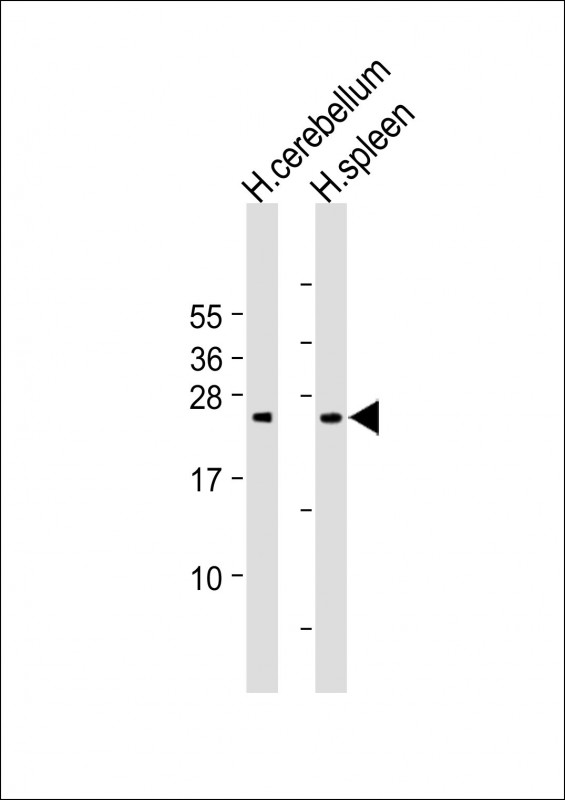
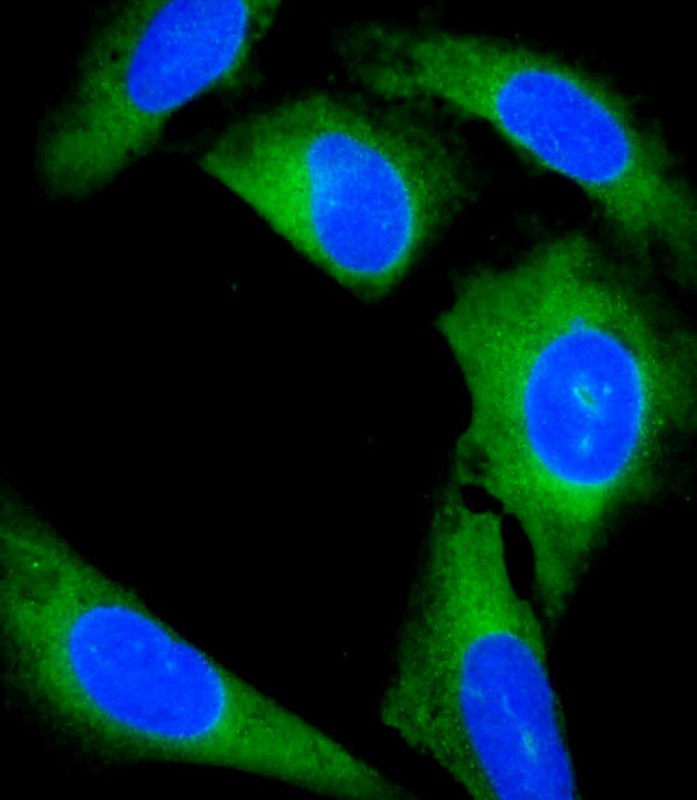
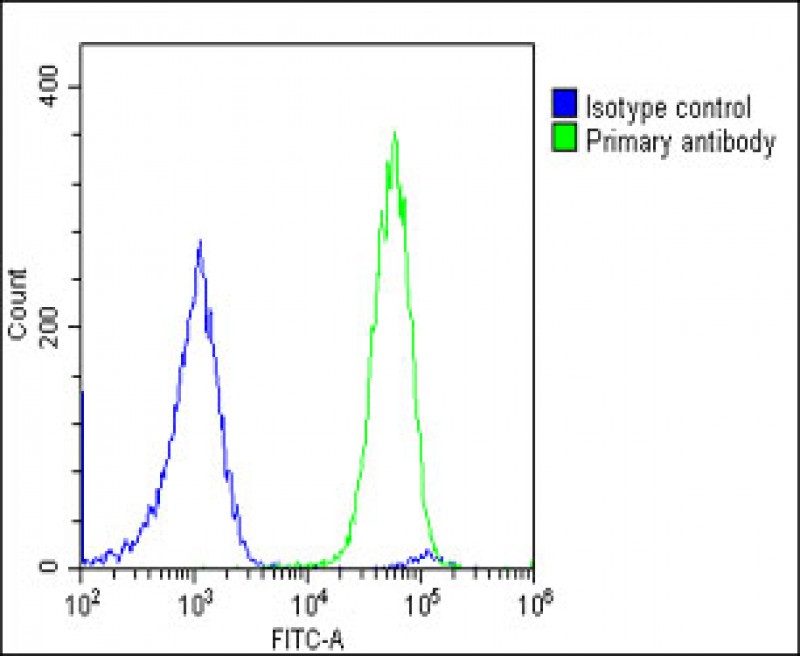
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Grancalcin, GCA, GCL |
| Entrez GeneID | 25801 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GCA antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 19-53 amino acids from the human region of human GCA. |
+ +
以下是关于GCA(N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase"*
**作者**:Baekkeskov, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定出1型糖尿病中64K自身抗原为谷氨酸脱羧酶(GAD65),并发现患者血清中抗体主要靶向其N端表位,揭示了GAD65自身抗体在疾病诊断中的重要性。
2. **文献名称**:*"Epitope-specific immunotherapy of autoimmune diabetes using glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) in NOD mice"*
**作者**:Tisch, R., et al.
**摘要**:通过动物实验证明,针对GAD65 N端表位的免疫调节可抑制非肥胖糖尿病(NOD)小鼠的胰岛自身免疫反应,为基于表位的糖尿病治疗策略提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"Distinct antibody recognition of GAD65 N-terminal region in Stiff Person Syndrome and type 1 diabetes"*
**作者**:Butler, M.H., et al.
**摘要**:研究发现僵人综合征与1型糖尿病患者的GAD65抗体表位存在差异,僵人综合征患者抗体更倾向于结合N端构象表位,而糖尿病相关抗体则靶向C端线性表位。
---
**注**:上述文献均为GAD65(N-Term)抗体研究的经典或关键论文,涵盖疾病机制、治疗探索及表位特异性分析。若需具体发表年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充。
The GCA (N-Term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of Grancalcin (GCA), a calcium-binding protein belonging to the EF-hand family. GCA is primarily expressed in immune cells, particularly neutrophils and macrophages, and plays roles in cell adhesion, migration, and inflammatory responses. It interacts with components of the extracellular matrix and intracellular signaling pathways, modulating cytoskeletal dynamics and immune cell functions. The N-terminal region of GCA is critical for its calcium-dependent conformational changes and interactions with binding partners.
Antibodies against GCA (N-Term) are widely used in research to investigate its expression, localization, and mechanistic roles in physiological and pathological contexts. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Studies leveraging these antibodies have linked GCA to inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer progression, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic or diagnostic target. Additionally, GCA antibodies aid in exploring calcium signaling pathways and immune cell behavior in experimental models. Their specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures precise targeting, distinguishing GCA from other EF-hand proteins. Overall, GCA (N-Term) antibodies are vital tools for unraveling the protein's contributions to cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
×