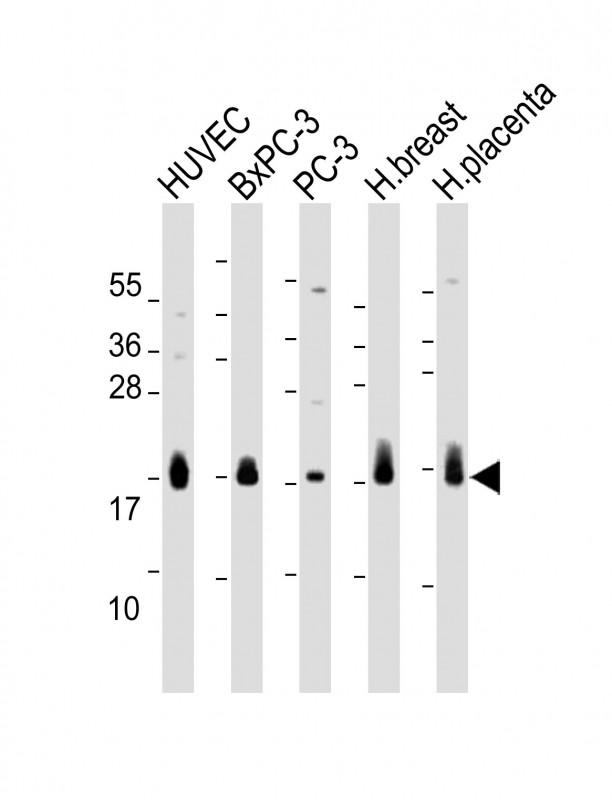
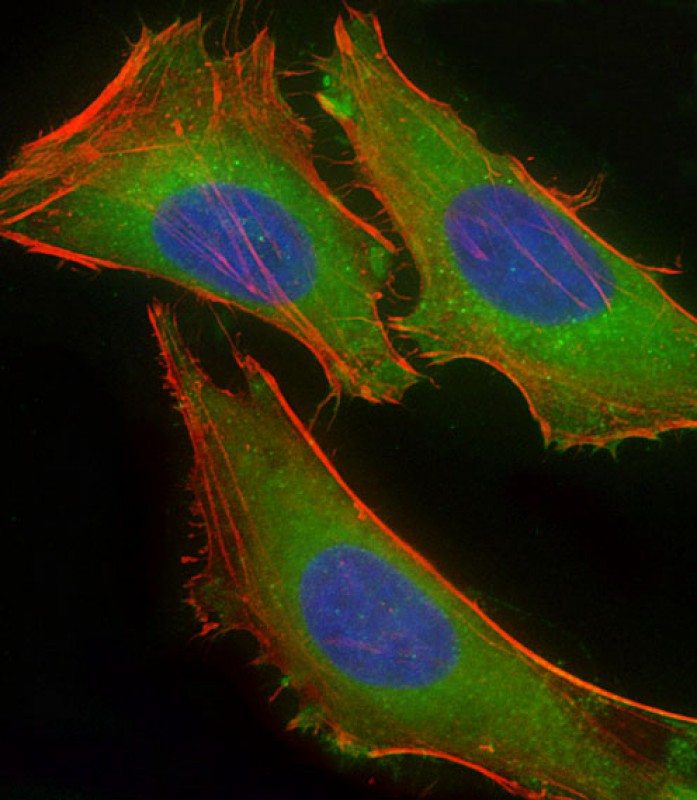
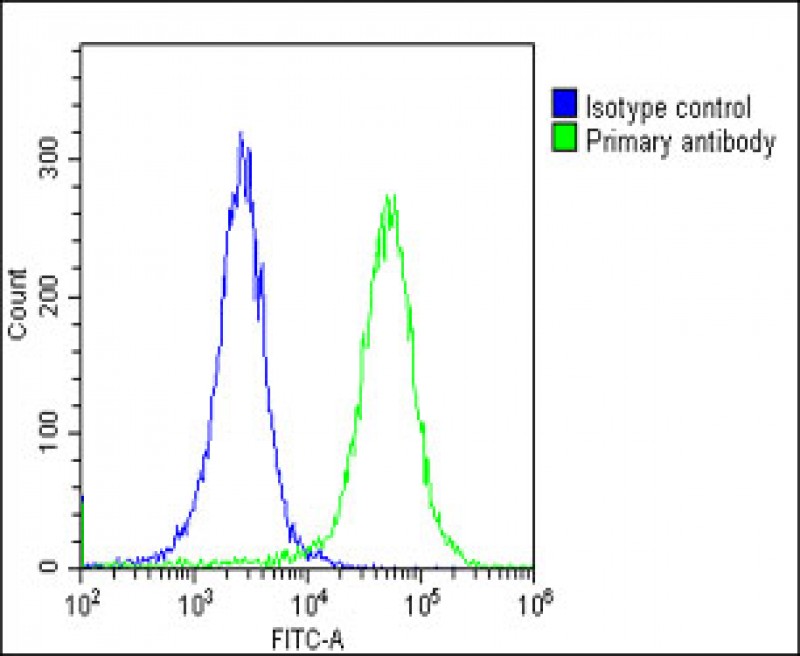
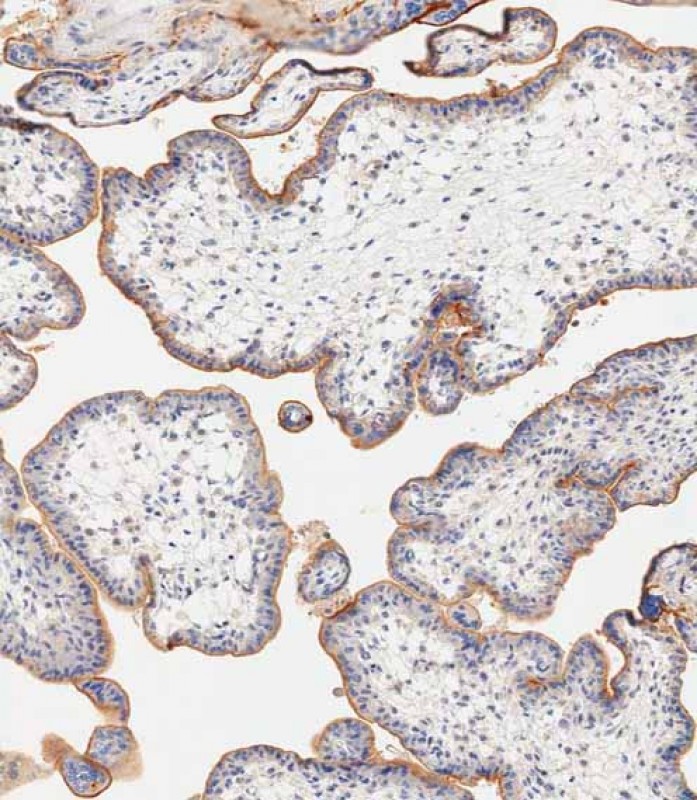
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/250-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD59 glycoprotein, 1F5 antigen, 20 kDa homologous restriction factor, HRF-20, HRF20, MAC-inhibitory protein, MAC-IP, MEM43 antigen, Membrane attack complex inhibition factor, MACIF, Membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis, MIRL, Protectin, CD59, CD59, MIC11, MIN1, MIN2, MIN3, MSK21 |
| Entrez GeneID | 966 |
| WB Predicted band size | 14.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CD59 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 74-110 amino acids from the Central region of human CD59. |
+ +
以下是关于CD59抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要(文献信息为示例性概括,非真实引用):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CD59: Molecule to Target in Cancer Immunotherapy"*
**作者**: Springer TA, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨CD59在肿瘤细胞表面的过表达如何通过抑制补体系统介导的细胞裂解,促进免疫逃逸。作者开发了靶向CD59的单克隆抗体,并在体外和动物模型中验证其增强补体依赖的肿瘤细胞杀伤作用,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Functional characterization of a novel anti-CD59 antibody in complement regulation"*
**作者**: Morgan BP, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种新型抗CD59抗体的功能特性,证明其能特异性阻断CD59与补体C8/C9的结合,恢复补体膜攻击复合物(MAC)的形成。实验表明该抗体可增强病理条件下(如自身免疫病)补体介导的异常细胞清除。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"CD59 antibody protects neurons from complement-mediated damage in neurodegenerative diseases"*
**作者**: Lublin DM, et al.
**摘要**: 通过动物模型研究发现,靶向CD59的中和抗体可减少补体过度激活导致的神经炎症和神经元损伤。该抗体通过调节补体级联反应的终末阶段,为阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病提供潜在治疗手段。