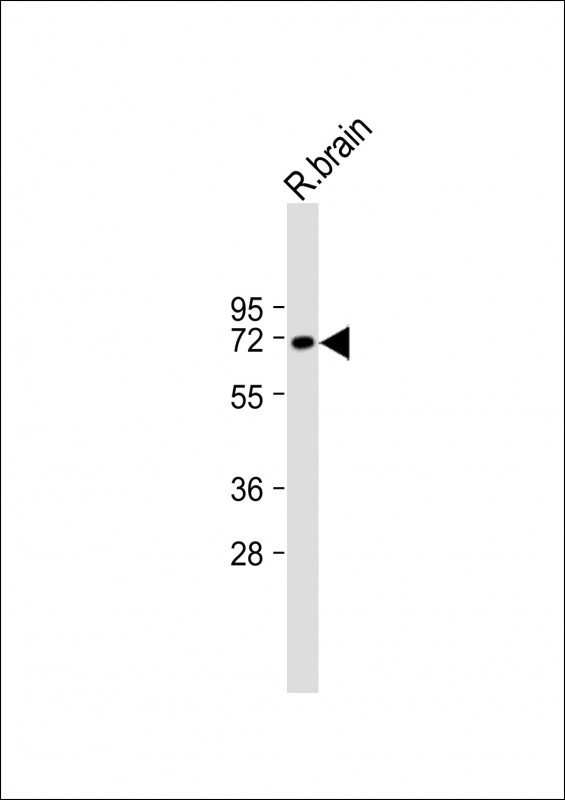
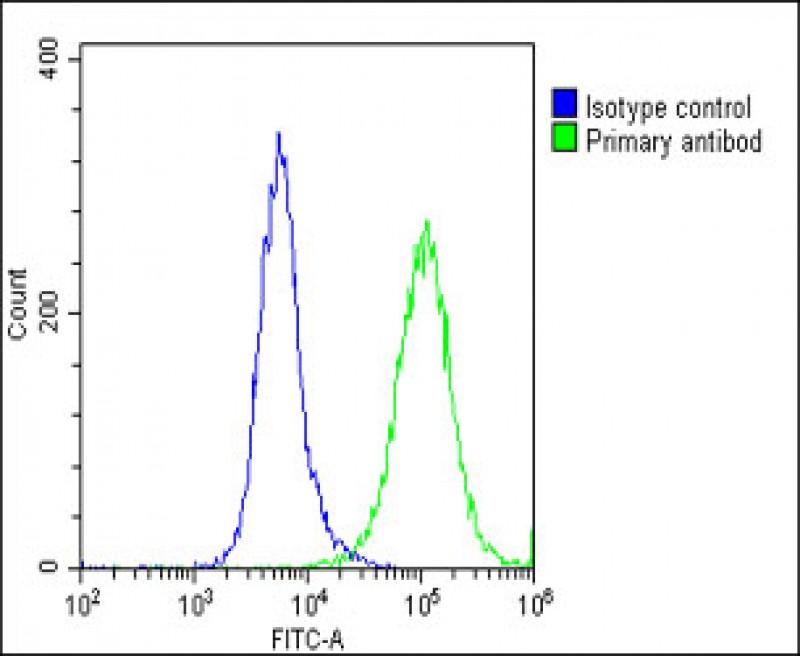
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Vesicular glutamate transporter 2, VGluT2, Differentiation-associated BNPI, Differentiation-associated Na(+)-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter, Solute carrier family 17 member 6, SLC17A6, DNPI, VGLUT2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57084 |
| WB Predicted band size | 64.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This SLC17A6 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 255-289 amino acids of human SLC17A6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SLC17A6(VGluT2)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Differential expression of vesicular glutamate transporters by sensory neurons in the mouse trigeminal ganglion"**
- **作者**: Fremeau RT et al. (2004)
- **摘要**: 本研究利用SLC17A6抗体(抗VGluT2)结合免疫组化技术,揭示了小鼠三叉神经节中不同感觉神经元亚群对VGluT2蛋白的差异性表达,证明VGluT2在特定痛觉传导通路中的关键作用。
2. **"Selective distribution of vesicular glutamate transporters in the central nervous system"**
- **作者**: Hioki H et al. (2007)
- **摘要**: 通过SLC17A6抗体的免疫荧光标记,作者系统定位了VGluT2蛋白在大脑中的分布,发现其高度富集于丘脑、小脑和脑干谷氨酸能突触,提示其在神经环路中的特异性调控功能。
3. **"VGLUT2-dependent glutamatergic transmission in primary afferents is required for chronic neuropathic pain"**
- **作者**: Scherrer G et al. (2010)
- **摘要**: 采用SLC17A6抗体进行蛋白表达分析,发现周围神经损伤后VGluT2在脊髓背角的上调与慢性神经病理性疼痛密切相关,基因敲除或抗体阻断VGluT2可显著缓解疼痛行为。
4. **"SLC17A6/VMAT2 double transgenic mice reveal segregated vesicular glutamate and monoamine storage systems"**
- **作者**: Birgner C et al. (2010)
- **摘要**: 研究通过SLC17A6抗体与单胺类转运体标记共定位实验,证明谷氨酸和单胺类递质在神经元内通过独立的囊泡系统储存,为神经递质共释放机制提供了分子证据。
以上文献均利用SLC17A6抗体探究VGluT2蛋白的神经解剖定位及生理病理功能。
The SLC17A6 antibody targets the solute carrier family 17 member 6 (SLC17A6), a transmembrane protein also known as vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGluT2). As one of three VGluT isoforms, SLC17A6/VGluT2 is primarily responsible for packaging glutamate into synaptic vesicles within glutamatergic neurons, enabling neurotransmitter release during synaptic transmission. It is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in regions like the thalamus, brainstem, cerebellum, and midbrain, distinguishing it from VGluT1 (cortical/hippocampal) and VGluT3 (sparse, neuromodulatory).
SLC17A6 antibodies are widely used in neuroscience research to identify and map glutamatergic pathways, study synaptic plasticity, and investigate disorders linked to glutamate dysregulation, such as schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease, and chronic pain. These antibodies enable techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and fluorescent labeling to visualize VGluT2 distribution in neural tissues. Specificity is often validated via knockout models or peptide-blocking assays.
As glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter, understanding SLC17A6’s role through antibody-based detection helps clarify its contributions to neural circuit formation, information processing, and disease mechanisms. Its selective expression makes it a critical marker for differentiating glutamatergic subpopulations in complex brain networks.
×