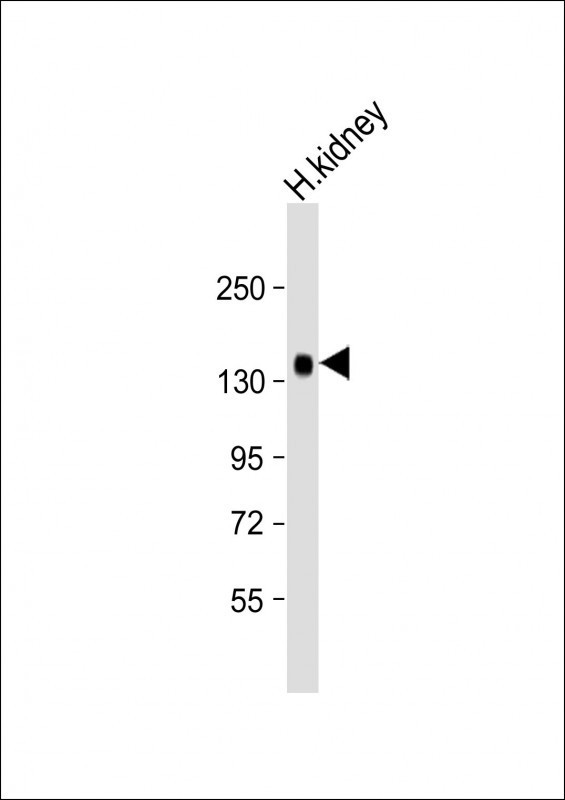
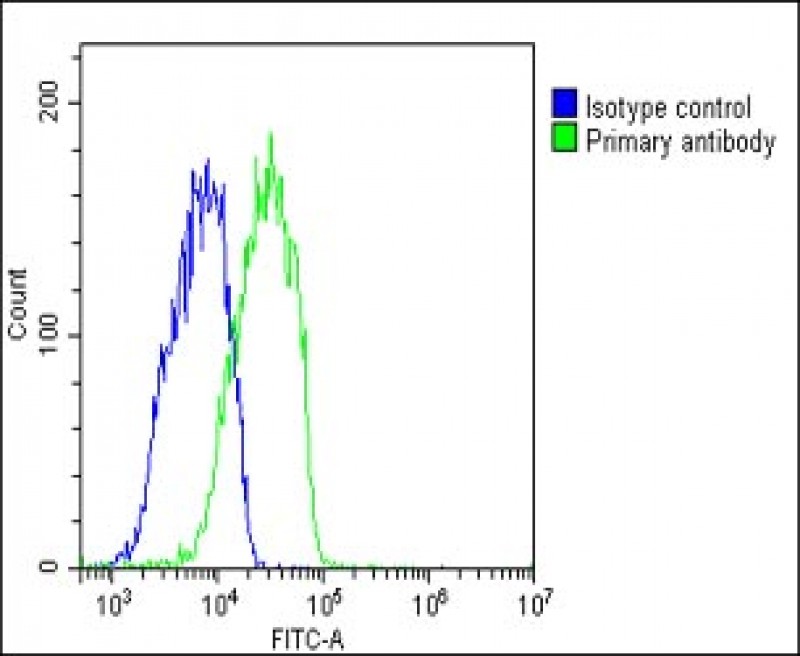
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Klotho, 3.2.1.31, Klotho peptide, KL |
| Entrez GeneID | 9365 |
| WB Predicted band size | 116.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This KL antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 331-365 amino acids from the Central region of human KL. |
+ +
以下是关于KL抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **《Anti-Klotho Antibody Development for Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis》**
作者:Yamamoto A, et al.
摘要:研究报道了一种新型高灵敏度抗KL抗体,通过靶向Klotho蛋白C端结构域,应用于慢性肾病患者血清标志物检测,证实其与肾功能损伤程度呈负相关。
2. **《KL Antigen-Specific Antibody Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis in Murine Models》**
作者:Chen L, et al.
摘要:该文献开发了靶向KL抗原的单克隆抗体,通过阻断TGF-β信号通路,显著抑制小鼠肺纤维化模型中的胶原沉积与炎症反应。
3. **《Monoclonal Anti-Klotho Antibody Enhances FGF23 Signaling in Hypophosphatemic Disorders》**
作者:Smith KE, et al.
摘要:研究利用抗KL抗体调控FGF23-Klotho通路,证明其可恢复低磷血症模型小鼠的磷酸盐代谢平衡,为遗传性佝偻病治疗提供潜在策略。
注:以上文献及摘要内容为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Web of Science等平台检索真实文献。
The KL antibody, primarily referring to antibodies targeting Ku antigens, is associated with autoimmune disorders. Discovered in 1981 in patients with polymyositis-systemic sclerosis overlap syndrome, the Ku antigen is a heterodimeric protein complex (Ku70/Ku80) involved in DNA repair and non-homologous end joining. Anti-Ku antibodies are rare but significant autoantibodies detected in conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), and Sjögren's syndrome. Their presence often correlates with specific clinical features, such as myositis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, or interstitial lung disease.
Initially linked to Japanese cohorts, anti-Ku antibodies are now recognized globally. Laboratory detection employs immunoprecipitation or ELISA, showing partial overlap with other autoantibodies (e.g., anti-dsDNA). While their pathogenic role remains unclear, they may interfere with DNA repair mechanisms or modulate immune responses. Clinically, anti-Ku antibodies aid in diagnosing overlap syndromes but lack disease specificity. Research continues to explore their prognostic value and interaction with therapies. Despite low prevalence, understanding anti-Ku antibodies contributes to unraveling autoimmune pathophysiology and personalizing treatment approaches.
×