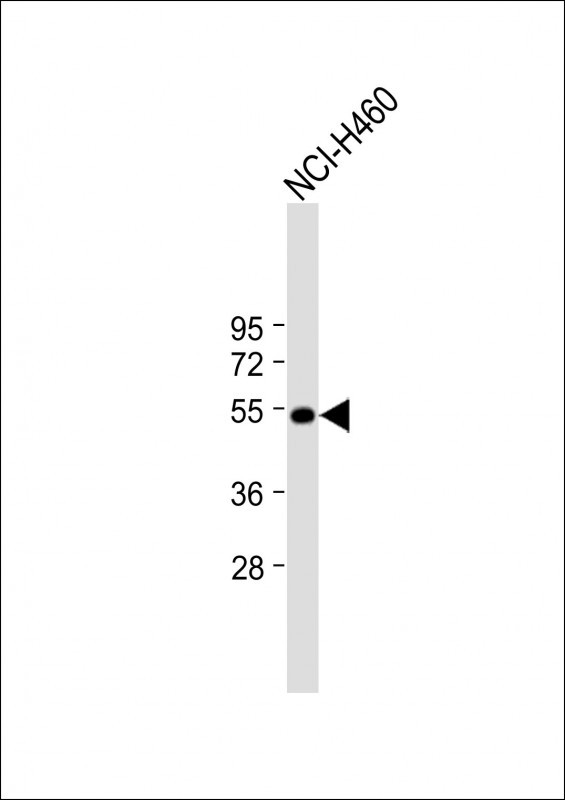
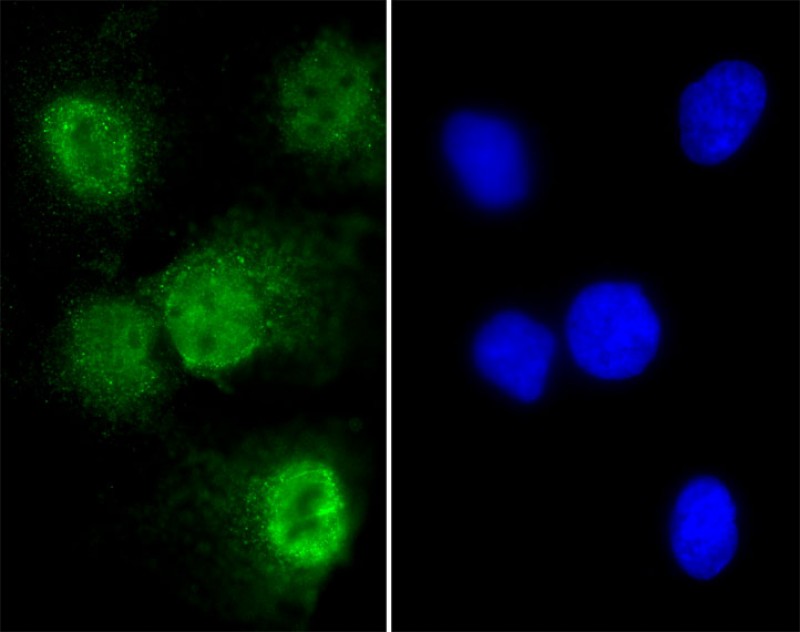
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Brachyury protein, Protein T, T |
| Entrez GeneID | 6862 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This T antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 15-43 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human T. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于T(N-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*Novel monoclonal antibody targeting N-terminal tau epitopes for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种靶向TAU蛋白N端表位的单克隆抗体,证实其在脑脊液及病理切片中可特异性识别磷酸化TAU,为阿尔茨海默病生物标志物检测提供了新工具。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of T-cell receptor β-chain N-terminal antibodies in autoimmune disorders*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:通过解析T细胞受体β链N端抗体结构,揭示其与自身抗原的交叉反应机制,为类风湿性关节炎等自身免疫疾病治疗提供潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*N-terminal specific anti-TDP-43 antibodies distinguish pathological aggregates in ALS*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种特异性识别TDP-43蛋白N端异常聚集体的抗体,可区分肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)患者与健康对照组的组织样本,具有诊断应用潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*Engineering high-affinity N-terminal HER2 antibodies for targeted cancer therapy*
**作者**:Chen H, et al.
**摘要**:利用噬菌体展示技术优化HER2受体N端结构域抗体亲和力,体外实验显示其可显著抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖并增强药物靶向递送效率。
---
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“N-terminal antibody T”、“T-protein N-term epitope”等检索。建议结合具体研究场景筛选相关文献。
T (N-term) antibodies are a class of immunoreagents specifically designed to target the N-terminal region of proteins, a critical area involved in numerous biological processes. The N-terminus, or amino terminus, often serves as a site for post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation, ubiquitination) and plays roles in protein stability, localization, and interaction with other molecules. Antibodies targeting this region are valuable tools for studying protein expression, maturation, and degradation, as many proteolytic cleavage events or truncations occur near the N-terminus.
These antibodies are typically generated using synthetic peptides corresponding to the N-terminal sequence of the target protein, ensuring specificity. However, challenges arise due to the variable accessibility of the N-terminus in folded proteins or its modification states. Despite this, T (N-term) antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to distinguish full-length proteins from truncated isoforms or degradation products.
In research, they aid in investigating diseases linked to aberrant protein processing, such as cancer (e.g., caspase cleavage in apoptosis) or neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., amyloid precursor protein processing in Alzheimer’s). Their utility in diagnostics and therapeutic development continues to grow, emphasizing their importance in both basic and applied biomedical sciences.
×