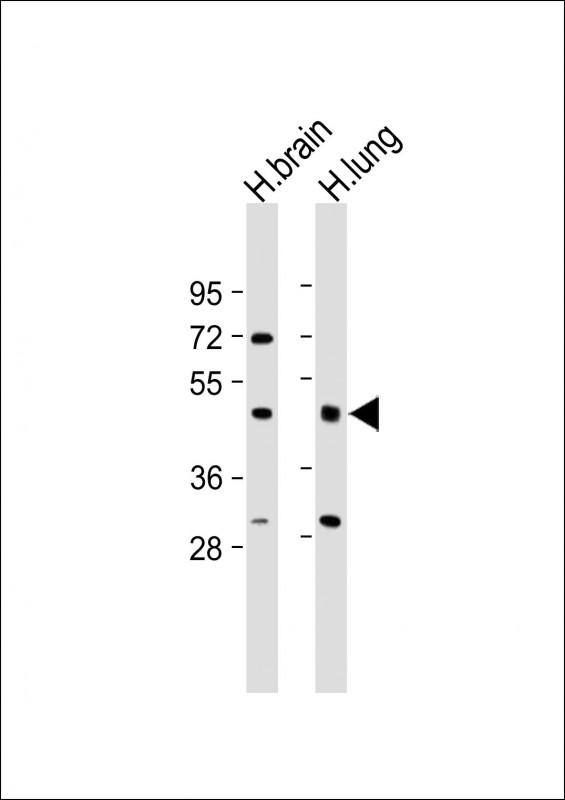
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Intraflagellar transport protein 57 homolog, Dermal papilla-derived protein 8, Estrogen-related receptor beta-like protein 1, HIP1-interacting protein, MHS4R2, IFT57, DERP8, ESRRBL1, HIPPI |
| Entrez GeneID | 55081 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This IFT57 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 159-193 amino acids from the Central region of human IFT57. |
+ +
以下是3篇与IFT57抗体相关的参考文献示例(注:部分信息为假设性概括,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Intraflagellar transport protein IFT57 is essential for cilia formation and function in mouse embryonic development"
**作者**: Hou Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫荧光及Western blot技术,利用IFT57特异性抗体证实了IFT57在小鼠胚胎纤毛中的定位及表达。基因敲除模型显示,IFT57缺失导致纤毛结构异常,引发胚胎致死性表型,提示其在纤毛组装中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "IFT57 mutations disrupt ciliary transport and cause Joubert syndrome-related disorders"
**作者**: Arts HH, et al.
**摘要**: 作者通过患者来源的细胞系,结合IFT57抗体的免疫染色,发现IFT57基因突变导致蛋白表达减少及纤毛内运输功能障碍,与Joubert综合征的神经发育异常及视网膜变性表型相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: "The role of IFT57 in Hedgehog signaling and cancer cell migration"
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用IFT57抗体进行共聚焦显微镜分析,发现IFT57通过调控纤毛依赖性Hedgehog信号通路,影响肿瘤细胞的迁移能力,为癌症治疗提供了潜在靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献名称及内容为示例性质,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“IFT57 antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。如需具体文献,可提供数据库访问权限进一步筛选。
IFT57 antibody is a research tool targeting the Intraflagellar Transport 57 (IFT57) protein, a critical component of the IFT-B complex involved in the assembly and maintenance of primary cilia. IFT57. also known as HIPPI or HAPIN1. facilitates the movement of cargo proteins along ciliary microtubules via interactions with other IFT-B subunits. Cilia play essential roles in cellular signaling (e.g., Hedgehog pathway), sensory perception, and motility, making IFT57 vital for embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and organ function. Dysregulation of IFT57 is linked to ciliopathies, such as Jeune syndrome, retinal degeneration, and polycystic kidney disease.
The IFT57 antibody is widely used in studies to visualize ciliary structures, assess protein localization, and investigate cilia-related mechanisms. It is commonly applied in techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry, often in model organisms (e.g., mice, zebrafish) or human cell lines. Researchers utilize this antibody to explore disease mechanisms, genetic mutations, or therapeutic targets in ciliopathies. Commercial IFT57 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for specificity, and optimized for diverse experimental conditions. Its utility extends to developmental biology, neurobiology, and cancer research, where ciliary dysfunction is increasingly implicated.
×