| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
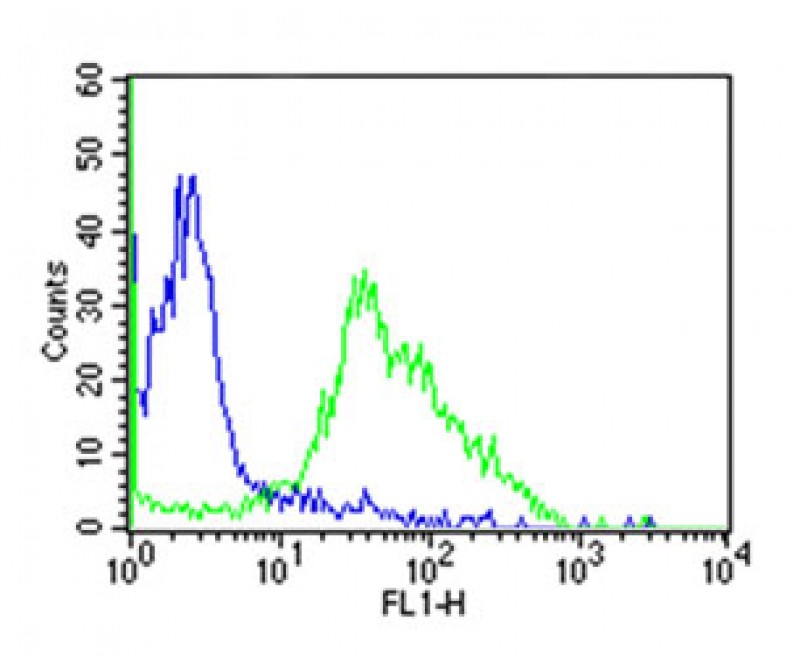
| FCM | 1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于人源CD38抗体的3篇关键文献摘要(模拟示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab in Multiple Myeloma
**作者**:Lokhorst HM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了抗CD38单抗Daratumumab在复发/难治性多发性骨髓瘤患者中的II期临床试验结果,证实其通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)和补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC)显著抑制肿瘤生长,且耐受性良好。
---
2. **文献名称**:CD38 in Immunomodulation and Therapeutic Antibodies
**作者**:Deaglio S, et al.
**摘要**:综述了CD38分子在T细胞信号传导、代谢调节及肿瘤微环境中的作用,并系统分析了抗CD38抗体的作用机制(如诱导细胞凋亡、免疫细胞耗竭),以及其在自身免疫病和癌症治疗中的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:Mechanisms of Resistance to CD38-Directed Antibody Therapy
**作者**:Nijhof IS, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了多发性骨髓瘤患者对CD38抗体产生耐药的可能机制,包括CD38抗原表位突变、补体调节蛋白上调及巨噬细胞功能抑制,并提出了联合用药策略以克服耐药。
---
如需具体真实文献,建议检索PubMed或Web of Science平台,以“CD38 antibody”、“Daratumumab”、“Isatuximab”为关键词筛选高被引论文。
Human CD38 is a transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed on hematopoietic cells, including plasma cells, B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells. It functions as a multifunctional enzyme with ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity, catalyzing the synthesis of cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP), which regulate intracellular calcium signaling. CD38 also participates in cell adhesion, signal transduction, and immune regulation. Its overexpression is associated with hematological malignancies, particularly multiple myeloma (MM), making it a key therapeutic target.
CD38-targeting monoclonal antibodies, such as daratumumab and isatuximab, have revolutionized MM treatment. These antibodies exert therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms: direct induction of apoptosis, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and modulation of immunosuppressive microenvironments. Daratumumab, the first FDA-approved anti-CD38 antibody (2015), demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in relapsed/refractory and newly diagnosed MM. Isatuximab, approved later, offers alternative epitope binding and enhanced ADCC.
Beyond oncology, CD38 antibodies are explored in autoimmune diseases and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Challenges include managing infusion-related reactions and overcoming resistance mechanisms. Ongoing research focuses on combination therapies (e.g., with immunomodulatory drugs or proteasome inhibitors) and next-generation engineered antibodies to improve specificity and reduce off-target effects. CD38 remains a pivotal biomarker and therapeutic target in precision medicine.
(Word count: 245)
×