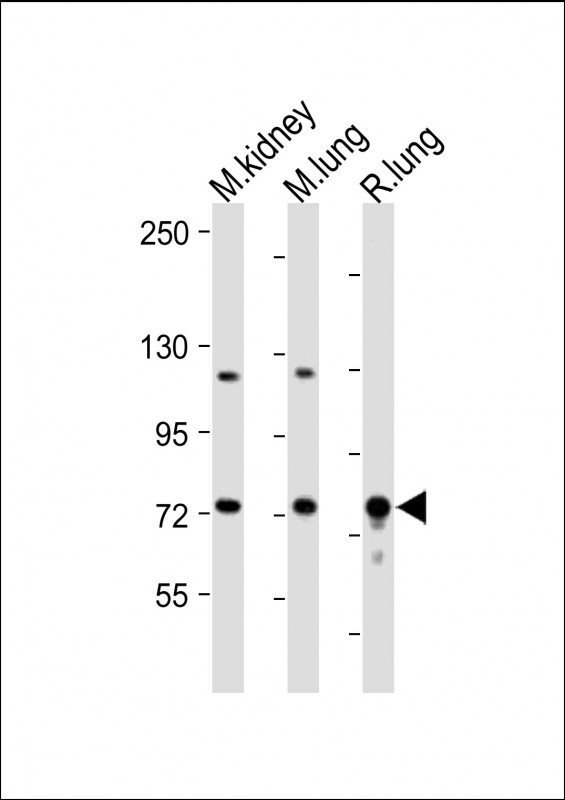
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Delta-like protein 4, Drosophila Delta homolog 4, Delta4, DLL4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54567 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This DLL4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a recombinant protein from the human region of human DLL4. |
+ +
以下是关于DLL4抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
---
1. **标题**:*DLL4 blockade inhibits tumor growth and reduces tumor-initiating cell frequency*
**作者**:Hoey, T., et al.
**摘要**:研究证明抗DLL4抗体通过抑制Notch信号通路,破坏肿瘤血管异常增生,同时降低肿瘤干细胞比例,从而抑制多种实体瘤的生长,为靶向DLL4的抗癌治疗提供依据。
---
2. **标题**:*Phase I study of demcizumab (anti-DLL4) in combination with chemotherapy*
**作者**:Smith, D.C., et al.
**摘要**:首次人体临床试验(I期)评估DLL4单抗demcizumab联合化疗的安全性,结果显示部分患者肿瘤缩小,但需注意心血管副作用,提示DLL4靶向治疗的潜在疗效与风险。
---
3. **标题**:*DLL4-Notch signaling mediates resistance to anti-VEGF therapy*
**作者**:Li, J.L., et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示肿瘤通过上调DLL4-Notch通路逃逸抗VEGF治疗,联合抑制DLL4与VEGF可显著增强抗血管生成效果,为克服耐药性提供新策略。
---
如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库检索上述关键词获取全文。
**Background of DLL4 Antibodies**
DLL4 (Delta-like ligand 4) is a transmembrane ligand in the Notch signaling pathway, a conserved system regulating cell differentiation, proliferation, and angiogenesis. DLL4 is primarily expressed in vascular endothelial cells and plays a critical role in vascular development, particularly in arterial specification and angiogenic sprouting. It interacts with Notch receptors (Notch1/Notch4) to establish "tip-stalk" cell dynamics during blood vessel formation, ensuring organized branching and preventing excessive vascular density.
Dysregulation of DLL4-Notch signaling is implicated in pathological angiogenesis, notably in cancers and ocular diseases. Tumors often upregulate DLL4 to promote abnormal, dysfunctional vasculature, facilitating hypoxia and metastasis. DLL4-blocking antibodies have thus emerged as therapeutic candidates to disrupt tumor angiogenesis. By inhibiting DLL4-Notch interactions, these antibodies induce hyper-sprouting of nonfunctional vessels, impairing tumor blood supply and growth.
Preclinical studies show DLL4 antibodies enhance anti-tumor effects when combined with VEGF inhibitors or chemotherapy. However, clinical trials reveal challenges, including on-target toxicity (e.g., vascular anomalies in normal tissues) and adaptive resistance. Beyond oncology, DLL4 targeting is explored in diseases like age-related macular degeneration.
Overall, DLL4 antibodies represent a dual-edged therapeutic strategy, balancing potent anti-angiogenic activity with the need for precise delivery and safety optimization. Research continues to refine their application in precision medicine.
(Word count: 249)
×