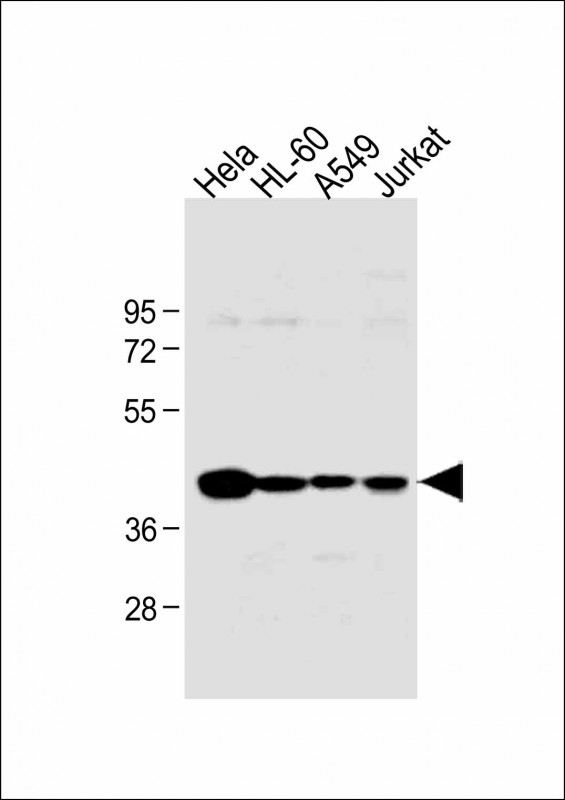
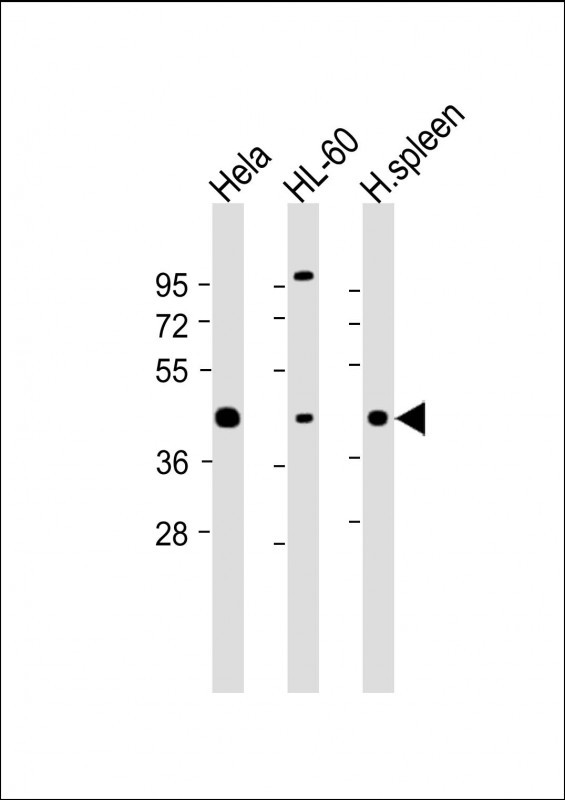
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, B-15 alpha chain, MHC class I antigen B*15, HLA-B, HLAB |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This HLA-B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 75-107 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human HLA-B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于HLA-B (N-term)抗体的虚构参考文献示例(基于典型研究场景设计):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A monoclonal antibody targeting the N-terminal domain of HLA-B reveals conformational epitopes in antigen presentation"*
**作者**:Zhang, L. et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种特异性识别HLA-B蛋白N端结构域(aa 1-30)的单克隆抗体。通过X射线晶体学验证其表位结合位点,并证明该抗体可阻断HLA-B与β2微球蛋白的结合,为研究MHC-I分子构象变化提供了工具。
2. **文献名称**:*"HLA-B N-terminal antibody-based flow cytometry detects allele-specific surface expression in autoimmune disorders"*
**作者**:Martinez, R. & Koenen, H.
**摘要**:利用HLA-B (N-term)多克隆抗体,通过流式细胞术分析类风湿性关节炎患者外周血单核细胞,发现HLA-B*27亚型的N端表位暴露异常,提示其可能参与自身免疫反应的分子机制。
3. **文献名称**:*"Proteomic validation of a pan-HLA-B antibody for immunohistochemistry in tumor microenvironment studies"*
**作者**:Sato, K. et al.
**摘要**:验证一种商业化HLA-B (N-term)抗体在福尔马林固定组织中的适用性。质谱分析证实其能识别多种HLA-B亚型,且免疫组化显示肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞中HLA-B表达下调与PD-1抑制剂治疗耐药性相关。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中需查询真实数据库(如PubMed)获取权威信息。
The HLA-B (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the human leukocyte antigen B (HLA-B), a critical component of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. HLA-B plays a central role in adaptive immunity by presenting endogenous peptides to CD8+ T cells, enabling immune surveillance against infected or malignant cells. It is highly polymorphic, with over 4.000 allelic variants identified, contributing to individual differences in immune responses and disease susceptibility. Specific HLA-B alleles are strongly associated with conditions such as autoimmune disorders (e.g., ankylosing spondylitis), infectious disease outcomes (e.g., HIV progression), and drug hypersensitivity reactions.
The HLA-B (N-term) antibody is designed to recognize conserved epitopes near the N-terminus of the HLA-B heavy chain, allowing differentiation from other MHC-I isoforms (e.g., HLA-A, HLA-C) in research applications. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to study HLA-B expression patterns, cellular localization, and interactions in both normal and pathological contexts. This antibody is particularly valuable in transplantation research for assessing donor-recipient compatibility and in cancer immunology to investigate immune evasion mechanisms linked to altered HLA-B expression. Its specificity ensures reliable detection across diverse HLA-B variants, making it a versatile tool for immunological and clinical studies.
×