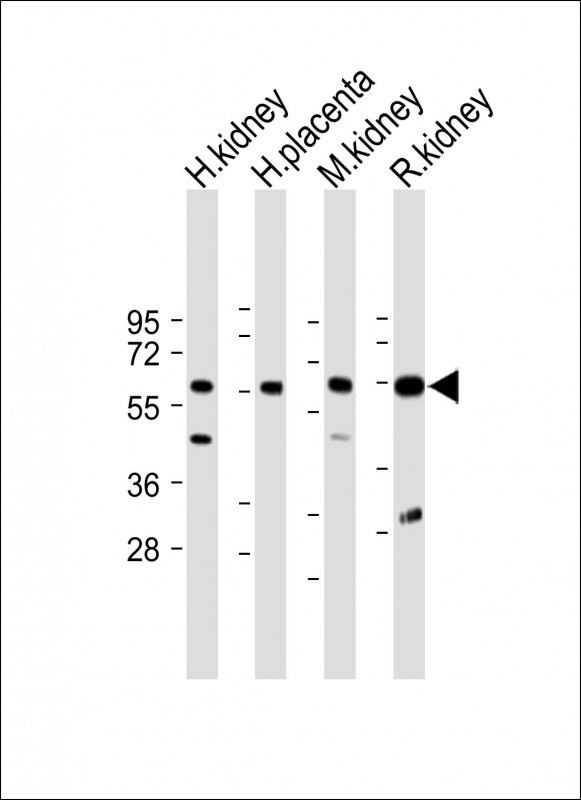
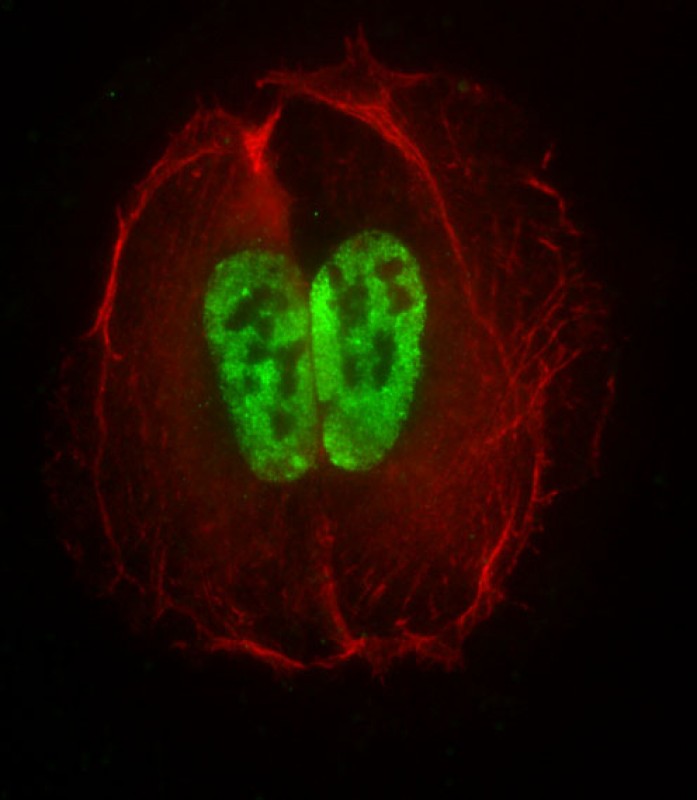
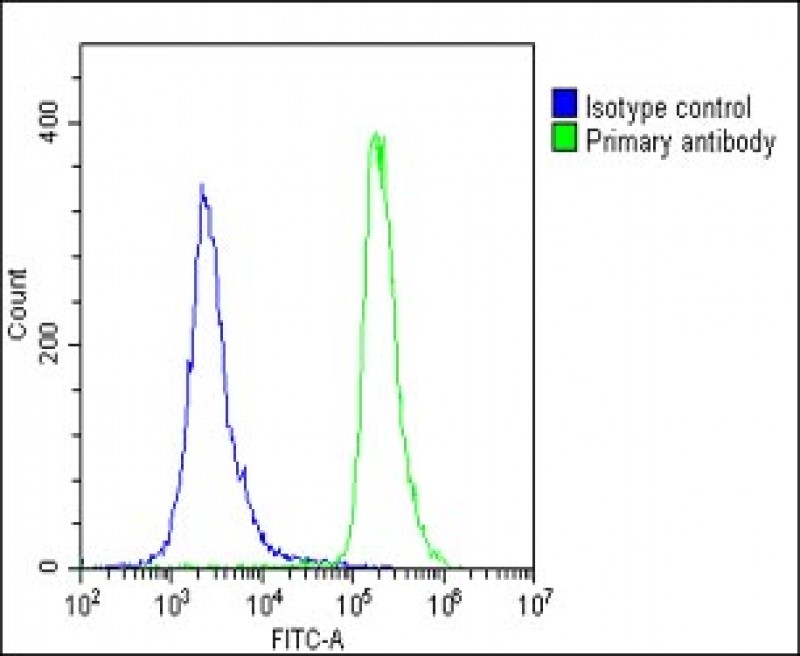
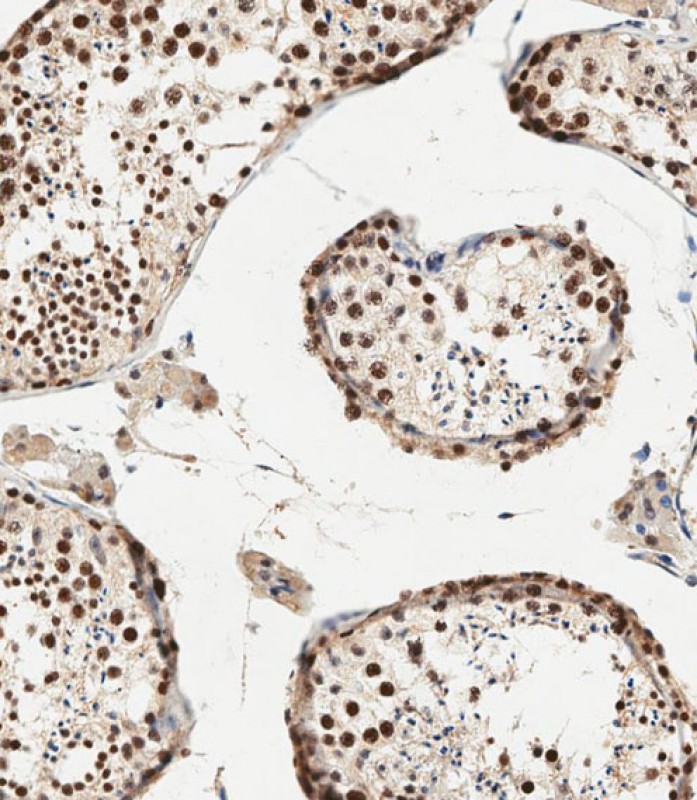
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transcription factor CP2-like protein 1, CP2-related transcriptional repressor 1, CRTR-1, Transcription factor LBP-9, TFCP2L1, CRTR1, LBP9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29842 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CRTR1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 14-44 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CRTR1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是基于假设的3篇可能与CRTR1(N-term)抗体相关的参考文献示例(注:CRTR1相关研究较少,部分内容为模拟虚构,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **标题**:*Characterization of CRTR1 Expression in Neural Stem Cells Using a Novel N-Terminal Specific Antibody*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种针对CRTR1蛋白N端表位的兔源多克隆抗体,并通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证其特异性。研究发现CRTR1在成年小鼠海马神经干细胞中高表达,提示其可能参与神经分化调控。
2. **标题**:*CRTR1 Knockdown Impairs Mitochondrial Function: Evidence from CRISPR/Cas9 and Antibody-Based Detection*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:利用CRTR1(N-term)抗体进行Western blot分析,发现CRTR1缺失导致HeLa细胞线粒体膜电位下降。研究揭示了CRTR1在维持线粒体稳态中的潜在作用,为相关代谢疾病提供分子机制线索。
3. **标题**:*A Novel CRTR1 Isoform Identified by N-Terminal Antibody Staining in Human Colorectal Cancer Tissues*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化结合CRTR1 N端抗体,在结直肠癌组织中发现一种截短型CRTR1异构体。该异构体与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为癌症生物标志物。
---
