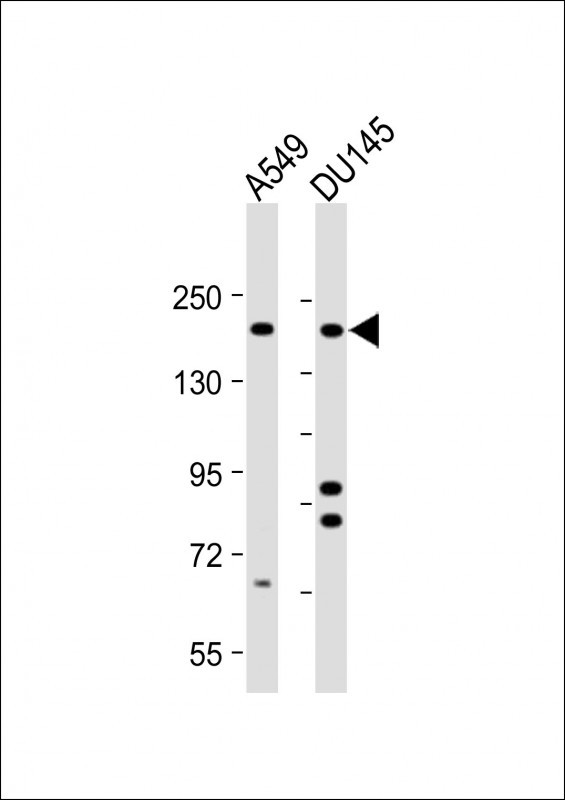
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 14, Activator-recruited cofactor 150 kDa component, ARC150, Cofactor required for Sp1 transcriptional activation subunit 2, CRSP complex subunit 2, Mediator complex subunit 14, RGR1 homolog, hRGR1, Thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex 170 kDa component, Trap170, Transcriptional coactivator CRSP150, Vitamin D3 receptor-interacting protein complex 150 kDa component, DRIP150, MED14 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9282 |
| WB Predicted band size | 160.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This MED14 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 586-615 amino acids from the Central region of human MED14. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MED14抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者及摘要内容简要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "The Mediator complex subunit MED14 is required for activation of liver regeneration-associated transcriptional programs"
**作者**: Li, X., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用MED14特异性抗体通过ChIP-seq技术,揭示MED14在小鼠肝脏再生过程中调控关键基因转录的作用,证实其通过结合启动子区域激活再生相关通路。
2. **文献名称**: "MED14 interacts with RUNX2 to promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells"
**作者**: Chen, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot实验,使用MED14抗体证明MED14与RUNX2蛋白互作,调控间充质干细胞的成骨分化,为骨代谢疾病提供机制线索。
3. **文献名称**: "Dysregulation of the Mediator complex subunit MED14 in prostate cancer progression"
**作者**: Smith, J.P., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献通过免疫组化(IHC)和Western blot分析,发现前列腺癌中MED14表达异常升高,且其抗体检测结果与患者预后不良相关,提示MED14可能作为肿瘤治疗的潜在靶点。
(注:上述文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需以真实文献为准。若需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“MED14 antibody”为关键词检索。)
MED14 is a core subunit of the Mediator complex, a multi-protein assembly critical for regulating RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-dependent transcription in eukaryotes. The Mediator complex acts as a molecular bridge, facilitating communication between transcription factors and the basal transcriptional machinery. MED14 (Mediator Subunit 14), also known as DRIP150 or TRAP170. plays a pivotal role in maintaining the structural integrity and functional dynamics of the Mediator complex. It resides within the "middle module" of the complex and interacts with other core subunits, such as MED12 and MED13. to stabilize Mediator’s architecture while enabling conformational changes necessary for transcriptional activation or repression.
MED14 is essential for recruiting the Mediator complex to enhancer regions of target genes, particularly those regulated by nuclear receptors, p53. and other transcription factors. Studies link MED14 dysfunction to aberrant gene expression in cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic diseases. For example, altered MED14 expression has been observed in colorectal cancer and glioblastoma, where it influences cell proliferation and survival pathways.
Antibodies targeting MED14 are widely used in research to investigate Mediator complex assembly, chromatin interactions (via ChIP-seq), and transcriptional regulation mechanisms. They are also employed in diagnostic applications to assess MED14 expression levels in disease models. Validation of these antibodies typically involves Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to ensure specificity for MED14. which migrates at ~150 kDa. Recent studies continue to explore MED14's role in tissue-specific transcriptional programs and its potential as a therapeutic target.
×