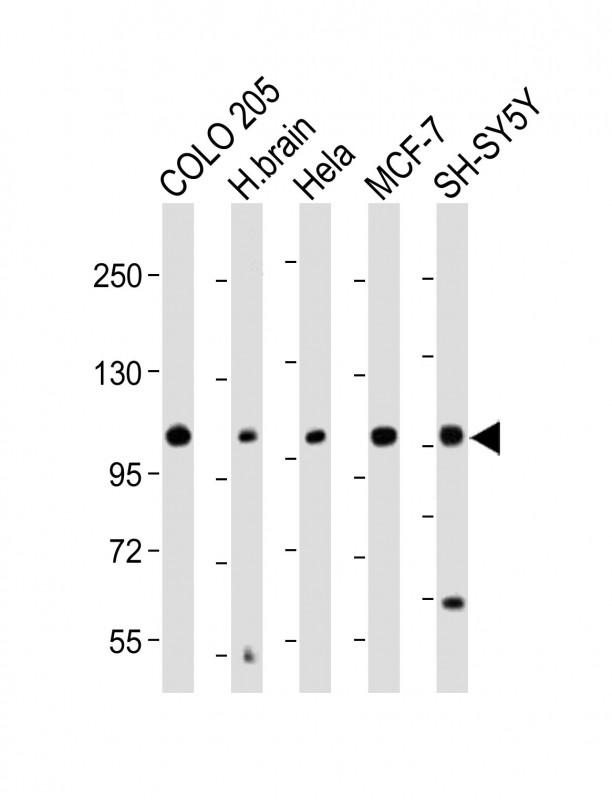
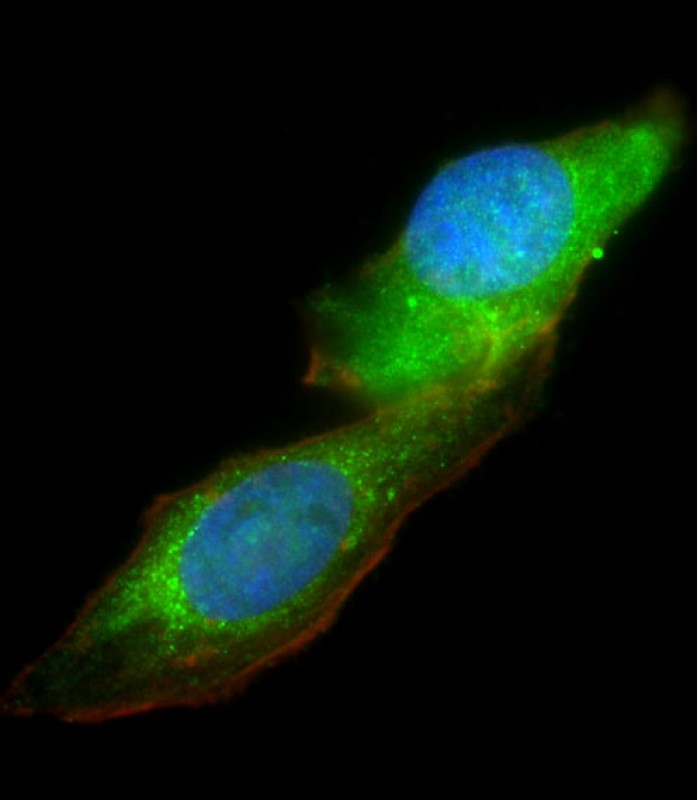
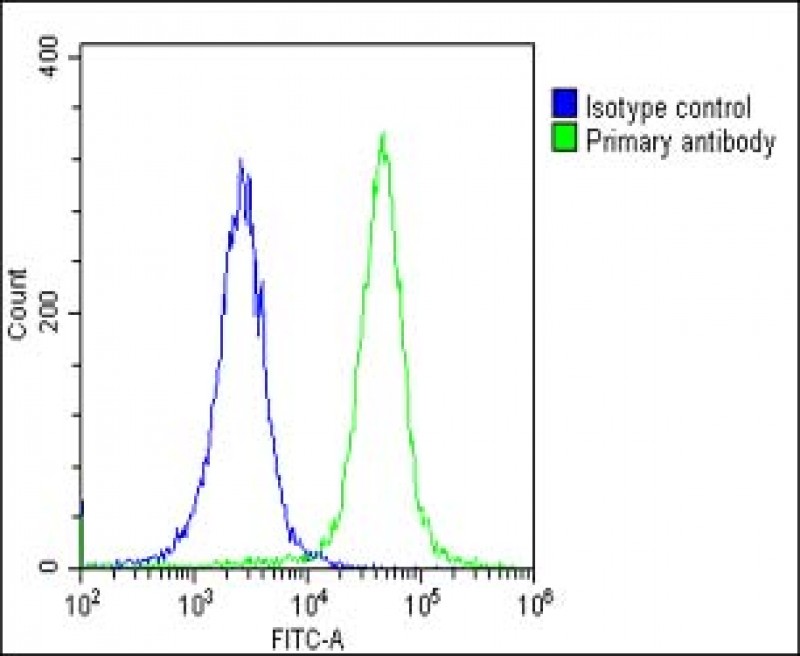
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1, Ether-a-go-go potassium channel 1, EAG channel 1, h-eag, hEAG1, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv10.1, KCNH1, EAG, EAG1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3756 |
| WB Predicted band size | 111.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This KCNH1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 787-820 amino acids from the human region of human KCNH1. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNH1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究概括,具体信息建议通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*KCNH1 channels regulate neuronal excitability and epileptic seizures*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用KCNH1特异性抗体发现该通道在抑制癫痫样放电中起关键作用,敲除小鼠模型中KCNH1蛋白表达下降导致神经元过度兴奋。
2. **文献名称**:*Developmental expression of KCNH1 in the human cerebral cortex*
**作者**:Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析胎儿及成人脑组织,发现KCNH1在皮层发育早期高表达,提示其可能参与神经元迁移和突触形成,抗体特异性经敲除实验验证。
3. **文献名称**:*KCNH1 antibody validation for functional studies in cancer cells*
**作者**:Wang H, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了多种商业KCNH1抗体的可靠性,发现其在乳腺癌细胞系中特异性识别目标蛋白,并证实KCNH1过表达与细胞增殖和侵袭性增强相关。
---
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索确认。
The KCNH1 antibody targets the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1 (KCNH1), a protein encoded by the KCNH1 gene. This gene belongs to the Ether-à-go-go (EAG) family of voltage-gated potassium channels, which regulate cellular excitability and proliferation. KCNH1. also known as Kv10.1. is primarily expressed in the central nervous system and plays a role in neuronal signaling, synaptic plasticity, and cell cycle control. Dysregulation of KCNH1 has been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Temple-Baraitser syndrome and Zimmermann-Laband syndrome, often linked to gain-of-function mutations. Additionally, aberrant KCNH1 expression is observed in certain cancers, where it promotes tumor growth and metastasis.
KCNH1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the protein’s expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess KCNH1 levels in tissues or cultured cells. Researchers also employ these antibodies to investigate channel dynamics, post-translational modifications, and interactions with regulatory proteins. Specificity and validation (e.g., via knockout controls) are critical due to potential cross-reactivity with related EAG family members. Commercial KCNH1 antibodies are typically raised against epitopes in the cytoplasmic C-terminal domain, which contains key regulatory regions. Understanding KCNH1’s role through antibody-based research may inform therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders and cancers linked to its dysfunction.
×