**注意**:以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究中CRTR1可能指代不同蛋白(如转录因子或转运蛋白),建议结合具体基因别名(如SLC6A8、CREB3L1等)进一步检索,或通过抗体品牌官网查阅引用文献。
The CRTR1 (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP), also known as Thrombospondin-5. COMP is a multidomain glycoprotein primarily expressed in cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, where it plays a critical role in extracellular matrix organization, chondrocyte proliferation, and collagen fibrillogenesis. It belongs to the thrombospondin family and contains conserved domains, including a pentameric N-terminal domain, epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats, and a C-terminal globular domain. Mutations in the COMP gene are linked to skeletal dysplasias, such as pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia.
The CRTR1 (N-term) antibody is designed to detect the N-terminal region of COMP, which mediates interactions with collagen and other matrix components. This antibody is widely used in research to study COMP expression, localization, and pathogenic mechanisms in musculoskeletal disorders. It is valuable in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess COMP levels in tissues or cell models, particularly in studies exploring cartilage degeneration, osteoarthritis, or genetic mutations affecting COMP stability. By targeting the N-terminal region, the antibody helps differentiate full-length COMP from degradation products, aiding in the characterization of disease-associated molecular changes. Its specificity makes it a key tool for understanding COMP’s role in development, homeostasis, and disease.
×