The macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (CSF1R), also known as CD115 or c-FMS, is a tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the *CSF1R* gene. It binds ligands such as CSF-1 (colony-stimulating factor 1) and interleukin-34 (IL-34), regulating the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of macrophages, monocytes, and other myeloid-lineage cells. CSF1R signaling plays critical roles in tissue homeostasis, immune regulation, and disease processes, including cancer, inflammatory disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions.
CSF1R-targeting antibodies are designed to modulate this pathway, primarily as antagonists to block receptor activation. By inhibiting CSF1R, these antibodies suppress the recruitment and function of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in cancers, thereby disrupting pro-tumorigenic microenvironments and enhancing anti-tumor immune responses. Some antibodies, like emactuzumab and cabiralizumab, have reached clinical trials for conditions such as tenosynovial giant cell tumor and pancreatic cancer, often combined with checkpoint inhibitors.
Additionally, CSF1R antibodies are explored in inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) to dampen pathogenic macrophage activity and in neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease) to modulate microglia responses. Challenges include balancing therapeutic efficacy with potential immunosuppressive side effects. Most CSF1R antibodies are monoclonal, engineered for specificity to extracellular domains, and may act by preventing ligand binding or receptor dimerization. Their development highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting myeloid cells in diverse pathologies.
×