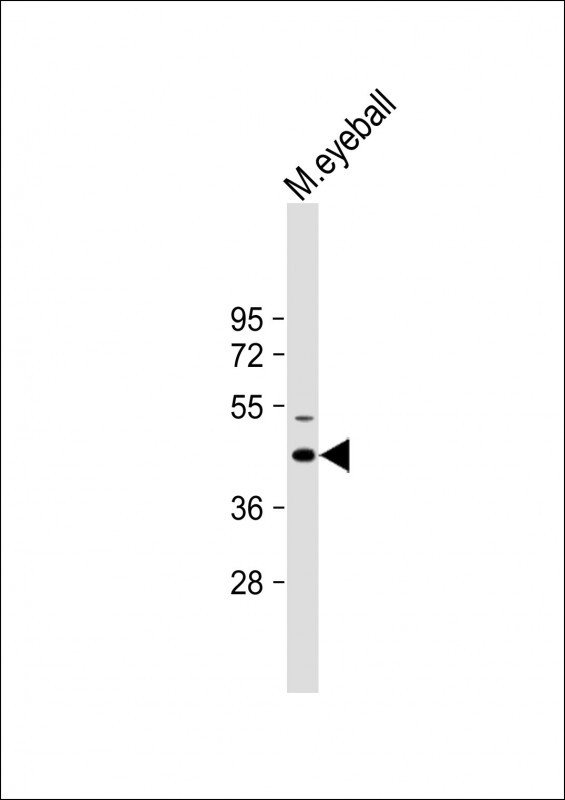
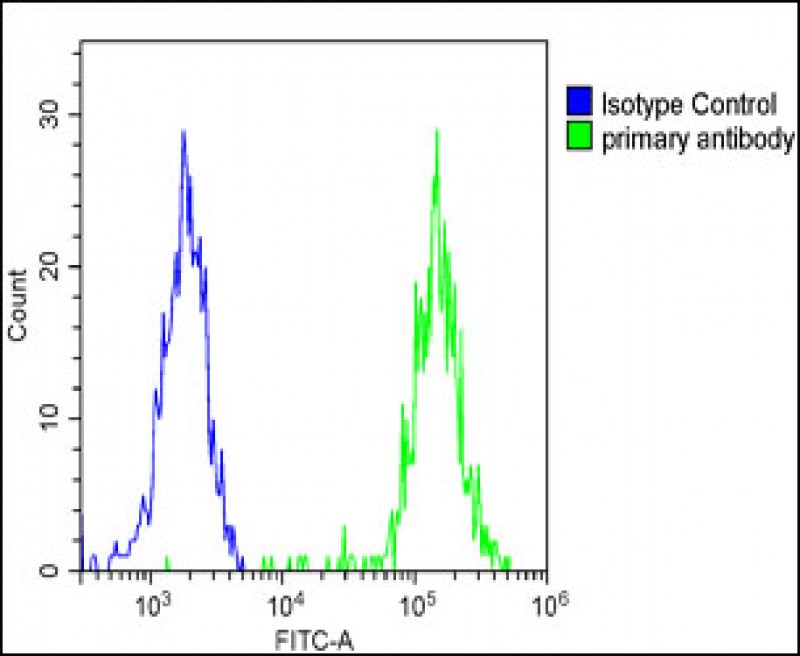
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Keratocan, KTN, Keratan sulfate proteoglycan keratocan, KERA, SLRR2B |
| Entrez GeneID | 11081 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This KERA antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 228-257 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KERA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KERA(Keratocan)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息:
---
1. **"Keratocan-deficient mice develop alterations in corneal structure and function"**
*Liu, C.Y., et al. (2003)*
摘要:研究通过敲除小鼠KERA基因,发现角膜基质胶原纤维排列紊乱,导致角膜混浊和机械强度下降,证明Keratocan对维持角膜透明性和结构至关重要。
2. **"Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of keratocan: A corneal keratan sulfate proteoglycan"**
*Hassell, J.R., et al. (1998)*
摘要:首次报道了KERA基因的克隆及其编码的角膜特异性蛋白聚糖,通过抗体检测证实其在角膜基质中高表达,提示其在角膜发育中的关键作用。
3. **"Altered expression of keratocan in corneal dystrophies"**
*Carlson, E.C., et al. (2005)*
摘要:利用KERA抗体分析多种角膜营养不良患者的组织样本,发现Keratocan表达异常与角膜基质病变相关,为疾病机制研究提供依据。
---
这些文献涵盖了KERA的基因功能、结构研究及临床应用方向,可作为相关抗体研究的理论基础。如需具体引用,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库核对原文细节。
**Background of KERA Antibody**
The KERA antibody targets keratocan, a protein encoded by the *KERA* gene, which belongs to the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family. Keratocan is primarily expressed in the corneal stroma and plays a critical role in maintaining corneal transparency and structural integrity by regulating collagen fibril organization and extracellular matrix (ECM) stability. Mutations in *KERA* are associated with corneal dystrophies, such as autosomal recessive cornea plana (CNA2), characterized by flattened corneas, reduced visual acuity, and structural abnormalities.
KERA antibodies are essential tools in research to investigate corneal development, disease mechanisms, and potential therapies. They enable the detection of keratocan expression in tissues, aiding in studies of corneal embryogenesis, wound healing, and ECM remodeling. Additionally, these antibodies help diagnose genetic corneal disorders by identifying aberrant keratocan levels or localization in clinical samples.
Recent studies explore KERA antibodies in regenerative medicine, particularly in bioengineered corneal implants and gene therapy approaches to restore corneal function. Their utility extends to animal models, where keratocan knockout mice exhibit corneal thinning and opacity, mimicking human pathologies. By elucidating keratocan's interactions with other ECM components (e.g., lumican and decorin), KERA antibodies contribute to understanding broader connective tissue disorders. Overall, KERA antibodies serve as vital reagents in both basic research and translational applications, bridging molecular insights with clinical advancements in ophthalmology.
×