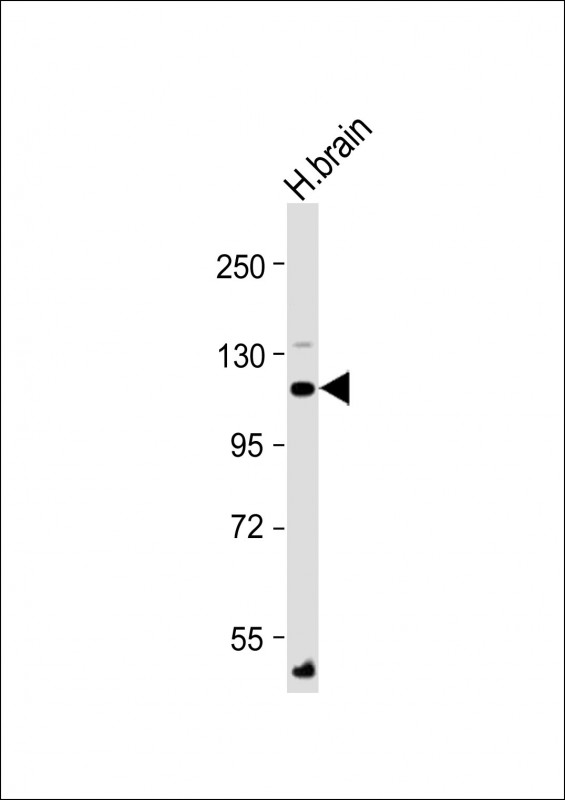
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
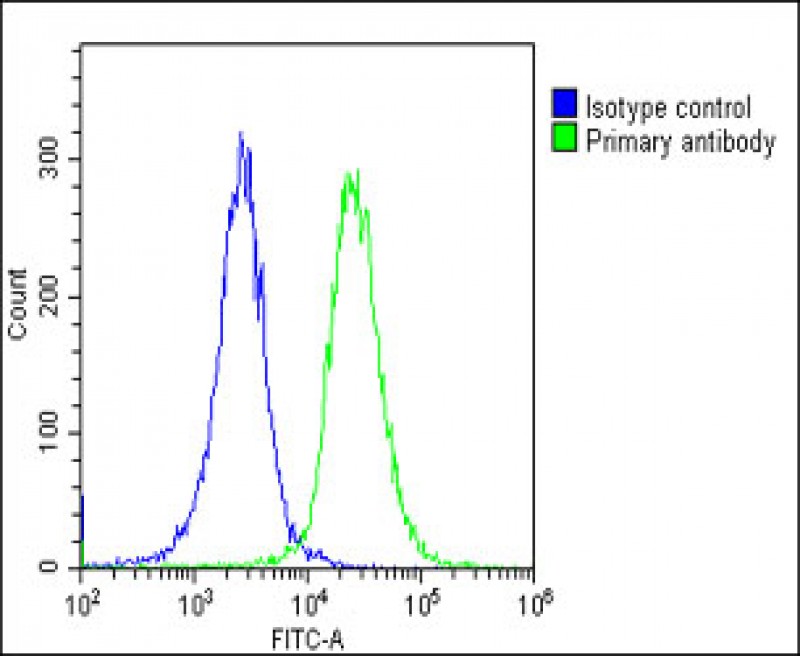
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-4, Na(+)/K(+) ATPase alpha-4 subunit, 3.6.3.9, Sodium pump subunit alpha-4, ATP1A4, ATP1AL2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 480 |
| WB Predicted band size | 114.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ATP1A4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 12-46 amino acids from the human region of human ATP1A4. |
+ +
以下是关于 ATP1A4 (N-Term) 抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Localization and functional characterization of the Na+/K+-ATPase α4 subunit in mammalian spermatozoa"**
- **作者**: Jimenez T. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用ATP1A4 (N-Term)抗体通过免疫荧光和Western blot,揭示了ATP1A4在精子头部和鞭毛的定位,并证明其参与精子运动调节。
2. **"Expression and hormonal regulation of the α4 isoform of Na+/K+-ATPase in the mouse testis"**
- **作者**: Sanchez G. & Blanco G.
- **摘要**: 通过N-Term抗体检测小鼠睾丸中ATP1A4的表达,发现其在生殖细胞中特异性表达,并受睾酮调控,提示其在精子发生中的作用。
3. **"Targeted disruption of the ATP1A4 gene in mice results in male infertility due to impaired sperm motility"**
- **作者**: Wagoner K. et al.
- **摘要**: 使用ATP1A4 (N-Term)抗体验证基因敲除模型,证实ATP1A4缺失导致精子活力下降,明确了其在雄性生育中的关键功能。
注:上述文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究核实来源及细节。
The ATP1A4 (N-Term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the ATP1A4 protein, a member of the sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase (Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase) family. ATP1A4. also known as the α4 subunit, is a P-type ATPase critical for maintaining electrochemical gradients by actively transporting Na⁺ and K⁺ ions across cell membranes. Unlike other α subunits (e.g., ATP1A1-3), ATP1A4 exhibits tissue-specific expression, primarily in male reproductive tissues such as testes and sperm. It plays a vital role in sperm motility, maturation, and fertilization, making it a key focus in studies of male fertility and reproductive disorders.
The ATP1A4 (N-Term) antibody is typically generated using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal domain of ATP1A4. This region is relatively unique among α subunits, aiding in minimizing cross-reactivity with other isoforms. Researchers employ this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study ATP1A4’s localization, expression levels, and functional interactions. Its applications extend to investigating pathologies linked to ATP1A4 dysfunction, such as infertility, or exploring ion transport mechanisms in specialized cells. Validated for specificity and sensitivity, this antibody serves as a crucial reagent in both basic reproductive biology and clinical research.
×