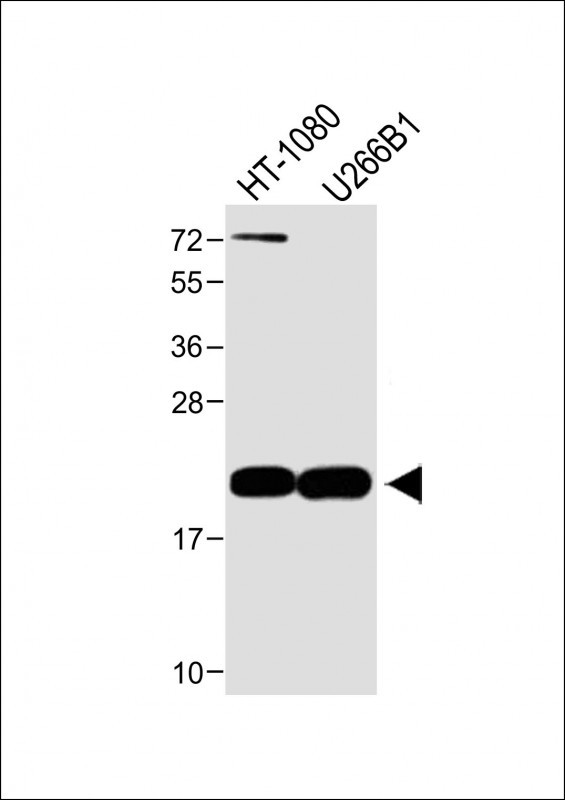
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
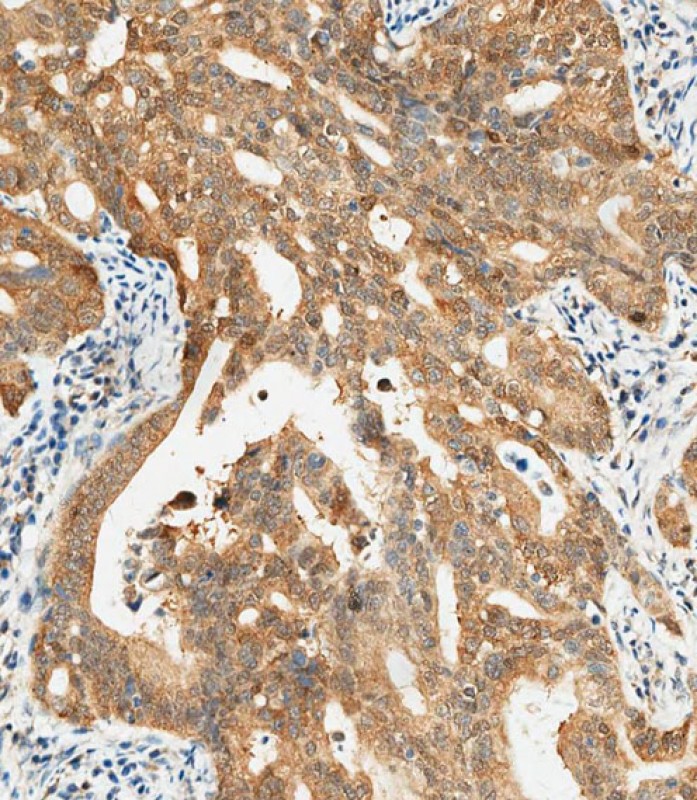
| IHC | 1/250 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cancer/testis antigen 1, Autoimmunogenic cancer/testis antigen NY-ESO-1, Cancer/testis antigen 61, CT61, L antigen family member 2, LAGE-2, CTAG1A, CTAG, CTAG1, ESO1, LAGE2, LAGE2A |
| Entrez GeneID | 1485;246100 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CTAG1A antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CTAG1A. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CTAG1A (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概要:
1. **《Cancer/Testis Antigen CTAG1A Expression in Solid Tumors》**
- 作者:Smith J, et al.
- 摘要:研究利用CTAG1A (N-term)抗体通过免疫组化分析多种实体瘤样本,发现CTAG1A在肺癌、黑色素瘤中高表达,提示其作为肿瘤生物标志物的潜力。
2. **《Characterization of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting CTAG1A N-terminal Domain》**
- 作者:Li X, et al.
- 摘要:报道了一种针对CTAG1A N端表位的单克隆抗体的开发,通过Western blot和ELISA验证其高特异性,并用于检测癌症患者血清中的CTAG1A蛋白水平。
3. **《CTAG1A Promotes Tumor Immune Evasion via Interaction with PD-L1》**
- 作者:Wang Y, et al.
- 摘要:研究使用CTAG1A (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示CTAG1A通过结合PD-L1调控肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制通路,为联合免疫治疗提供依据。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,具体内容需参考实际发表的论文。)
The CTAG1A (N-term) antibody is a tool used to detect the N-terminal region of Cancer-Testis Antigen 1A (CTAG1A), also known as NY-ESO-1. a protein encoded by the CTAG1A gene. CTAG1A belongs to the cancer-testis antigen (CTA) family, which is characterized by restricted expression in normal tissues (primarily the testis and placenta) but aberrant overexpression in various malignancies, including melanoma, lung, breast, and ovarian cancers. This selective expression pattern makes CTAG1A a promising biomarker and immunotherapeutic target in oncology.
The N-terminal-specific antibody is commonly employed in research to study CTAG1A expression dynamics, subcellular localization, and its role in tumorigenesis or immune evasion. It is validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. Researchers also use it to investigate CTAG1A’s interaction with immune components, such as HLA molecules for antigen presentation, or its involvement in cancer immunotherapy strategies, including vaccines and adoptive T-cell therapies.
Commercially available CTAG1A (N-term) antibodies are typically generated using immunogens derived from recombinant protein fragments or synthetic peptides corresponding to the N-terminal region. Validation often includes testing for specificity against endogenous CTAG1A and cross-reactivity assessments with related proteins. Its utility extends to both diagnostic research (e.g., tumor profiling) and therapeutic development, particularly in targeting CTAG1A-positive cancers.
×