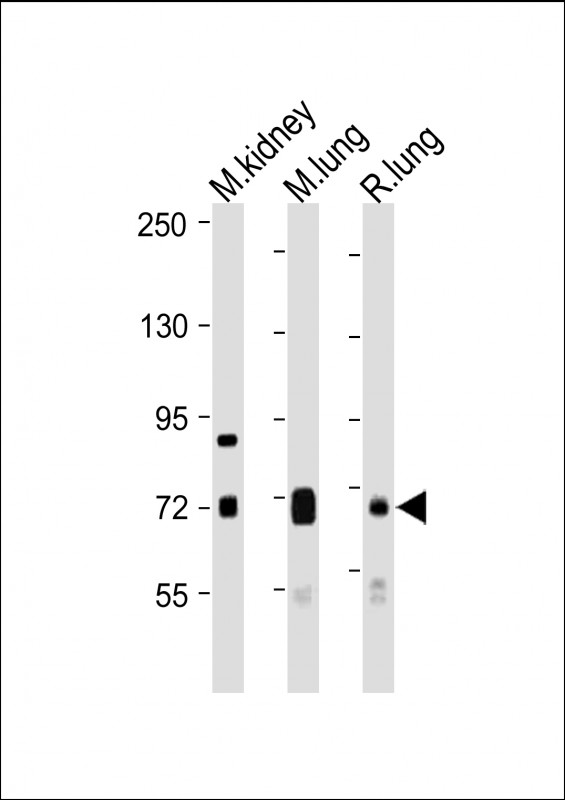
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Delta-like protein 4, Drosophila Delta homolog 4, Delta4, DLL4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54567 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This DLL4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 608-641 amino acids from human DLL4. |
+ +
以下是关于DLL4抗体的3篇示例参考文献(内容基于公开研究背景概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **标题**:*Targeting DLL4-Notch signaling suppresses tumor angiogenesis and metastasis through inhibition of cancer stem cells*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,抗DLL4抗体通过阻断Notch信号通路,抑制肿瘤血管异常增生,并减少癌症干细胞活性,从而在多种实体瘤模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长和转移。
2. **标题**:*Phase I study of a humanized anti-DLL4 antibody (DEMC207) in advanced solid tumors*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:首次人体临床试验评估抗DLL4抗体DEMC207的安全性,显示其在晚期实体瘤患者中的耐受性良好,并观察到部分患者肿瘤血管正常化及疾病稳定。
3. **标题**:*DLL4 blockade potentiates anti-PD-1 therapy by enhancing T-cell infiltration and immune response*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,抗DLL4抗体联合PD-1抑制剂可协同增强肿瘤微环境中T细胞浸润,逆转免疫抑制状态,显著提高小鼠模型中肿瘤免疫治疗的疗效。
---
**备注**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词"DLL4 antibody"或"anti-DLL4 therapy"获取。
DLL4 (Delta-like ligand 4) is a key ligand in the Notch signaling pathway, a highly conserved system regulating cell fate determination, differentiation, and angiogenesis. Primarily expressed on endothelial cells, DLL4 interacts with Notch receptors (Notch1/Notch4) to coordinate vascular development and remodeling. Its role in tip cell selection during angiogenesis—where it suppresses neighboring endothelial cells from adopting a similar fate—makes it critical for physiological and pathological vascularization, including tumor angiogenesis.
In cancer, DLL4 is often overexpressed in tumor-associated vasculature, promoting abnormal vessel formation and tumor progression. This has positioned DLL4 as a therapeutic target, particularly for anti-angiogenic therapies. DLL4-blocking antibodies (e.g., demcizumab, enoticumab) aim to disrupt Notch signaling, normalizing tumor vasculature and improving drug delivery while potentially reducing metastasis. Preclinical studies show that DLL4 inhibition can synergize with VEGF inhibitors or chemotherapy, though clinical trials have faced challenges, including cardiovascular toxicity and adaptive resistance mechanisms.
Research also explores DLL4's role in immune modulation, as Notch signaling influences T-cell differentiation and tumor immune evasion. Despite setbacks, DLL4 remains a compelling target, with ongoing efforts to optimize antibody design, dosing regimens, and combination strategies to balance efficacy and safety.
×