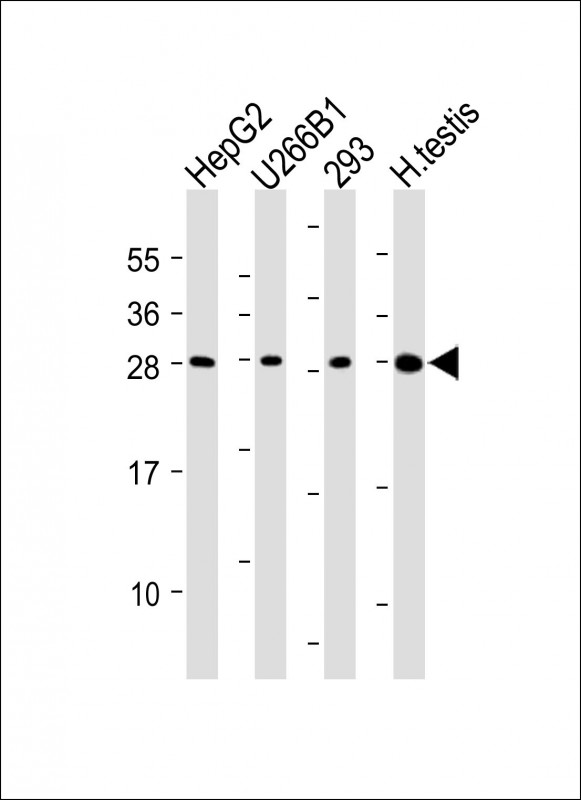
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C-type lectin domain family 1 member B, C-type lectin-like receptor 2, CLEC-2, CLEC1B, CLEC2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 51266 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CLEC1B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 44-78 amino acids from the human region of human CLEC1B. |
+ +
以下是关于 **CLEC1B (N-Term)** 抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CLEC-2 supports platelet aggregation in mouse but not human blood under high shear"*
**作者**: Bender M. et al.
**摘要**:
该研究通过使用针对CLEC1B N端结构域的特异性抗体,揭示了CLEC-2在血小板高剪切力诱导聚集中的作用。实验表明,CLEC-2在小鼠血液中通过结合配体podoplanin介导血栓形成,但在人类血液中该功能存在差异,提示物种特异性调控机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"A novel CLEC-2 antibody reveals distinct roles for CLEC-2 in hemostasis and tumor metastasis"*
**作者**: Suzuki-Inoue K. et al.
**摘要**:
研究团队开发了一种靶向CLEC1B N端表位的新型单克隆抗体,并验证其在抑制血小板活化及肿瘤转移中的双重功能。实验显示,该抗体能有效阻断CLEC-2与肿瘤细胞表面podoplanin的相互作用,减少小鼠模型中癌症转移的发生。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Targeting CLEC-2 in thrombo-inflammatory disease: Insights from antibody-based inhibition studies"*
**作者**: Watson S.P. et al.
**摘要**:
本文探讨了CLEC-2在血栓炎症中的病理作用,利用N端特异性抗体抑制CLEC-2信号通路,显著减轻小鼠模型中深静脉血栓和炎症反应,为抗CLEC-2抗体在治疗血栓性疾病中的潜力提供了依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science平台检索最新研究。
The CLEC1B (C-type lectin domain family 1 member B) protein, also known as CLEC-2. is a transmembrane receptor belonging to the C-type lectin superfamily. It is primarily expressed on platelets, megakaryocytes, and certain immune cells, where it plays a critical role in platelet activation, lymphatic development, and immune responses. CLEC1B interacts with ligands such as podoplanin (PDPN), a glycoprotein overexpressed in certain cancers and stromal cells, facilitating platelet-cancer cell interactions that influence thrombosis, metastasis, and tumor progression.
The CLEC1B (N-Term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal extracellular domain of the CLEC1B protein. This region is essential for ligand binding and receptor dimerization, making the antibody a valuable tool for studying CLEC1B's functional mechanisms. Researchers utilize this antibody in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to detect CLEC1B expression, investigate its role in platelet signaling pathways, or explore its involvement in pathological conditions, including thrombosis, cancer metastasis, and inflammatory diseases. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other C-type lectin receptors, enhancing experimental reliability. Studies employing this antibody have contributed to understanding CLEC1B's dual roles in hemostasis and immunity, as well as its potential as a therapeutic target in clotting disorders or cancer.
×