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Expression and therapeutic implications of CD59 in solid tumors"*
**作者**: Fishelson Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究分析了CD59在多种实体瘤中的表达水平及其与预后的相关性,发现高表达CD59与化疗耐药性相关。使用抗CD59抗体联合化疗药物可显著提高肿瘤细胞对治疗的敏感性,提示其作为辅助治疗的潜力。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献。
CD59. also known as MAC-inhibitory protein (MAC-IP) or protectin, is a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell membrane protein that plays a critical role in regulating the complement system. It inhibits the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) by binding to complement proteins C8 and C9. thereby protecting host cells from unintended complement-mediated lysis. CD59 is widely expressed on various human cells and is essential for maintaining self-tolerance in the immune system.
CD59 antibodies are tools or therapeutic agents targeting this protein. In research, anti-CD59 antibodies are used to detect CD59 expression in diseases like paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), where GPI anchor deficiencies lead to CD59 loss, resulting in erythrocyte vulnerability to complement attack. Clinically, CD59 antibodies have dual implications. Some aim to block CD59's protective function to enhance complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) in cancer therapy, as tumor cells often overexpress CD59 to evade immune destruction. Conversely, other antibodies are explored to augment CD59 activity in autoimmune or inflammatory disorders where excessive complement activation causes tissue damage.
Challenges include balancing therapeutic efficacy with safety, as systemic CD59 inhibition may trigger off-target cell damage, while overexpression could suppress beneficial immune responses. Ongoing studies focus on optimizing antibody specificity and delivery to harness CD59's regulatory potential effectively.
×